Toyota 2013 Annual Report Download - page 48
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 48 of the 2013 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.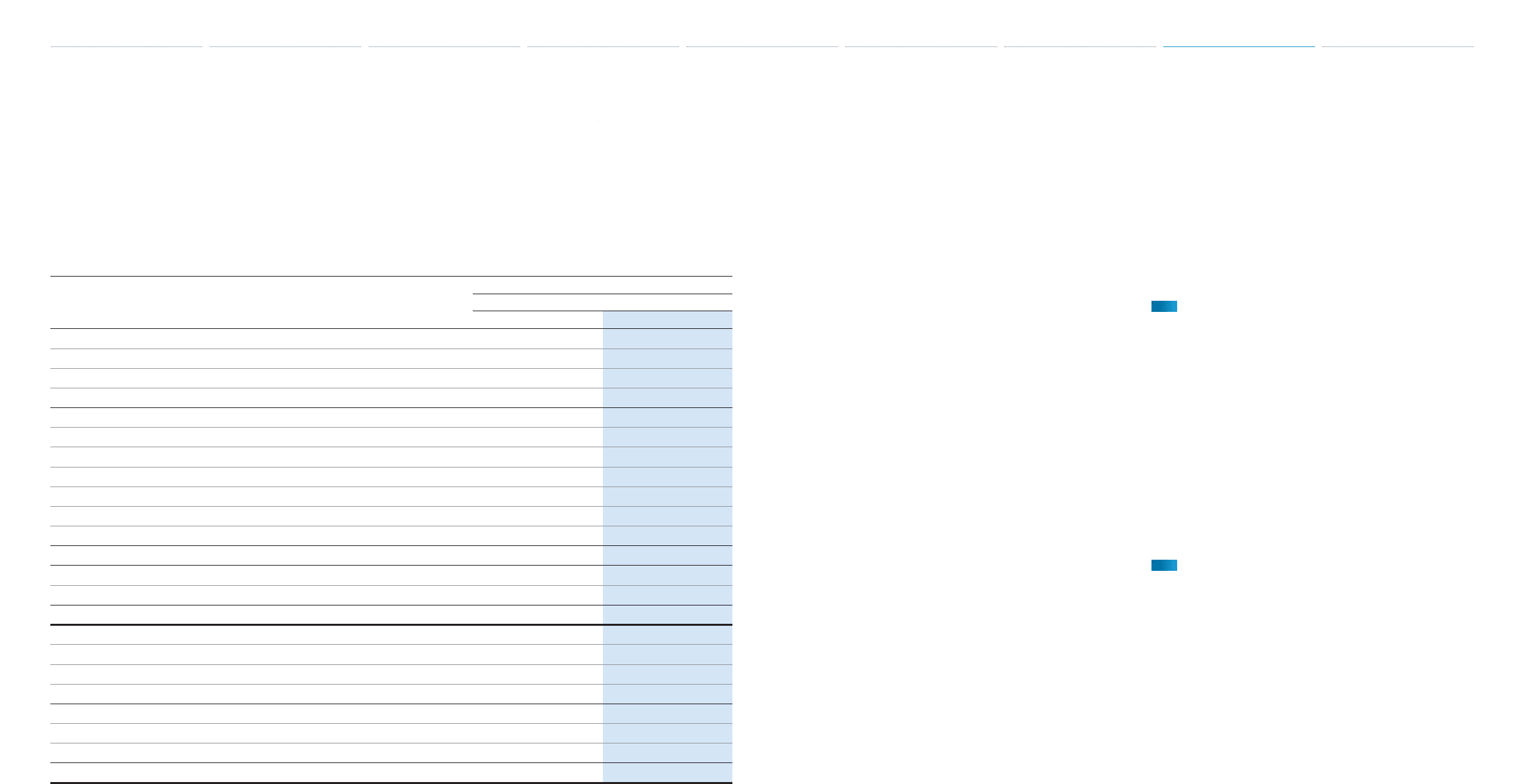
Toyota Global Vision President’s Message Launching a New Structure Special Feature Review of Operations
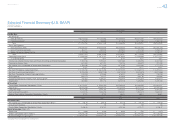
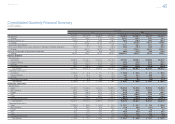
Consolidated Performance
Highlights
Management and
Corporate Information Investor InformationFinancial Section
Page 48
NextPrev
ContentsSearchPrint
ANNUAL REPORT 2013
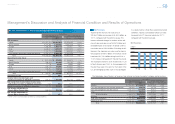
The following table provides information regarding Toyota’s fi nance receivables and operating leases in the
past two fi scal years.
