Sony 2006 Annual Report Download - page 112
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 112 of the 2006 Sony annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
110
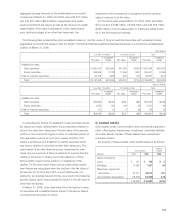
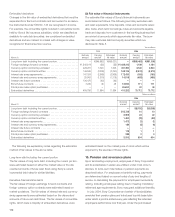
Aggregate amounts of annual maturities of long-term debt
during the next five years are as follows:
Yen in Dollars in
millions millions
Year ending March 31:
2007 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
¥193,555 $1,654
2008 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
32,781 280
2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
285,924 2,444
2010 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
66,431 568
2011 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
110,762 947
At March 31, 2006, Sony had unused committed lines of credit
amounting to ¥676,449 million ($5,782 million) and can generally
borrow up to 90 days from the banks with whom Sony has
committed line contracts. Furthermore, Sony has Commercial
Paper Programs, the size of which was ¥1,321,940 million
($11,299 million). There was no commercial paper outstanding at
March 31, 2006. Under those programs, Sony can issue com-
mercial paper for the period generally not in excess of 270 days
up to the size of the programs. In addition, Sony has Medium
Term Notes programs, the size of which was ¥587,100 million
($5,018 million). At March 31, 2006, the total outstanding balance
of Medium Term Notes was ¥58,698 million ($502 million).
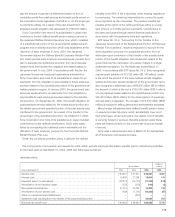
13. Deposits from customers in the banking
business
All deposits from customers in the banking business are interest
bearing deposits, and are owned by a Japanese bank subsidiary
which was established as an Online Internet bank for individuals.
At March 31, 2005 and 2006, the balance of time deposits
issued in amounts of ¥10 million ($85 thousand) or more were
¥67,387 million and ¥75,459 million ($645 million), respectively.
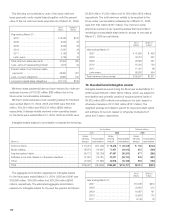
At March 31, 2006, aggregate amounts of annual maturities of
time deposits with a remaining term of more than one year are
as follows:
Yen in Dollars in
millions millions
Year ending March 31:
2008 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
¥30,568 $261
2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
20,657 177
2010 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
200 2
2011 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6,637 57
2012 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
38 0
14. Financial instruments
(1) Derivative instruments and hedging activities:
Sony has certain financial instruments including financial assets
and liabilities incurred in the normal course of business. Such
financial instruments are exposed to market risk arising from the
changes of foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates.
In applying a consistent risk management strategy for the
purpose of reducing such risk, Sony uses derivative financial
instruments, which include foreign exchange forward contracts,
foreign currency option contracts, and interest rate and currency
swap agreements. Foreign exchange forward contracts and
foreign currency option contracts are utilized primarily to limit the
exposure affected by changes in foreign currency exchange
rates on cash flows generated by anticipated intercompany
transactions and intercompany accounts receivable and payable
denominated in foreign currencies. Interest rate and currency
swap agreements are utilized primarily to lower funding costs, to
diversify sources of funding and to limit Sony’s exposure associ-
ated with underlying debt instruments and available-for-sale
debt securities resulting from adverse fluctuations in interest
rates, foreign currency exchange rates and changes in the fair
value. These instruments are executed with creditworthy finan-
cial institutions, and virtually all foreign currency contracts are
denominated in U.S. dollars, euros and other currencies of
major countries. Although Sony may be exposed to losses in
the event of nonperformance by counterparties or unfavorable
interest and currency rate movements, it does not anticipate
significant losses due to the nature of Sony’s counterparties or
the hedging arrangements. These derivatives generally mature
or expire within 6 months after the balance sheet date. Sony
does not use these derivative financial instruments for trading or
speculative purposes except for certain derivatives utilized for
portfolio investments such as interest rate swap agreements and
bond future contracts in the Financial Services segment. These
derivative transactions utilized for portfolio investments in the
Financial Services segment are executed within a certain limit in
accordance with an internal risk management policy.
Derivative financial instruments held by Sony are classified and
accounted for as described below pursuant to FAS No. 133.
Fair value hedges
The derivatives designated as fair value hedges include interest
rate and currency swap agreements.
Both the derivatives designated as fair value hedges and the
hedged items are reflected at fair value in the consolidated
balance sheet. Changes in the fair value of the derivatives
designated as fair value hedges as well as offsetting changes in
the carrying value of the underlying hedged items are recognized
in income.
For the fiscal years ended March 31, 2004 and 2005, the
amount of ineffectiveness of these fair value hedges, that was
reflected in earnings, was not material. For the fiscal year ended
March 31, 2006, these fair value hedges were fully effective. In
addition, there were no amounts excluded from the assessment
of hedge effectiveness of fair value hedges.
Cash flow hedges
The derivatives designated as cash flow hedges include foreign