Toyota 2007 Annual Report Download - page 118
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 118 of the 2007 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
116 ANNUAL REPORT 2007
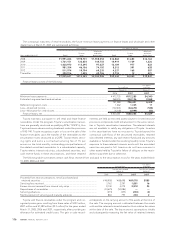
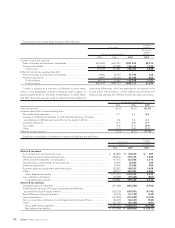
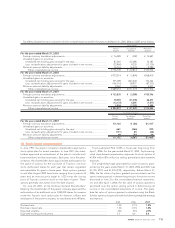
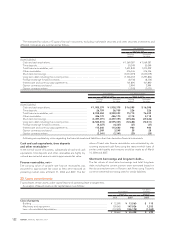
The following table summarizes Toyota’s stock option activity:
Yen
Yen in millions
Weighted-
average
Weighted- remaining Aggregate
Number of average contractual intrinsic
options exercise price life in years value
Options outstanding at March 31, 2004 ........................................ 4,896,400 ¥ 3,401 3.83
Granted ............................................................................................. 2,021,000 4,541
Exercised........................................................................................... (810,300) 2,995
Canceled ........................................................................................... (606,800) 4,105
Options outstanding at March 31, 2005 ........................................ 5,500,300 3,802 3.86
Granted ............................................................................................. 2,104,000 4,377
Exercised........................................................................................... (1,354,000) 3,052
Canceled ........................................................................................... (1,463,400) 4,085
Options outstanding at March 31, 2006 ........................................ 4,786,900 4,180 4.52
Granted ............................................................................................. 3,176,000 6,140
Exercised........................................................................................... (1,233,100) 4,008
Canceled ........................................................................................... (437,100) 4,590
Options outstanding at March 31, 2007 ........................................ 6,292,700 ¥ 5,175 5.53 ¥14,947
Options exercisable at March 31, 2005 .............................................. 1,740,300 ¥ 3,641 1.69
Options exercisable at March 31, 2006 .............................................. 946,900 ¥ 3,078 3.09
Options exercisable at March 31, 2007 .............................................. 1,282,700 ¥ 3,990 2.90 ¥4,567
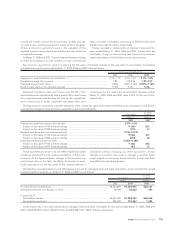
The total intrinsic value of options exercised for the years
ended March 31, 2005, 2006 and 2007 was ¥897 million, ¥3,273
million and ¥3,866 million ($33 million), respectively.
As of March 31, 2007, there were unrecognized compensa-
tion expenses of ¥2,423 million ($21 million) for stock options
granted. Those expenses are expected to be recognized over a
weighted-average period of 1.2 years.
Cash received from the exercise of stock options for the years
ended March 31, 2005, 2006 and 2007 was ¥2,427 million, ¥4,133
million and ¥4,942 million ($42 million), respectively.
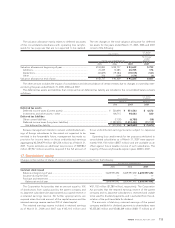
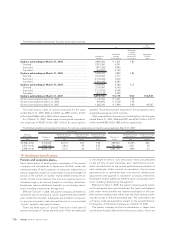
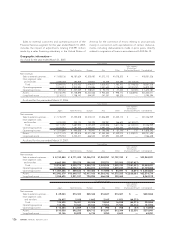
The following table summarizes information for options outstanding and options exercisable at March 31, 2007:
Outstanding Exercisable
Exercise Weighted-average Weighted-average Weighted-average Weighted-average Weighted-average
price range exercise price exercise price remaining life exercise price exercise price
Yen Yen Dollars Years Yen Dollars
¥2,958–4,500 2,370,000 ¥4,112 $35 3.89 489,000 ¥3,095 $26
4,501–6,140 3,922,700 5,816 49 6.52 793,700 4,541 38
2,958–6,140 6,292,700 5,175 44 5.53 1,282,700 3,990 34
Number of
shares
Pension and severance plans—
Upon terminations of employments, employees of the parent
company and subsidiaries in Japan are entitled, under the
retirement plans of each company, to lump-sum indemnities or
pension payments, based on current rates of pay and lengths of
service or the number of “points” mainly determined by those.
Under normal circumstances, the minimum payment prior to
retirement age is an amount based on voluntary retirement.
Employees receive additional benefits on involuntary retire-
ment, including retirement at the age limit.
Effective October 1, 2004, the parent company amended its
retirement plan to introduce a “point” based retirement benefit
plan. Under the new plan, employees are entitled to lump-sum
or pension payments determined based on accumulated
“points” vested in each year of service.
There are three types of “points” that vest in each year of
service consisting of “service period points” which are attributed
to the length of service, “job title points” which are attributed
to the job title of each employee, and “performance points”
which are attributed to the annual performance evaluation of
each employee. Under normal circumstances, the minimum
payment prior to retirement age is an amount reflecting an
adjustment rate applied to represent voluntary retirement.
Employees receive additional benefits upon involuntary retire-
ment, including retirement at the age limit.
Effective October 1, 2005, the parent company partly mend-
ed its retirement plan and introduced the quasi cash-balance
plan under which benefits are determined based on the vari-
able-interest crediting rate rather than the fixed-interest credit-
ing rate as was in the pre-amended plan. The amendment did
not have a material quantitative impact on the projected bene-
fit obligation of the parent company as of March 31, 2006.
The parent company and most subsidiaries in Japan have
contributory funded defined benefit pension plans, which are
19. Employee benefit plans:
Number of
shares