Cabela's 2006 Annual Report Download - page 70
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 70 of the 2006 Cabela's annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
66
CABELA’S INCORPORATED AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Dollars in Thousands Except Share and Per Share Amounts)
WFB is required to maintain a cash reserve account as part of certain securitization programs. In addition,
WFB owns Class B securities from one of its securitizations. The fair value of the cash reserve account is estimated
by discounting future cash flows using a rate that reflects the risks commensurate with similar types of instruments.
For the Class B securities, the fair value approximates the book value of the underlying loans. Interest-only strips
are measured like investments in debt securities classified as trading under SFAS 115, Accounting for Certain
Investments in Debt and Equity Securities.
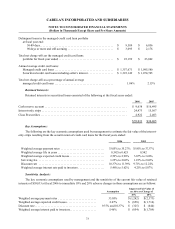
Inventories — Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. Cost is determined using the last-in,
first-out method (dollar value, link-chain) for all inventories except those inventories owned by Van Dyke Supply
Company and Wild Wings, wholly-owned subsidiaries of the Company, which use the first-in, first-out method. If
all inventories had been valued using the first-in, first-out method, which approximates replacement cost, the stated
value would not have been greater at the fiscal years ended 2006 and 2005, respectively. All inventories are in one
inventory class and are classified as finished goods. A provision for shrink is estimated, based on historical cycle
count adjustments and periodic physical inventories. The shrink reserve was $3,193 and $2,350 at the end of fiscal
2006 and 2005, respectively. The allowance for damaged goods from returns is based upon historical experience.
Inventory is adjusted for obsolete or slow moving inventory based on inventory aging reports and, in some cases, by
specific identification of slow moving or obsolete inventory. The obsolete and damaged goods reserve was $5,862
and $7,904 at the end of fiscal 2006 and 2005, respectively.
Accounting for Vendor Allowances — Vendor allowances include allowances, rebates and cooperative
advertising funds received from vendors. These funds are determined for each fiscal year primarily based on various
quantitative contract terms. Amounts expected to be received from vendors relating to purchase of merchandise
inventories are recognized as a reduction of costs of goods sold as the merchandise is sold. Amounts that represent a
reimbursement of costs incurred, such as advertising, are recorded as a reduction to the related expense in the period
that the related expense is incurred. Fair value of expenses reimbursed is determined using actual costs incurred,
such as print and production costs for media or catalog advertising. Reimbursements received from vendors that
exceed related expenses are classified as a reduction of merchandise costs of goods sold when the merchandise is
sold.
The Company records an estimate of earned allowances based on the latest projected purchase volumes.
Historical program results, current purchase volumes, and inventory projections are reviewed when establishing the
estimate for earned allowances, and a reserve based on historical adjustments is recorded as a reduction to the total
estimated allowance.
Deferred Catalog Costs and Advertising — The Company expenses the production cost of advertising as the
advertising takes place, except for catalog advertising costs, which are capitalized and amortized over the expected
period of future benefits. Advertising consists primarily of catalogs for the Company’s products. The capitalized
costs of the advertising are amortized over a three to twelve month period following the mailing of the catalogs.
Catalog costs totaling $34,869 and $36,987 at the end of fiscal 2006 and 2005, respectively, were included in
prepaid expenses in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Advertising expense, including amortization of
catalog costs, was $191,533, $170,024 and $157,623 for fiscal 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively. Advertising vendor
allowances recorded as a reduction to amortized catalog costs included in the amounts above were approximately
$4,546, $4,783 and $3,290 for fiscal 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively.
Store Preopening Expenses — Non-capital costs associated with the opening of new stores is expensed as
incurred.
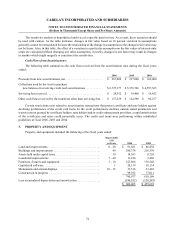
Property and Equipment — Property and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation and amortization are
provided for in amounts sufficient to relate the cost of depreciable assets to operations over their estimated service
lives. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the lives of the respective leases or the service lives of the
improvements whichever is shorter. The straight-line method of depreciation is used for financial reporting. Assets