Toyota 2006 Annual Report Download - page 119
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 119 of the 2006 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
117
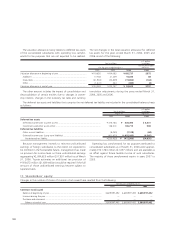
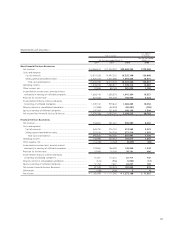
Toyota has certain financial instruments, including financial
assets and liabilities and off-balance sheet financial instru-
ments which arose in the normal course of business. These
financial instruments are executed with creditworthy financial
institutions, and virtually all foreign currency contracts are
denominated in U.S. dollars, euros and other currencies of
major industrialized countries. Financial instruments involve,
to varying degrees, market risk as instruments are subject to
price fluctuations, and elements of credit risk in the event a
counterparty should default. In the unlikely event the counter-
parties fail to meet the contractual terms of a foreign currency
or an interest rate instrument, Toyota’s risk is limited to the
fair value of the instrument. Although Toyota may be exposed
to losses in the event of non-performance by counterparties
on financial instruments, it does not anticipate significant
losses due to the nature of its counterparties. Counterparties
to Toyota’s financial instruments represent, in general, inter-
national financial institutions. Additionally, Toyota does not
have a significant exposure to any individual counterparty.
Based on the creditworthiness of these financial institutions,
collateral is generally not required of the counterparties or of
Toyota. Toyota believes that the overall credit risk related to its
financial instruments is not significant.
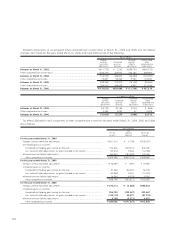
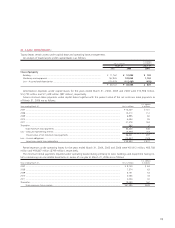
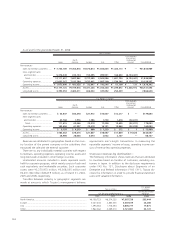
21. Other financial instruments:
Postretirement benefits other than pensions and
postemployment benefits—
Toyota’s U.S. subsidiaries provide certain health care and life
insurance benefits to eligible retired employees. In addition,
Toyota provides benefits to certain former or inactive employ-
ees after employment, but before retirement. These benefits
are currently unfunded and provided through various insur-
ance companies and health care providers. The costs of these
benefits are recognized over the period the employee provides
credited service to Toyota. Toyota’s obligations under these
arrangements are not material.
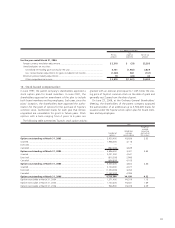
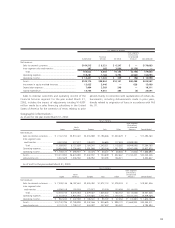
20. Derivative financial instruments:
Toyota employs derivative financial instruments, including for-
eign exchange forward contracts, foreign currency options,
interest rate swaps, interest rate currency swap agreements
and interest rate options to manage its exposure to fluctua-
tions in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates.
Toyota does not use derivatives for speculation or trading.
Fair value hedges—
Toyota enters into interest rate swaps, and interest rate cur-
rency swap agreements mainly to convert its fixed-rate debt to
variable-rate debt. Toyota uses interest rate swap agreements
in managing its exposure to interest rate fluctuations. Interest
rate swap agreements are executed as either an integral part
of specific debt transactions or on a portfolio basis. Toyota
uses interest rate currency swap agreements to entirely hedge
exposure to currency exchange rate fluctuations on principal
and interest payments for borrowings denominated in foreign
currencies. Notes and loans payable issued in foreign curren-
cies are hedged by concurrently executing interest rate curren-
cy swap agreements, which involve the exchange of foreign
currency principal and interest obligations for each functional
currency obligations at agreed-upon currency exchange and
interest rates.
For the years ended March 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006, the
ineffective portion of Toyota’s fair value hedge relationships
which are included in cost of financing operations in the
accompanying consolidated statements of income were not
material. For fair value hedging relationships, the components
of each derivative’s gain or loss are included in the assessment
of hedge effectiveness.
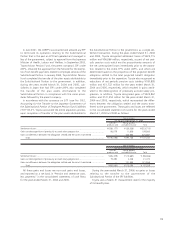
Undesignated derivative financial instruments—
Toyota uses foreign exchange forward contracts, foreign cur-
rency options, interest rate swaps, interest rate currency swap
agreements, and interest rate options, to manage its exposure
to foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations and interest
rate fluctuations from an economic perspective, and which
Toyota is unable or has elected not to apply hedge account-
ing. Unrealized gains or losses on these derivative instruments
are reported in the cost of financing operations and foreign
exchange gain, net in the accompanying consolidated state-
ments of income together with realized gains or losses on
those derivative instruments.