APC 2007 Annual Report Download - page 110
Download and view the complete annual report
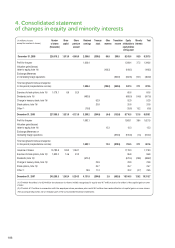
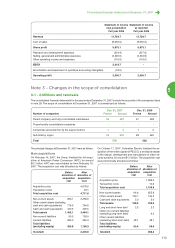
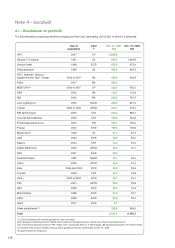
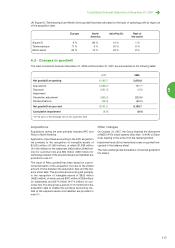
Please find page 110 of the 2007 APC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Companies acquired or sold during the year are included
in or removed from the consolidated financial statements
as of the date when effective control is acquired or relin-
quished.
Intragroup balances and transactions are eliminated in
consolidation.
The list of consolidated subsidiaries and associates is pro-
vided in note 29.
Group consolidation is based on closing figures as of De-
cember 31 of the period.
1.5 - Business combinations
Business combinations are accounted for using the pur-
chase method, in accordance with IFRS 3 –
Business
Combinations
. In accordance with the option provided by
IFRS 1 –
First-Time Adoption of IFRS
– business combi-
nations recorded before January 1, 2004 have not been
restated.
All identified acquired assets, liabilities and contingent lia-
bilities are recognized at their fair value as of the date of ac-
quisition. Provisional fair values are adjusted within a
maximum of twelve months following the date of acquisi-
tion.
If the cost of acquisition is higher than the fair value of as-
sets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of acqui-
sition, the excess is recorded under goodwill. If the cost of
acquisition is lower than the fair value of assets acquired
and liabilities assumed at the date of acquisition, the neg-
ative goodwill is immediately recognized in the income
statement.
Goodwill is not amortized, but tested for impairment at
least annually and when there is an indication that it may
be impaired (note 1.10). Any impairment losses are rec-
ognized under "Other operating income/(expense)".
1.6 - Translation of the financial
statements of foreign subsidiaries
The consolidated financial statements are drawn up in
euros.
The financial statements of subsidiaries that use another
functional currency are translated into euros as follows:
Assets and liabilities are translated at official year-end
exchange rates.
Income statement and cash flow items are translated at
weighted-average annual exchange rates.
Differences arising on translation are recorded in equity
under "Translation reserve". In accordance with IFRS 1 –
First Time Adoption of IFRS
– cumulative translation ad-
justments were reset to zero at January 1, 2004 by ad-
justing opening retained earnings, without any impact on
total equity.
1.7 - Foreign currency transactions
Foreign currency transactions are recorded using the offi-
cial exchange rate in effect at the date the transaction is
recorded or the hedging rate. At year-end, foreign currency
payables and receivables are translated into the reporting
currency at year-end exchange rates or the hedging rate.
Gains or losses on foreign currency conversion are
recorded in the income statement under "Other financial
income and expense, net". Foreign currency hedging is de-
scribed below, in note 1.22.
1.8 - Intangible assets
Intangible assets acquired separately or as
part of a business combination
Intangible assets acquired separately are initially recog-
nized in the balance sheet at historical cost. They are sub-
sequently measured using the cost model, in accordance
with IAS 38 –
Intangible Assets
.
Trademarks, customer lists and other identifiable assets of
acquired companies are recognized in the balance sheet
at fair value, determined by qualified experts for the most
significant assets and internally for the rest. The valuations
are performed using generally accepted methods, based
on expected future cash flows. The assets are regularly
tested for impairment.
Intangible assets other than trademarks are amortized on
a straight-line basis over their useful life or the period of
legal protection. Amortized intangible assets are tested for
impairment when there is any indication that their recover-
able amount may be less than their carrying amount.
Amortization and impairment losses on intangible assets
recognized on business combinations are presented under
"Amortization and impairment of purchase accounting in-
tangibles" in the income statement.
Impairment losses on other intangible assets are recog-
nized under "Other operating income/(expense)".
Trademarks
Trademarks acquired as part of a business combination
are not amortized when they are considered to have an in-
definite life.
This is determined on the basis of:
Brand awareness.
The Group’s strategy for integrating the trademark into its
existing portfolio.
Non-amortized trademarks are tested for impairment at
least annually and when there is any indication that their
recoverable amount may be less than their carrying
amount. When necessary, an impairment loss is recorded.
Internally-generated intangible assets
Research and development costs
Research costs are recognized in the income statement
when incurred.
Systems were set up to track and capitalize development
costs in 2004. As a result, only development costs for new
products launched since 2004 are capitalized in the IFRS
accounts.
Development costs for new projects are capitalized if, and
only if:
The project is clearly identified and the related costs are
separately identified and reliably tracked.
The project’s technical feasibility has been demon-
strated and the Group has the intention and financial re-
sources to complete the project and to use or sell the
related products.
It is probable that the future economic benefits attribut-
able to the project will flow to the Group.
Development costs that do not meet these criteria are ex-
pensed in the year in which they are incurred.
Capitalized development costs are amortized over the es-
timated life of the underlying technology, which generally
108