General Motors 2013 Annual Report Download - page 123
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 123 of the 2013 General Motors annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
GENERAL MOTORS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
• Intangible asset impairment charges of $1.8 billion in GME.
• Charge of $525 million for GM Korea hourly wage litigation.
• Charge of $402 million which represents the premium paid to purchase our common stock from the UST in Corporate.
The three months ended March 31, 2012 included the following on a pre-tax and pre-noncontrolling interests basis:
• Goodwill impairment charges of $617 million in GMIO and GME.
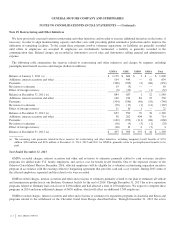
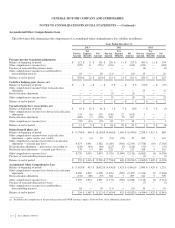
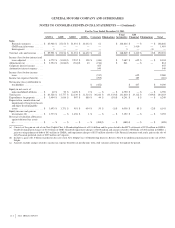
Note 25. Segment Reporting
We analyze the results of our business through our five segments: GMNA, GME, GMIO, GMSA and GM Financial. The chief
operating decision maker evaluates the operating results and performance of our automotive segments through Income (loss) before
interest and income taxes, as adjusted for additional amounts, which are presented net of noncontrolling interests, and evaluates GM
Financial through income before income taxes. Each segment has a manager responsible for executing our strategies. Our automotive
manufacturing operations are integrated within the segments, benefit from broad-based trade agreements and are subject to regulatory
requirements, such as Corporate Average Fuel Economy regulations. While not all vehicles within a segment are individually
profitable on a fully allocated cost basis, those vehicles are needed in our product mix in order to attract customers to dealer
showrooms and to maintain sales volumes for other, more profitable vehicles. Because of these and other factors, we do not manage
our business on an individual brand or vehicle basis.
In the three months ended March 31, 2013 we changed our managerial and financial reporting structure to measure our reportable
segments revenue and profitability based on the geographic area in which we sell vehicles to third party customers. We record certain
transactions between our automotive and finance segments as intersegment activity and eliminate them in consolidation. The new
reporting structure provides clearer profit and revenue visibility across geographic areas and identifies our profitability at the point of
sale. Previously, it was based on the geographic area in which the vehicles originated and our managerial and financial reporting
structure included intercompany sales and cost of sales in our segment results. Certain expenses such as engineering, warranty, recall
campaigns and selling, general and administrative are allocated to the geographic area in which the vehicle is sold to third party
customers. We have retrospectively revised the segment presentation for all periods presented.
Substantially all of the cars, trucks and parts produced are marketed through retail dealers in North America, and through
distributors and dealers outside of North America, the substantial majority of which are independently owned.
In addition to the products sold to dealers for consumer retail sales, cars and trucks are also sold to fleet customers, including daily
rental car companies, commercial fleet customers, leasing companies and governments. Sales to fleet customers are completed
through the network of dealers and in some cases sold directly to fleet customers. Retail and fleet customers can obtain a wide range
of aftersale vehicle services and products through the dealer network, such as maintenance, light repairs, collision repairs, vehicle
accessories and extended service warranties.
GMNA primarily meets the demands of customers in North America with vehicles developed, manufactured and/or marketed under
the following four brands:
• Buick • Cadillac • Chevrolet • GMC
The demands of customers outside of North America are primarily met with vehicles developed, manufactured and/or marketed
under the following brands:
• Buick • Chevrolet • Holden • Vauxhall
• Cadillac • GMC • Opel
121