American Express 2014 Annual Report Download - page 101
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 101 of the 2014 American Express annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
AMERICAN EXPRESS COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Company’s derivatives are carried at fair value on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The accounting for changes in fair value depends
on the instruments’ intended use and the resulting hedge designation, if any, as discussed below. Refer to Note 15 for a description of the
Company’s methodology for determining the fair value of derivatives.
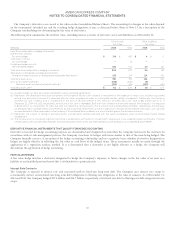
The following table summarizes the total fair value, excluding interest accruals, of derivative assets and liabilities as of December 31:
Other Assets
Fair Value
Other Liabilities
Fair Value
(Millions) 2014 2013 2014 2013
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments:
Interest rate contracts
Fair value hedges $314$455$4$2
Total return contract
Fair value hedge —8——
Foreign exchange contracts
Net investment hedges 492 174 46 116
Total derivatives designated as hedging instruments 806 637 50 118
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments:
Foreign exchange contracts, including certain embedded derivatives(a) 185 64 114 95
Total derivatives, gross 991 701 164 213
Less: Cash collateral netting(b) (158) (336) (4) —
Derivative asset and derivative liability netting(c) (122) (36) (122) (36)
Total derivatives, net(d) $711$329$38$177
(a) Includes foreign currency derivatives embedded in certain operating agreements.
(b) Represents the offsetting of derivative instruments and the right to reclaim cash collateral (a receivable) or the obligation to return cash collateral (a payable)
arising from derivative instrument(s) executed with the same counterparty under an enforceable master netting arrangement. Additionally, the Company
received non-cash collateral from a counterparty in the form of security interest in U.S. Treasury securities with a fair value of $91 million and nil asof
December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, none of which was sold or repledged. Such non-cash collateral economically reduces the Company’s risk exposure
to $620 million as of December 31, 2014, but does not reduce the net exposure on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets. Additionally, the Company
posted $114 million and $26 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, as initial margin on its centrally cleared interest rate swaps; such amounts
are recorded within Other receivables on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets and are not netted against the derivative balances.
(c) Represents the amount of netting of derivative assets and derivative liabilities executed with the same counterparty under an enforceable master netting
arrangement.
(d) The Company has no individually significant derivative counterparties and therefore, no significant risk exposure to any single derivative counterparty. The total
net derivative assets and derivative liabilities are presented within Other assets and Other liabilities on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets.
DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS THAT QUALIFY FOR HEDGE ACCOUNTING
Derivatives executed for hedge accounting purposes are documented and designated as such when the Company enters into the contracts. In
accordance with its risk management policies, the Company structures its hedges with terms similar to that of the item being hedged. The
Company formally assesses, at inception of the hedge accounting relationship and on a quarterly basis, whether derivatives designated as
hedges are highly effective in offsetting the fair value or cash flows of the hedged items. These assessments usually are made through the
application of a regression analysis method. If it is determined that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge, the Company will
discontinue the application of hedge accounting.
FAIR VALUE HEDGES
A fair value hedge involves a derivative designated to hedge the Company’s exposure to future changes in the fair value of an asset or a
liability, or an identified portion thereof that is attributable to a particular risk.
Interest Rate Contracts
The Company is exposed to interest rate risk associated with its fixed-rate long-term debt. The Company uses interest rate swaps to
economically convert certain fixed-rate long-term debt obligations to floating-rate obligations at the time of issuance. As of December 31,
2014 and 2013, the Company hedged $17.6 billion and $14.7 billion, respectively, of its fixed-rate debt to floating-rate debt using interest rate
swaps.
101