Coca Cola 2011 Annual Report Download - page 104
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 104 of the 2011 Coca Cola annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
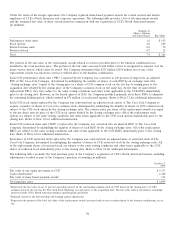
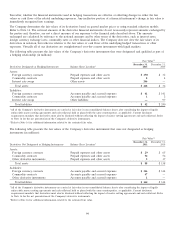
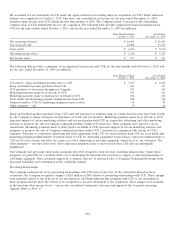
The following table summarizes the pretax impact that changes in the fair values of derivatives designated as fair value hedges had
on earnings during the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010 (in millions):
Location of Gain (Loss) Gain (Loss)
Hedging Instruments and Hedged Items Recognized in Income Recognized in Income
2011
Interest rate swaps Interest expense $ 343
Fixed-rate debt Interest expense (333)
Total $10
2010
Interest rate swaps Interest expense $ (97)
Fixed-rate debt Interest expense 102
Total $5
Hedges of Net Investments in Foreign Operations Strategy
The Company uses forward contracts to protect the value of our investments in a number of foreign subsidiaries. For derivative
instruments that are designated and qualify as hedges of net investments in foreign operations, the changes in fair values of the
derivative instruments are recognized in net foreign currency translation gain (loss), a component of AOCI, to offset the changes
in the values of the net investments being hedged. Any ineffective portions of net investment hedges are reclassified from AOCI
into earnings during the period of change. The total notional value of derivatives under this hedging program as of December 31,
2011, was $1,681 million. The Company had no outstanding derivative instruments under this hedging program as of
December 31, 2010.
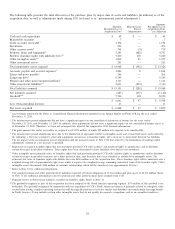
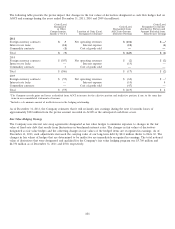
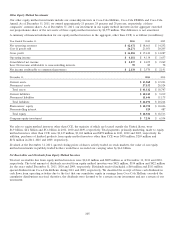
The following table presents the pretax impact that changes in the fair values of derivatives designated as net investment hedges
had on AOCI during the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010 (in millions):
Gain (Loss)
Recognized in OCI
Year Ended December 31, 2011 2010
Foreign currency contracts $(3) $ (15)
The Company did not reclassify any deferred gains or losses related to net investment hedges from AOCI to earnings during the
years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009. In addition, the Company did not have any ineffectiveness related to net
investment hedges during the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009.
Economic (Non-Designated) Hedging Strategy
In addition to derivative instruments that are designated and qualify for hedge accounting, the Company also uses certain
derivatives as economic hedges of foreign currency and commodity exposure. Although these derivatives were not designated
and/or did not qualify for hedge accounting, they are effective economic hedges. The changes in fair value of economic hedges are
immediately recognized into earnings.
The Company uses foreign currency economic hedges to offset the earnings impact that fluctuations in foreign currency exchange
rates have on certain monetary assets and liabilities denominated in nonfunctional currencies. The changes in fair value of
economic hedges used to offset the monetary assets and liabilities are recognized into earnings in the line item other income
(loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income. In addition, we use foreign currency economic hedges to minimize the
variability in cash flows associated with changes in foreign currency exchange rates. The changes in fair value of economic hedges
used to offset the variability in U.S. dollar net cash flows are recognized into earnings in the line items net operating revenues
and cost of goods sold in our consolidated statements of income. The total notional value of derivatives related to our foreign
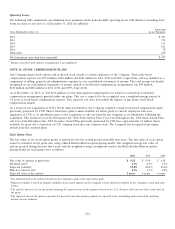
currency economic hedges as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, was $3,629 million and $2,312 million, respectively.
In 2010, the Company initiated certain commodity hedging programs as a result of our acquisition of CCE’s North American
business. The Company uses these types of derivatives as economic hedges to mitigate the price risk associated with the
purchases of materials used in the manufacturing process and for vehicle fuel. The changes in fair values of these economic
hedges are immediately recognized into earnings in the line items cost of goods sold and selling, general and administrative
102