Humana 2011 Annual Report Download - page 87
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 87 of the 2011 Humana annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
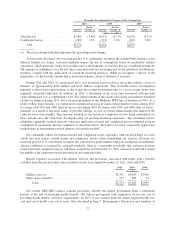
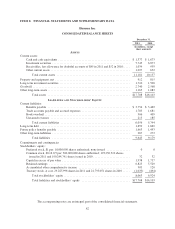
Investment Securities
Investment securities totaled $9.5 billion, or 53% of total assets at December 31, 2011, and $8.4 billion, or
52% of total assets at December 31, 2010. Debt securities, detailed below, comprised this entire investment
portfolio at December 31, 2011 and at December 31, 2010. The fair value of debt securities were as follows at
December 31, 2011 and 2010:
December 31,
2011
Percentage
of Total
December 31,
2010
Percentage
of Total
(dollars in millions)
U.S. Treasury and other U.S. government corporations and
agencies:
U.S. Treasury and agency obligations ............. $ 725 7.7% $ 712 8.5%
Mortgage-backed securities ..................... 1,784 18.9% 1,664 19.9%
Tax-exempt municipal securities ..................... 2,856 30.2% 2,433 29.1%
Mortgage-backed securities:
Residential .................................. 44 0.4% 56 0.6%
Commercial ................................. 381 4.0% 321 3.8%
Asset-backed securities ............................ 83 0.9% 150 1.8%
Corporate debt securities ........................... 3,580 37.9% 3,032 36.2%
Redeemable preferred stock ........................ 0 0.0% 5 0.1%
Total debt securities ....................... $9,453 100.0% $8,373 100.0%
Approximately 95% of our debt securities were investment-grade quality, with a weighted average credit
rating of AA- by S&P at December 31, 2011. Most of the debt securities that were below investment-grade were
rated BB, the higher end of the below investment-grade rating scale. Our investment policy limits investments in
a single issuer and requires diversification among various asset types.
Tax-exempt municipal securities included pre-refunded bonds of $332 million at December 31, 2011 and
$344 million at December 31, 2010. These pre-refunded bonds were secured by an escrow fund consisting of
U.S. government obligations sufficient to pay off all amounts outstanding at maturity. The ratings of these
pre-refunded bonds generally assume the rating of the government obligations at the time the fund is established.
Tax-exempt municipal securities that were not pre-refunded were diversified among general obligation bonds of
U.S. states and local municipalities and special revenue bonds. General obligation bonds, which are backed by
the taxing power and full faith of the issuer, accounted for $1.1 billion of these municipals in the
portfolio. Special revenue bonds, issued by a municipality to finance a specific public works project such as
utilities, water and sewer, transportation, and education, and supported by the revenues of that project, accounted
for $1.4 billion of these municipals. Our general obligation bonds are diversified across the U.S. with no
individual state exceeding 11%. In addition, certain monoline insurers guarantee the timely repayment of bond
principal and interest when a bond issuer defaults and generally provide credit enhancement for bond issues
related to our tax-exempt municipal securities. We have no direct exposure to these monoline insurers. We
owned $634 million and $597 million at December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively, of tax-exempt securities
guaranteed by monoline insurers. The equivalent weighted average S&P credit rating of these tax-exempt
securities without the guarantee from the monoline insurer was AA.
Our direct exposure to subprime mortgage lending is limited to investment in residential mortgage-backed
securities and asset-backed securities backed by home equity loans. The fair value of securities backed by Alt-A
and subprime loans was $3 million at December 31, 2011 and December 31, 2010. There are no collateralized
debt obligations or structured investment vehicles in our investment portfolio.
The percentage of corporate securities associated with the financial services industry was 19.3% at
December 31, 2011 and 29.4% at December 31, 2010.
77