Sysco 2011 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2011 Sysco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
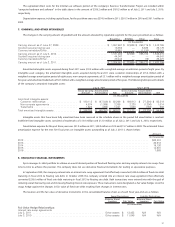
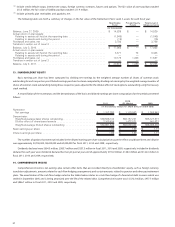
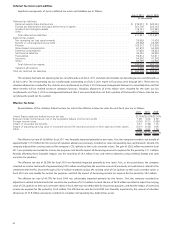
The company’s target and actual investment allocation as of July 2, 2011 is as follows:
Target Asset
Allocation Range
Actual Asset
Allocation
U.S. equity .............................................................. 23-31% 33%
International equity ......................................................... 23-31 28
Core fixed income ......................................................... 11-17 15
Long duration fixed income ................................................... 10-18 13
High yield fixed income ...................................................... 6-12 9
Alternative investments ..................................................... 5-15 2
100%
Sysco’s investment strategy is implemented through a combination of balanced and specialist investment managers, passive investment
funds and actively-managed investment funds. U.S. equity consists of both large-cap and small-to-mid-cap securities. Core fixed income
investments include intermediate range U.S. government and agency securities, corporate bonds from diversified industries, asset-backed
securities, mortgage-backed securities, other debt securities and derivative securities. Long duration fixed income investments include
U.S. government and agency securities, corporate bonds from diversified industries, asset-backed securities, mortgage-backed securities, other
debt securities and derivative securities. High yield fixed income consists of below investment grade corporate debt securities and may include
derivative securities. Alternative investments may include private equity, private real estate, timberland, and commodities investments.
Investment funds are selected based on each fund’s stated investment strategy to align with Sysco’s overall target mix of investments. Actual
asset allocation is regularly reviewed and periodically rebalanced to the target allocation when considered appropriate. As of July 2, 2011, actual
asset allocation varied from the stated target in certain categories, as alternative investment funding, primarily in private equity funds require
contributions over a multi-year period. Until such capital is required, the company has chosen to invest these amounts in U.S. equities.
As discussed above, the Retirement Plan’s investments in equity, fixed income and alternative investments provide a range of returns and also
expose the plan to investment risk. However, the investment policies put in place by the company require diversification of plan assets across
issuers, industries and countries. As such, the Retirement Plan does not have significant concentrations of risk in plan assets.
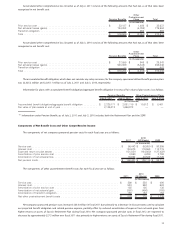
Fair Value of Plan Assets
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market
participants at the measurement date (i.e. an exit price). See Note 3, “Fair Value Measurements,” for a description of the fair value hierarchy that
prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The following is a description of the valuation methodologies used for
assets and liabilities measured at fair value.
Cash and cash equivalents: Valued at amortized cost, which approximates fair value. Cash and cash equivalents is included as a Level 2
measurement in the table below.
Equity securities: Valued at the closing price reported on the exchange market. If a stock is not listed on a public exchange, such as an
American Depository Receipt or some preferred stocks, the stock is valued using an evaluated bid price based on a compilation of observable
market information. Inputs used include yields, the underlying security “best price”, adjustments for corporate actions and exchange prices of
underlying and common stock of the same issuer. Equity securities valued at the closing price reported on the exchange market are classified as a
Level 1 measurement in the table below; all other equity securities are included as a Level 2 measurement.
Fixed income securities: Valued using evaluated bid prices based on a compilation of observable market information or a broker quote in a
non-active market. Inputs used vary by type of security, but include spreads, yields, rate benchmarks, rate of prepayment, cash flows, rating
changes and collateral performance and type. All fixed income securities are included as a Level 2 measurement in the table below.
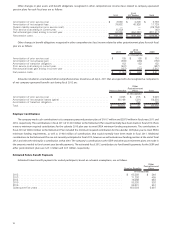
Investment funds: Valued at the net asset value (NAV) provided by the manager of each fund. The NAV is calculated as the underlying net
assets owned by the fund, divided by the number of shares outstanding. The NAV is based on the fair value of the underlying securities within the
fund. The real estate fund is valued at the NAV of shares held by the Retirement Plan, which is based on the valuations of the underlying real estate
investments held by the fund. Each real estate investment is valued on the basis of a discounted cash flow approach. Inputs used include future
rental receipts, expenses and residual values from a market participant view of the highest and best use of the real estate as rental property. All
investment funds, with the exception of the real estate fund and private equity funds, are included as a Level 2 measurement in the table below.
The real estate fund and private equity funds are included as Level 3 measurements.
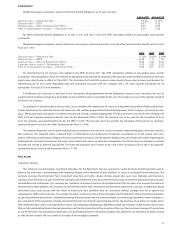
Derivatives: Valuation method varies by type of derivative security.
•Credit default and interest rate swaps: Valued using evaluated bid prices based on a compilation of observable market information. Inputs
used for credit default swaps include spread curves and trade data about the credit quality of the counterparty. Inputs used for interest
rate swaps include benchmark yields, swap curves, cash flow analysis, and interdealer broker rates. Credit default and interest rate swaps
are included as a Level 2 measurement in the table below.
•Foreign currency contracts: Valued using a standardized interpolation model that utilizes the quoted prices for standard-length forward
foreign currency contracts and adjusts to the remaining term outstanding on the contract being valued. Foreign currency contracts are
included as a Level 2 measurement in the table below.
58