General Motors 2011 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
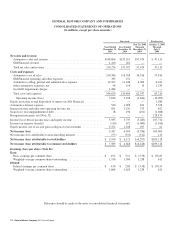
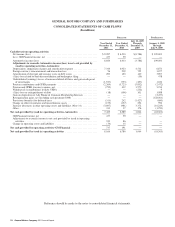
Please find page 68 of the 2011 General Motors annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.GENERAL MOTORS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Automotive
We enter into a variety of foreign currency exchange and commodity forward contracts and options to manage exposures arising
from market risks resulting from changes in certain foreign currency exchange rates and commodity prices. We do not enter into
derivative transactions for speculative purposes.
The overall financial risk management program is under the responsibility of the Risk Management Committee, which reviews and,
where appropriate, approves strategies to be pursued to mitigate these risks. The Risk Management Committee is composed of
members of our Management and functions under the oversight of the Finance and Risk Committee, a committee of the Board of
Directors. The Finance and Risk Committee assists and guides the Board in its oversight of our financial and risk management
strategies. A risk management control framework is utilized to monitor the strategies, risks and related hedge positions, in accordance
with the policies and procedures approved by the Risk Management Committee. Our risk management policy intends to protect
against risk arising from extreme adverse market movements on our key exposures.
Further information on our exposure to market risk is included in Note 19 to our consolidated financial statements.
The following analyses provide quantitative information regarding exposure to foreign currency exchange rate risk, interest rate
risk, commodity price risk and equity price risk. Sensitivity analysis is used to measure the potential loss in the fair value of financial
instruments with exposure to market risk. The models used assume instantaneous, parallel shifts in exchange rates, interest rate yield
curves and commodity prices. For options and other instruments with nonlinear returns, models appropriate to these types of
instruments are utilized to determine the effect of market shifts. There are certain shortcomings inherent in the sensitivity analyses
presented, due primarily to the assumption that interest rates and commodity prices change in a parallel fashion and that spot
exchange rates change instantaneously. In addition, the analyses are unable to reflect the complex market reactions that normally
would arise from the market shifts modeled and do not contemplate the effects of correlations between foreign currency pairs, or
offsetting long-short positions in currency pairs which may significantly reduce the potential loss in value.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
We have foreign currency exposures related to buying, selling, and financing in currencies other than the functional currencies of
the operations. Derivative instruments, such as foreign currency forwards, swaps and options are used primarily to hedge exposures
with respect to forecasted revenues, costs and commitments denominated in foreign currencies. At December 31, 2011 such contracts
have remaining maturities of up to 12 months. At December 31, 2011 our three most significant foreign currency exposures are the
Euro/British Pound, U.S. Dollar/Korean Won and Euro/Korean Won.
At December 31, 2011 and 2010 the net fair value liability of financial instruments with exposure to foreign currency risk was
$4.2 billion and $3.3 billion. This presentation utilizes a population of foreign currency exchange derivatives, embedded derivatives
and foreign currency denominated debt and excludes the offsetting effect of foreign currency cash, cash equivalents and other assets.
The potential loss in fair value for such financial instruments from a 10% adverse change in all quoted foreign currency exchange
rates would be $637 million and $513 million at December 31, 2011 and 2010.
We are exposed to foreign currency risk due to the translation and remeasurement of the results of certain international operations
into U.S. Dollars as part of the consolidation process. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates can therefore create volatility in
the results of operations and may adversely affect our financial position.
66 General Motors Company 2011 Annual Report