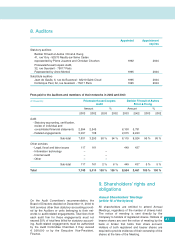
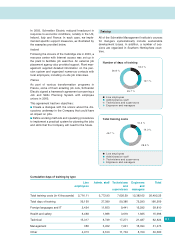
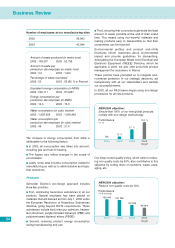
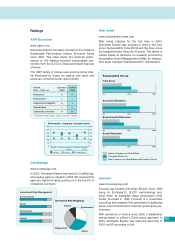
APC 2003 Annual Report Download - page 48
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 48 of the 2003 APC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Nevertheless, our business will depend on intellectu-
al property rights to a greater extent as we broaden
the portfolio with products that contain expanded
electronic, IT and communication functions. As a
result, the risk of counterfeiting or false use is likely
to increase. We hold patents with significant busi-
ness value, particularly in these new technologies.
4. Quantitative and
Qualitative Disclosures
about Market Risk
Currency risk
Because a significant proportion of transactions are
denominated in currencies other than the euro,
Schneider Electric is exposed to risk arising from
changes in exchange rates. Our currency hedging
policy is to protect subsidiaries against risks on all
transactions denominated in a currency other than
their accounting currency. These mainly consist of
intercompany transactions between global plants or
international distribution centers and local sub-
sidiaries, but they also include direct exports and
purchases. More than twenty currencies are
involved, with the US dollar, Hong Kong dollar and
British pound representing the most significant
sources of risk.
Fluctuations in exchange rates between the euro and
these currencies can have a significant impact on
Group operating margin and distort year-on-year
performance comparisons.
We actively manage our exposure to currency risk to
reduce the sensitivity of earnings to changes in
exchange rates. Our hedging programs mainly con-
cern foreign currency receivables, payables and
operating cash flows, which are generally hedged by
means of forward sales.
We also hedge intercompany loans and borrowings
in foreign currencies. However, no other foreign cur-
rency assets and liabilities carried in the consolidat-
ed balance sheet are hedged.
Interest rate risk
Interest rate risk on borrowings is managed at Group
level, based on consolidated debt and according to
market conditions. The main goal of interest rate
management policies is to optimize Group financing
costs. All bond debt is fixed rate. Where long-term
variable rate debt is swapped for fixed rate, the swap
contracts only apply to the long-term portion and the
current portion is left at variable rate. In the last two
years, the current portion of long-term debt has not
been material.
Since the divestment of Legrand in December 2002,
cash and cash equivalents have exceeded total debt.
Depending on market conditions, interest rate risk on
cash equivalents may be hedged using interest rate
swaps.
Commodity risk
Certain metals traded on organized commodity mar-
kets are used in the manufacture of our products. We
are therefore exposed to commodity risk arising from
changes in market prices of copper, aluminum, silver,
nickel and zinc.
The purchasing departments of our operating enti
ties
report their purchasing forecasts to the Corporate
Treasury Center unit twice a year. Purchase commit-
ments are hedged using forward contracts, swaps
and, to a lesser extent, options.
Counterparty risk
Transactions involving foreign currency and long-
and short-term interest rate hedging instruments are
entered into with selected counterparties. Banking
counterparties are chosen according to the custom-
ary criteria, including the credit rating issued by an
independent rating agency.
Group policy consists of diversifying counterparty
risks and periodic controls are performed to check
compliance with the related rules.
Equity risk
Exposure to equity risk primarily relates to treasury
stock and shares in Finaxa. These positions are not
hedged.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity is provided by our cash and cash equiva-
lents and our commercial paper programs. These
programs are backed by undrawn confirmed lines of
credit.
Our credit rating enables us to raise significant long-
term financing and attract a diverse investor base.
Currency and interest rate risks are generally man-
aged at Group level, with the aim of limiting the
impact on results of changes in exchange and inter-
est rates without entering into any trading transac-
tions. Hedging decisions are made by the Finance &
Control – Legal Affairs Department and are reviewed
at monthly intervals based on changes in financial
market conditions.
Business Review
46