General Motors 2014 Annual Report Download - page 71
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 71 of the 2014 General Motors annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
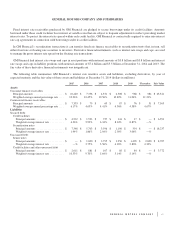
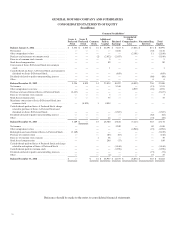
GENERAL MOTORS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Nature of Operations and Basis of Presentation
General Motors Company was incorporated as a Delaware corporation in 2009. We design, build and sell cars, trucks and
automobile parts worldwide. We also provide automotive financing services through GM Financial. We analyze the results of our
business through the following segments: GMNA, GME, GMIO, GMSA and GM Financial. Nonsegment operations are classified as
Corporate. Corporate includes certain centrally recorded income and costs, such as interest, income taxes and corporate expenditures
and certain nonsegment specific revenues and expenses.
As discussed in Note 13 we announced recalls of approximately 42 million vehicles and recorded charges of approximately $2.9
billion in Automotive cost of sales relating to recall campaigns and courtesy transportation in the year ended December 31, 2014 and
as discussed in Note 17 we announced the creation of a compensation program related to faulty ignition switches on certain vehicles
and recorded a charge of $400 million in the three months ended June 30, 2014.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements are prepared in conformity with U.S. GAAP. All intercompany balances and transactions
have been eliminated in consolidation. Certain prior year amounts were reclassified to conform to our current year presentation. In the
three months ended March 31, 2014 we changed our managerial and financial reporting structure to reclassify the results of our
Russian subsidiaries previously reported in our GMIO segment to our GME segment. We have retrospectively revised the segment
presentation for all periods presented. Refer to Note 25 for additional information on our segment reporting.
We consolidate entities that we control due to ownership of a majority voting interest and we consolidate variable interest entities
(VIEs) when we have variable interests and are the primary beneficiary. We continually evaluate our involvement with VIEs to
determine when these criteria are met. Our share of earnings or losses of nonconsolidated affiliates is included in our consolidated
operating results using the equity method of accounting when we are able to exercise significant influence over the operating and
financial decisions of the affiliate. We use the cost method of accounting if we are not able to exercise significant influence over the
operating and financial decisions of the affiliate.
Use of Estimates in the Preparation of the Financial Statements
Accounting estimates are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements. These estimates require the use of judgments and
assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of
the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses in the periods presented. We believe that the accounting
estimates employed are appropriate and the resulting balances are reasonable; however, due to the inherent uncertainties in making
estimates actual results could differ from the original estimates, requiring adjustments to these balances in future periods.
Change in Accounting Estimate
We historically accrued estimated costs related to recall campaigns in GMNA when they are probable and reasonably estimable,
which typically occurs once it is determined a specific recall campaign is needed and announced. During the three months ended
June 30, 2014, following the significant increase in the number of vehicles subject to recall in GMNA, the results of our ongoing
comprehensive safety review, additional engineering analysis, the creation of a new Global Product Integrity organization, the
appointment of a new Global Vice President of Vehicle Safety responsible for the safety development of our vehicle systems and our
overall commitment to customer satisfaction, we accumulated sufficient historical data in GMNA to support the use of an actuarial-
based estimation technique for recall campaigns. As such we now accrue at the time of vehicle sale in GMNA the costs for recall
campaigns. Based on expanded historical data, we recorded a catch-up adjustment of $874 million in Automotive cost of sales in the
three months ended June 30, 2014 to adjust the estimate for recall costs for previously sold vehicles. In other geographical regions the
historical claims data did not support the application of an actuarial-based model; therefore, recall campaigns are accrued when
probable and reasonably estimable, which typically occurs once it is determined a specific recall campaign is needed and announced.
71