General Motors 2012 Annual Report Download - page 140
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 140 of the 2012 General Motors annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
GENERAL MOTORS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
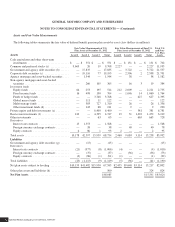
Transfers In and/or Out of Level 3
There were no significant transfers into and/or out of Level 3 within U.S. or non-U.S. plan assets during the years ended
December 31, 2012 and 2011.
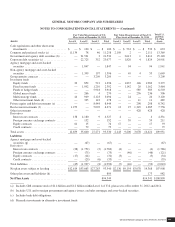
Investment Fund Strategies
Equity funds include funds that invest in U.S. common and preferred stocks as well as similar equity securities issued by companies
incorporated, listed or domiciled in developed and/or emerging markets countries. Certain fund managers may attempt to profit from
security mispricing in equity markets. Equity long/short managers typically construct portfolios consisting of long and short positions,
which may be determined by a variety of techniques including fundamental, quantitative and technical analysis. Index funds,
exchange traded funds and derivatives may be used for hedging purposes to limit exposure to various risk factors.
Fixed income funds include investments in high quality and high yield funds as well as in credit arbitrage funds. High quality fixed
income funds invest in U.S. government securities, investment-grade corporate bonds, mortgages and asset-backed securities. High
yield fixed income funds invest in U.S. high yield fixed income securities issued by corporations which are rated below investment
grade, are unrated but are believed by the investment manager to have similar risk characteristics or are rated investment grade or
higher but are priced at yields comparable to securities rated below investment grade and believed to have similar risk characteristics.
Credit arbitrage funds invest in a variety of credit and credit-related instruments that allow fund managers to profit from mispricing of
these credit instruments. Certain derivatives may be used for hedging purposes by some fixed income fund managers to limit exposure
to various risk factors.
Funds of hedge funds include funds that invest in a portfolio of hedge funds. Funds of hedge fund managers typically seek to
achieve their objectives by allocating capital across a broad array of funds and/or investment managers.
Global macro funds include funds that enter into leveraged transactions utilizing a variety of equity, fixed income and derivative
instruments to benefit from anticipated price movements of stock, interest rates, foreign exchange currencies and physical
commodities markets while minimizing downside risk. Global macro managers may invest in a variety of markets to participate in
expected market movements.
Multi-strategy funds include funds that invest in broadly diversified portfolios of equity, fixed income and derivative instruments.
Certain funds may also employ multiple alternative investment strategies, in combination, such as global macro, event-driven (which
seeks to profit from opportunities created by significant transactional events such as spin-offs, mergers and acquisitions, bankruptcy
reorganizations, recapitalizations and share buybacks) and relative value (which seeks to take advantage of pricing discrepancies
between instruments including equities, debt, options and futures).
Other investment funds generally consist of funds that employ broad-ranging strategies and styles. The objective of such funds is to
deliver returns having relatively low volatility and correlation to movements in major equity and bond markets. Funds in this category
employ single strategies such as event-driven or relative value.
Private equity and debt investments principally consists of investments in private equity and debt funds. These investments are
made to gain exposure to and benefit from long-term equity investments in private companies, including leveraged buy-outs, venture
capital and distressed debt strategies.
Real estate investments include funds that invest in entities which are principally engaged in the ownership, acquisition,
development, financing, sale and/or management of income-producing real estate properties, both commercial and residential. These
funds typically seek long-term growth of capital and current income that is above average relative to public equity funds.
General Motors Company 2012 ANNUAL REPORT 137