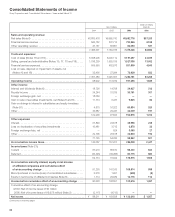
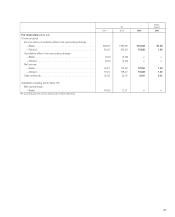
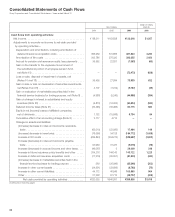
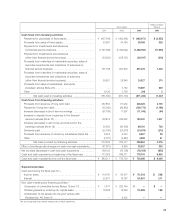
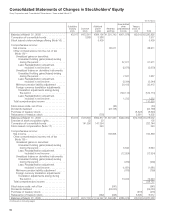
Sony 2006 Annual Report Download - page 98
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 98 of the 2006 Sony annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.96
■ Use of estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in
conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make
estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of
assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and
liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported
amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period.
Actual results could differ from those estimates.
■ Translation of foreign currencies
All asset and liability accounts of foreign subsidiaries and
affiliates are translated into Japanese yen at appropriate year-
end current rates and all income and expense accounts are
translated at rates that approximate those rates prevailing at the
time of the transactions. The resulting translation adjustments
are accumulated as a component of accumulated other
comprehensive income.
Foreign currency receivables and payables are translated at
appropriate year-end current rates and the resulting translation
gains or losses are taken into income.
■ Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include all highly liquid investments,
generally with original maturities of three months or less, that are
readily convertible to known amounts of cash and are so near
maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value
because of changes in interest rates.
■ Marketable debt and equity securities
Debt and equity securities designated as available-for-sale, whose
fair values are readily determinable, are carried at fair value with
unrealized gains or losses included as a component of accumu-
lated other comprehensive income, net of applicable taxes. Debt
and equity securities classified as trading securities are carried at
fair value with unrealized gains or losses included in income. Debt
securities that are expected to be held-to-maturity are carried at
amortized cost. Individual securities classified as either available-
for-sale or held-to-maturity are reduced to net realizable value by
a charge to income for other than temporary declines in fair value.
Realized gains and losses are determined on the average cost
method and are reflected in income.
■ Equity securities in non-public companies
Equity securities in non-public companies are carried at cost as fair
value is not readily determinable. If the value of a non-public equity
investment is estimated to have declined and such decline is
judged to be other than temporary, Sony recognizes the impair-
ment of the investment and the carrying value is reduced to its fair
value. Determination of impairment is based on the consideration
of such factors as operating results, business plans and estimated
future cash flows. Fair value is determined through the use of such
methodologies as discounted cash flows, valuation of recent
financings and comparable valuations of similar companies.
■ Inventories
Inventories in electronics and game as well as non-film inventories
for pictures are valued at cost, not in excess of market, cost
being determined on the “average cost” basis except for the
cost of finished products carried by certain subsidiary companies
in electronics which is determined on the “first-in, first-out” basis.
■ Film costs
Film costs related to theatrical and television product (which
includes direct production costs, production overhead and
acquisition costs) are stated at the lower of unamortized cost or
estimated fair value and classified as non-current assets. Film
costs are amortized, and the estimated liabilities for residuals
and participations are accrued, for an individual product based
on the proportion that current period actual revenues bear to the
estimated remaining total lifetime revenues. These estimates are
reviewed on a periodic basis.
■ Property, plant and equipment and depreciation
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation
of property, plant and equipment is primarily computed on the
declining-balance method for Sony Corporation and its Japanese
subsidiaries, except for certain semiconductor manufacturing
facilities whose depreciation is computed on the straight-line
method, and on the straight-line method for its foreign subsidiar-
ies at rates based on estimated useful lives of the assets, princi-
pally, ranging from 15 years up to 50 years for buildings and
from 2 years up to 10 years for machinery and equipment.
Significant renewals and additions are capitalized at cost. Main-
tenance and repairs, and minor renewals and betterments are
charged to income as incurred.
■ Goodwill and other intangible assets
Goodwill and certain other intangible assets that are determined
to have an indefinite life are not amortized and are tested for
impairment during the fourth quarter of fiscal year on an annual
basis and between annual tests if an event occurs or circum-
stances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair
value below its carrying amount. Fair value for those assets is
generally determined using a discounted cash flow analysis.
Intangible assets with finite lives that are determined not to have
an indefinite life mainly consist of artist contracts, music catalogs,
acquired patent rights and software to be sold, leased or otherwise
marketed. Artist contracts and music catalogs are amortized on a
straight-line basis over 10 to 40 years. Acquired patent rights and
software to be sold, leased or otherwise marketed are amortized on
a straight-line basis over 3 to 10 years.