American Express 2014 Annual Report Download - page 102
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 102 of the 2014 American Express annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
AMERICAN EXPRESS COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
To the extent the fair value hedge is effective, the gain or loss on the hedging instrument offsets the loss or gain on the hedged item
attributable to the hedged risk. Any difference between the changes in thefairvalueofthederivativeandthehedgeditemisreferredtoas
hedge ineffectiveness and is reflected in earnings as a component of other expenses. Hedge ineffectiveness may be caused by differences
between the debt’s interest coupon and the benchmark rate, primarily due to credit spreads at inception of the hedging relationship that are
not reflected in the valuation of the interest rate swap. Furthermore, hedge ineffectiveness may be caused by changes in the relationship
between 3-month LIBOR and 1-month LIBOR, as well as between the overnight indexed swap rate (OIS) and 1-month LIBOR, as basis
spreads may impact the valuation of the interest rate swap without causing an offsetting impact in the value of the hedged debt. If a fair value
hedge is de-designated or no longer considered to be effective, changesinfairvalueofthederivativecontinuetoberecordedthrough
earnings but the hedged asset or liability is no longer adjusted for changes in fair value resulting from changes in interest rates. The existing
basis adjustment of the hedged asset or liability is amortized or accreted as an adjustment to yield over the remaining life of that asset or
liability.
Total Return Contract
The Company hedged its exposure to changes in the fair value of its equity investment in ICBC in local currency. The Company used a TRC
to transfer this exposure to its derivative counterparty. On July 18, 2014, the Company sold its remaining 34.3 million shares in ICBC and
terminated the TRC. As of December 31, 2013 only, the fair value of the equity investment in ICBC was $122 million (180.7 million shares).
Prior to termination, to the extent the hedge was effective, the gain or loss on the TRC offset the gain or loss on the investment in ICBC. Any
difference between the changes in the fair value of the derivative and the hedged item resulted in hedge ineffectiveness and was recognized in
Other expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
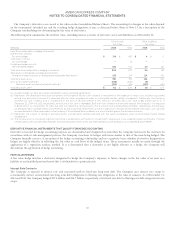
The following table summarizes the impact on the Consolidated Statements of Income associated with the Company’s hedges of its fixed-rate
long-term debt and its investment in ICBC for the years ended December 31:
Gains (losses) recognized in income
(Millions) Derivative contract Hedged item
Net hedge ineffectiveness
Derivative
relationship
Income Statement
Line Item
Amount Income Statement
Line Item
Amount
2014 2013 2012 2014 2013 2012 2014 2013 2012
Interest rate
contracts Other expenses $(143) $ (370) $ (178) Other expenses $148 $351$132$5$(19)$ (46)
Total return contract Other non-interest
revenues $11$15$(53)
Other non-interest
revenues $ (11) $ (15) $ 54 $—$—$ 1
The Company also recognized a net reduction in interest expense on long-term debt of $283 million, $346 million and $491 million for the
years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, primarily related to the net settlements (interest accruals) on the Company’s
interest rate derivatives designated as fair value hedges.
CASH FLOW HEDGES
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company did not have any designated cash flow hedges.
During the year ended December 31, 2012 only, the Company reclassified $(1) million from AOCI into earnings as a component of
interest expense. Any ineffective portion of the gain or loss on the derivatives is reported as a component of other expenses. No
ineffectiveness associated with cash flow hedges was reclassified from AOCI into income for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and
2012.
NET INVESTMENT HEDGES
A net investment hedge is used to hedge future changes in currency exposure of a net investment in a foreign operation. The Company
primarily designates foreign currency derivatives, typically foreign exchange forwards, and on occasion foreign currency denominated debt,
as hedges of net investments in certain foreign operations. These instruments reduce exposure to changes in currency exchange rates on the
Company’s investments in non-U.S. subsidiaries. The effective portion of the gain or (loss) on net investment hedges, net of taxes, recorded
in AOCI as part of the cumulative translation adjustment, was $455 million, $253 million and $(288) million for the years ended 2014, 2013
and 2012, respectively. Any ineffective portion of the gain or (loss) on net investment hedges is recognized in other expenses during the
period of change. During the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company reclassified $10 million, nil and nil, respectively,
from AOCI to earnings as a component of Other expenses. No ineffectiveness associated with net investment hedges was reclassified from
AOCI into income during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
102