Sony 2005 Annual Report Download - page 104
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 104 of the 2005 Sony annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Sony Corporation 101
Fair value hedges
The derivatives designated as fair value hedges include interest
rate and currency swap agreements.
Both the derivatives designated as fair value hedges and
hedged items are reflected at fair value in the consolidated
balance sheet. Changes in the fair value of the derivatives
designated as fair value hedges as well as offsetting changes in
the carrying value of the underlying hedged items are recognized
in income.
The amount of ineffectiveness of these fair value hedges, that
was reflected in earnings, was not material for the years ended
March 31, 2003, 2004 and 2005. In addition, there were no
amounts excluded from the assessment of hedge effectiveness
of fair value hedges.
Cash flow hedges
The derivatives designated as cash flow hedges include foreign
exchange forward contracts, foreign currency option contracts
and interest rate and currency swap agreements.
Changes in the fair value of derivatives designated as cash
flow hedges are initially recorded in other comprehensive income
and reclassified into earnings when the hedged transaction
affects earnings. For the years ended March 31, 2003 and
2004, these cash flow hedges were fully effective. For the year
ended March 31, 2005, the amount of ineffectiveness of these
cash flow hedges that was reflected in earnings was not mate-
rial. In addition, there were no amounts excluded from the
assessment of hedge effectiveness of cash flow hedges. At
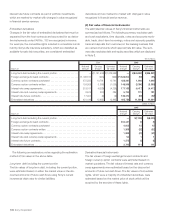
March 31, 2005, amounts related to derivatives qualifying as
cash flow hedges amounted to a net reduction of equity of
¥2,490 million ($23 million). Within the next twelve months,
¥1,615 million ($15 million) is expected to be reclassified from
equity into earnings as loss. For the year ended March 31,
2005, there were no forecasted transactions that failed to occur
which resulted in the discontinuance of cash flow hedges.
Derivatives not designated as hedges
The derivatives not designated as hedges under FAS No. 133
include foreign exchange forward contracts, foreign currency
option contracts, interest rate and currency swap agreements,
convertible rights included in convertible bonds and other.
Changes in the fair value of derivatives not designated as
hedges are recognized in income.
A description of the purpose and classification of the deriva-
tive financial instruments held by Sony is as follows:
Foreign exchange forward contracts and foreign currency option
contracts
Sony enters into foreign exchange forward contracts and pur-
chased and written foreign currency option contracts primarily to
fix the cash flows from intercompany accounts receivable and
payable and forecasted transactions denominated in functional
currencies (Japanese yen, U.S. dollars and euros) of Sony’s
major operating units. The majority of written foreign currency
option contracts are a part of range forward contract arrange-
ments and expire in the same month with the corresponding
purchased foreign currency option contracts.
Sony also enters into foreign exchange forward contracts,
which effectively fix the cash flows from foreign currency
denominated debt. Accordingly, these derivatives have been
designated as cash flow hedges in accordance with FAS
No. 133.
Foreign exchange forward contracts and foreign currency
option contracts that do not qualify as hedges are marked-
to-market with changes in value recognized in other income
and expenses.
Interest rate and currency swap agreements
Sony enters into interest rate and currency swap agreements,
which are used for reducing the risk arising from the changes in
the fair value of fixed rate debt and available-for-sale debt
securities. For example, Sony enters into interest rate and
currency swap agreements, which effectively swap foreign
currency denominated fixed rate debt for functional currency
denominated variable rate debt. These derivatives are consid-
ered to be a hedge against changes in the fair value of Sony’s
foreign denominated fixed-rate obligations. Accordingly, these
derivatives have been designated as fair value hedges in accor-
dance with FAS No. 133.
Sony also enters into interest rate and currency swap agree-
ments that are used for reducing the risk arising from the
changes in anticipated cash flow of variable rate debt and
foreign currency denominated debt. For example, Sony enters
into interest rate and currency swap agreements, which effec-
tively swap foreign currency denominated variable rate debt for
functional currency denominated fixed rate debt. These deriva-
tives are considered to be a hedge against changes in the
anticipated cash flow of Sony’s foreign denominated variable
rate obligations. Accordingly, these derivatives have been desig-
nated as cash flow hedges in accordance with FAS No. 133.
Certain subsidiaries in the Financial Services segment have
interest rate swap agreements as part of portfolio investments,
which are marked-to-market with changes in value recognized
in financial service revenue.
Any other interest rate and currency swap agreements that do
not qualify as hedges, which are used for reducing the risk
arising from changes of variable rate and foreign currency
dominated intercompany debt, are marked-to-market with
changes in value recognized in other income and expenses.
Interest rate future contracts
Certain subsidiaries in the Financial Services segment have
BH6/30 Adobe PageMaker 6.0J /PPC