Nike 2010 Annual Report Download - page 43
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 43 of the 2010 Nike annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
program, other conversion gains and losses arising from remeasurement of monetary assets and liabilities in non− functional currencies, and gains and
losses resulting from the difference between actual foreign currency rates and standard rates assigned to each entity in NIKE Brand geographic operating
segments, which are used to record any non−functional currency product purchases into the entity’s functional currency. Prior to fiscal 2010, all foreign
currency results, including hedge results and other conversion gains and losses, generated by the Western Europe and Central and Eastern Europe
geographies were recorded in their respective geographic results.
Fiscal 2010 Compared to Fiscal 2009
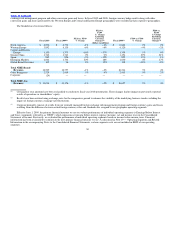
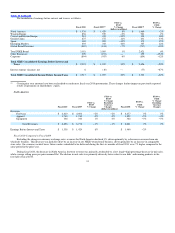
In fiscal 2009, results for Corporate included a pre−tax restructuring charge of $195 million. Excluding this restructuring charge, loss before interest
and taxes for Corporate would have increased by 18%, primarily driven by an increase in performance−based compensation.
Fiscal 2009 Compared to Fiscal 2008
The increase in Corporate’s loss before interest and taxes in fiscal 2009 was primarily attributable to pre−tax restructuring charges of $195 million,
consisting primarily of cash charges related to severance costs.
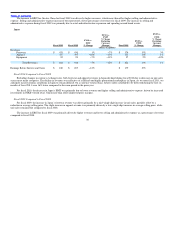
In fiscal 2009, foreign currency conversion gains (losses) reported in Corporate expense totaled $46 million compared to ($76) million in fiscal 2008,
which was primarily driven by a net gain from currency hedges in fiscal 2009 versus a net hedge loss in fiscal 2008.
Foreign Currency Exposures and Hedging Practices
Overview
As a global company with significant operations outside the U.S. we are exposed to risk arising from changes in currency exchange rates in the
normal course of business. Foreign currency fluctuations affect the recording of transactions, such as sales, purchases and intercompany transactions
denominated in non−functional currencies and the translation of foreign currency denominated results of operations, financial position and cash flows into
U.S. dollars for consolidated reporting. Our primary foreign currency exposures are related to U.S. dollar transactions at wholly−owned foreign subsidiaries,
as well as transactions and translation of results denominated in Euros, British Pounds, Chinese Renminbi and Japanese Yen.
Our foreign exchange risk management program is intended to minimize both the positive and negative effects of currency fluctuations on our
reported consolidated results of operations, financial position and cash flows. This also has the effect of delaying the impact of current market rates on our
consolidated financial statements, dependent upon hedge horizons. We manage global foreign exchange risk centrally, on a portfolio basis, to manage those
risks that are material to NIKE, Inc. on a consolidated basis. We manage these exposures by taking advantage of natural offsets and currency correlations
that exist within the portfolio and by hedging remaining material exposures, where practical, using derivative instruments such as forward contracts and
options. The Company’s hedging policy is designed to partially or entirely offset changes in the underlying exposures being hedged. We do not hold or
issue derivative financial instruments for speculative trading purposes.
Transactional exposures
We transact business in various currencies and have significant revenues and costs denominated in currencies other than the functional currency of the
relevant subsidiary, which subjects us to foreign currency risk. Our most significant transactional foreign currency exposures are:
1. Inventory Purchases — Most of our inventory purchases around the world are denominated in U.S. dollars. This generates foreign currency
exposures for all subsidiaries with a functional currency other than the U.S. dollar. A weaker U.S. dollar reduces the inventory cost in the
purchasing subsidiary’s functional currency whereas a stronger U.S. dollar increases the inventory cost.
40