Toyota 2006 Annual Report Download - page 94
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 94 of the 2006 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.92
Toyota generally warrants its products against certain man-
ufacturing and other defects. Provisions for product war-
ranties are provided for specific periods of time and/or usage
of the product and vary depending upon the nature of the
product, the geographic location of the sale and other factors.
Toyota records a provision for estimated product warranty
costs at the time the related sale is recognized based on esti-
mates that Toyota will incur to repair or replace product parts
that fail while under warranty. The amount of accrued esti-
mated warranty costs is primarily based on historical experi-
ence as to product failures as well as current information on
repair costs. The amount of warranty costs accrued also con-
tains an estimate of warranty claim recoveries to be received
from suppliers.
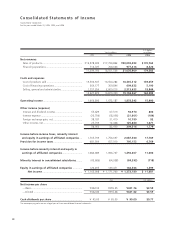
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred
and ¥682,279 million, ¥755,147 million and ¥812,648 million
($6,918 million) for the years ended March 31, 2004, 2005
and 2006, respectively.
Cash and cash equivalents—
Cash and cash equivalents include all highly liquid investments
with original maturities of three months or less, that are readi-
ly convertible to known amounts of cash and are so near
maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value
because of changes in interest rates.
Marketable securities—
Marketable securities consist of debt and equity securities.
Debt and equity securities designated as available-for-sale are
carried at fair value with unrealized gains or losses included as
a component of accumulated other comprehensive income in
shareholders’ equity, net of applicable taxes. Debt securities
designated as held-to-maturity investments are carried at
amortized cost. Individual securities classified as either avail-
able-for-sale or held-to-maturity are reduced to net realizable
value for other-than-temporary declines in market value. In
determining if a decline in value is other-than-temporary,
Toyota considers the length of time and the extent to which
the fair value has been less than the carrying value, the finan-
cial condition and prospects of the company and Toyota’s
ability and intent to retain its investment in the company for a
period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery
in market value. Realized gains and losses, which are deter-
mined on the average-cost method, are reflected in the state-
ment of income when realized.
Security investments in non-public companies—
Security investments in non-public companies are carried at
cost as fair value is not readily determinable. If the value of a
non-public security investment is estimated to have declined
and such decline is judged to be other-than-temporary,
Toyota recognizes the impairment of the investment and the
carrying value is reduced to its fair value. Determination of
impairment is based on the consideration of such factors as
operating results, business plans and estimated future cash
flows. Fair value is determined principally through the use of
the latest financial information.
Finance receivables—
Finance receivables are recorded at the present value of the
related future cash flows including residual values for finance
leases.
Allowance for credit losses—
Allowance for credit losses are established to cover probable
losses on receivables resulting from the inability of customers
to make required payments. The allowance for credit losses is
based primarily on the frequency of occurrence and loss sever-
ity. Other factors affecting collectibility are also evaluated in
determining the amount to be provided.
Losses are charged to the allowance when it has been
determined that payments will not be received and collateral
cannot be recovered or the related collateral is repossessed
and sold. Any shortfall between proceeds received and the
carrying cost of repossessed collateral is charged to the
allowance. Recoveries are reversed from the allowance for
credit losses.
Allowance for residual value losses—
Toyota is exposed to risk of loss on the disposition of off-lease
vehicles to the extent that sales proceeds are not sufficient to
cover the carrying value of the leased asset at lease termina-
tion. Toyota maintains an allowance to cover probable esti-
mated losses related to unguaranteed residual values on its
owned portfolio. The allowance is evaluated considering pro-
jected vehicle return rates and projected loss severity. Factors
considered in the determination of projected return rates and
loss severity include historical and market information on used
vehicle sales, trends in lease returns and new car markets, and
general economic conditions. Management evaluates the fore-
going factors, develops several potential loss scenarios, and
reviews allowance levels to determine whether reserves are
considered adequate to cover the probable range of losses.
The allowance for residual value losses is maintained in
amounts considered by Toyota to be appropriate in relation to
the estimated losses on its owned portfolio. Upon disposal
of the assets, the allowance for residual losses is adjusted for
the difference between the net book value and the proceeds
from sale.
Inventories—
Inventories are valued at cost, not in excess of market, cost
being determined on the “average-cost” basis, except for
the cost of finished products carried by certain subsidiary