General Motors 2014 Annual Report Download - page 60
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 60 of the 2014 General Motors annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
GENERAL MOTORS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
We have foreign currency exposures related to buying, selling and financing in currencies other than the functional currencies of
the operations. At December 31, 2014 our most significant foreign currency exposures were the Euro/U.S. Dollar, Euro/British Pound,
U.S. Dollar/South Korean Won and U.S. Dollar/Mexican Peso. Derivative instruments such as foreign currency forwards, swaps and
options are used primarily to hedge exposures with respect to forecasted revenues, costs and commitments denominated in foreign
currencies. At December 31, 2014 such contracts had remaining maturities of up to 23 months.
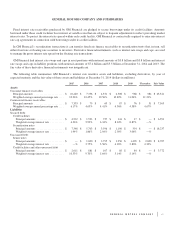
At December 31, 2014 and 2013 the net fair value liability of financial instruments with exposure to foreign currency risk was $0.9
billion and $1.0 billion. This presentation utilizes a population of foreign currency exchange derivatives, embedded derivatives and
foreign currency denominated debt and excludes the offsetting effect of foreign currency cash, cash equivalents and other assets. The
potential loss in fair value for such financial instruments from a 10% adverse change in all quoted foreign currency exchange rates
would be $0.2 billion at December 31, 2014 and 2013.
We are exposed to foreign currency risk due to the translation and remeasurement of the results of certain international operations
into U.S. Dollars as part of the consolidation process. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates can therefore create volatility in
the results of operations and may adversely affect our financial condition.
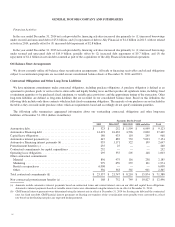
The following table summarizes the amounts of automotive foreign currency translation and transaction and remeasurement losses
(dollars in millions):
Years Ended December 31,
2014 2013
Foreign currency translation losses recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive loss .............. $ 19 $ 729
Losses resulting from foreign currency transactions and remeasurements recorded in earnings ........ $ 430 $ 352
Interest Rate Risk
We are subject to market risk from exposure to changes in interest rates related to certain financial instruments, primarily debt,
capital lease obligations and certain marketable securities. At December 31, 2014 and 2013 we did not have any interest rate swap
positions to manage interest rate exposures in our automotive operations. At December 31, 2014 and 2013 the fair value liability of
debt and capital leases was $9.8 billion and $6.8 billion. The potential increase in fair value resulting from a 10% decrease in quoted
interest rates would be $0.4 billion and $0.3 billion at December 31, 2014 and 2013.
At December 31, 2014 and 2013 we had marketable securities of $8.0 billion and $7.2 billion classified as available-for-sale and
$1.3 billion and $1.7 billion classified as trading. The potential decrease in fair value from a 50 basis point increase in interest rates
would be insignificant at December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Automotive Financing — GM Financial
Interest Rate Risk
Fluctuations in market interest rates can affect GM Financial’s gross interest rate spread, which is the difference between:
(1) interest earned on finance receivables; and (2) interest paid on debt, and could be affected by changes in interest rates. Typically
consumer finance receivables purchased by GM Financial bear fixed interest rates and are funded by variable or fixed rate debt.
Commercial finance receivables originated by GM Financial bear variable interest rates and are funded by variable rate debt. The
variable rate debt is subject to adjustments to reflect prevailing market interest rates. To help mitigate interest rate risk or mismatched
funding, GM Financial may employ hedging strategies to lock in the interest rate spread.
60