APC 2006 Annual Report Download - page 131
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 131 of the 2006 APC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
129
5
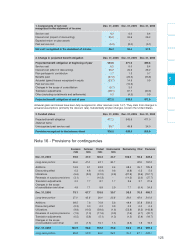
Note 20 - Financial instruments
The Group uses financial instruments to hedge its
exposure to fluctuations in interest rates, exchange
rates and metal prices.
20.1 - Currency risk
Because a significant proportion of transactions are
denominated in currencies other than the euro, the
Group is exposed to risk arising from changes in
exchange rates. If the Group is not able to hedge them,
fluctuations in exchange rates between the euro and
these currencies can have a significant impact on our
results of operations and distort year-on-year perform-
ance comparisons.
The Group actively manages its exposure to currency
risk to reduce the sensitivity of earnings to changes in
exchange rates. Hedging programs mainly concern
foreign currency receivables, payables and operating
cash flows, which are generally hedged by means of
forward sales. Depending on market conditions, risks
in the main currencies may be hedged based on recur-
ring forecast flows using contracts that expire in 12
months or less.
The Group’s currency hedging policy is to protect sub-
sidiaries against risks on all transactions denominated
in a currency other than their functional currency. More
than twenty currencies are involved, with the US dollar,
Hong Kong dollar and British pound representing the
most significant sources of risk.
20.2 - Interest rate risk
The Group is exposed to risks associated with the
effect of changing interest rates. Interest rate risk on
borrowings is managed at Group level, based on con-
solidated debt and according to market conditions.The
core aim of interest rate management policies is to
optimize overall borrowing costs. Most bond debt is
fixed rate. Interest rate risk is managed primarily by
means of swaps.
20.3 - Commodity price risk
The Group is exposed to fluctuations in energy and
raw material prices (in particular steel, copper, alu-
minum, silver, nickel, zinc and plastic). If the Group is
not able to hedge, compensate or pass on our
increased costs to customers, this could have an
adverse impact on our financial results.
Schneider Electric has, however, implemented certain
procedures to limit our exposure to rising non-ferrous
raw material prices. Purchase commitments are
hedged using forward contracts, swaps and, to a less-
er extent, options.
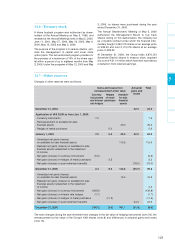
20.4 - Carrying amount and notional amount
of derivative financial instruments
December December December
31, 2005 31, 2006 31, 2006
IFRS Carrying Other Equity Cash Carrying Nominal amount
designation amount financial (2) and cash amount Purchase Sale
income and equivale
expense (1)
Foreign exchange
Futures - cash flow hedges CFH* 5.9 (5.9) (74.0) - (74.0) 1,393.6 -
Futures - hedges
of balance sheet items Trading (25.7) 44.8 - - 19.1 136.9 563.8
Options and Trading
other hedging instruments and CFH* (0.3) (0.6) - - (0.9) 507.0 -
Metal prices
Futures and options CFH* 13.1 - (17.5) - (4.4) 115.8 -
Interest rates
Swaps on credit lines Trading - - - - - - -
Other interest rate swaps Trading (20.1) - (1.7) 20.1 (1.7) 500.0 -
Hedging instruments (27.1) 38.3 (93.2) 20.1 (61.9) - -
* Cash flow hedge.
(1) Gains and losses on hedging instruments for the period are offset by changes in the fair value of the underlying, which are
also recognized in other financial income and expenses.
(2) Reported in equity under other reserves.
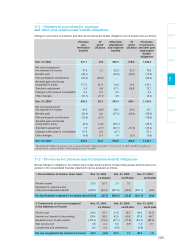
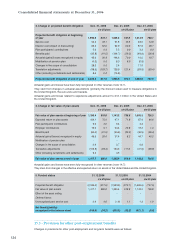
The market value of financial instruments, which corresponds to their carrying amount, is estimated either inter-
nally by discounting future differential cash flows at current market interest rates or by third party banks.