Yen in millions
March 31,
2012 2013
Finance Receivables
Retail ¥ 7,248,793 ¥ 9,047,782
Finance leases 955,430 1,029,887
Wholesale and other dealer loans 2,033,954 2,615,728
10,238,177 12,693,397
Deferred origination costs 105,533 135,398
Unearned income (494,123) (628,340)
Allowance for credit losses
Retail (77,353) (83,858)
Finance leases (30,637) (28,928)
Wholesale and other dealer loans (24,238) (26,243)
(132,228) (139,029)
Total fi nance receivables, net 9,717,359 12,061,426
Less—Current portion (4,114,897) (5,117,660)
Noncurrent fi nance receivables, net ¥ 5,602,462 ¥ 6,943,766
Operating Leases
Vehicles ¥ 2,536,595 ¥ 2,999,294
Equipment 87,848 104,351
Less—Deferred income and other (49,090) (65,634)
2,575,353 3,038,011
Less—Accumulated depreciation (667,406) (749,238)
Less—Allowance for credit losses (8,135) (8,020)
Vehicles and equipment on operating leases, net ¥ 1,899,812 ¥ 2,280,753
Toyota enters into interest rate swap agreements
and cross currency interest rate swap agreements
to convert its fi xed-rate debt to variable-rate func-
tional currency debt. A portion of the derivative
instruments are entered into to hedge interest rate
risk from an economic perspective and are not des-
ignated as a hedge of specifi c assets or liabilities on
Toyota’s consolidated balance sheet and according-
ly, unrealized gains or losses related to derivatives
that are not designated as a hedge are recognized
currently in operations. See discussion in “Critical
Accounting Estimates—Derivatives and Other
Contracts at Fair Value” and “Quantitative and
Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk” and
notes 20 and 26 to the consolidated fi nancial
statements.
The fl uctuations in funding costs can affect the
profi tability of Toyota’s fi nancial services operations.
Funding costs are affected by a number of factors,
some of which are not in Toyota’s control. These
factors include general economic conditions, pre-
vailing interest rates and Toyota’s fi nancial strength.
Funding costs decreased during fi scal 2012 and
2013, mainly as a result of lower interest rates.
Toyota launched its credit card business in Japan
in April 2001. As of March 31, 2012, Toyota had
10.9 million cardholders, an increase of 2.0 million
cardholders compared with March 31, 2011. As of
March 31, 2013, Toyota had 11.8 million cardhold-
ers, an increase of 0.9 million cardholders compared
with March 31, 2012. The credit card receivables at
March 31, 2012 increased by ¥44.0 billion from
March 31, 2011 to ¥307.5 billion. The credit card
receivables at March 31, 2013 increased by ¥30.5
billion from March 31, 2012 to ¥338.1 billion.
Other Business Operations
Toyota’s other business operations consist of hous-
ing including the manufacture and sale of prefabri-
cated homes, information technology related
businesses including information technology and
telecommunications, intelligent transport systems
and GAZOO, and other businesses.
Toyota does not expect its other business opera-
tions to materially contribute to Toyota’s consolidat-
ed results of operations.
Currency Fluctuations
Toyota is affected by fl uctuations in foreign currency
exchange rates. Toyota is exposed to fl
uctuations in
the value of the Japanese yen against the U.S. dollar
and the euro and, to a lesser extent, the Australian
dollar, the Russian ruble, the Canadian dollar, the
British pound, and others. Toyota’s consolidated
fi nancial statements, which are presented in
Japanese yen, are affected by foreign currency
exchange fl uctuations through both translation risk
and transaction risk.
Translation risk is the risk that Toyota’s consoli-
dated fi nancial statements for a particular period or
for a particular date will be affected by changes in
the prevailing exchange rates of the currencies in
those countries in which Toyota does business
compared with the Japanese yen. Even though the
fl uctuations of currency exchange rates to the
Japanese yen can be substantial, and, therefore,
Toyota’s fi nance receivables are subject to col-
lectability risks. These risks include consumer and
dealer insolvencies and insuffi cient collateral values
(less costs to sell) to realize the full carrying values
of these receivables. See discussion in “Critical
Accounting Estimates—Allowance for Doubtful
Accounts and Credit Losses” and note 11 to the
consolidated fi nancial statements.
Toyota continues to originate leases to fi nance new
Toyota vehicles. These leasing activities are subject
to residual value risk. Residual value losses could be
incurred when the lessee of a vehicle does not exer-
cise the option to purchase the vehicle at the end of
the lease term. See discussion in “Critical Accounting
Estimates—Investment in Operating Leases” and
note 2 to the consolidated fi nancial statements.
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Selected Financial Summary (U.S. GAAP) Consolidated Segment Information Consolidated Quarterly Financial Summary Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations [3 of 26] Consolidated Financial Statements Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm