Philips 2005 Annual Report Download - page 134
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 134 of the 2005 Philips annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Philips Annual Report 2005134
Accounting policies
Theconsolidatednancialstatementsarepreparedinaccordancewith
generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (US GAAP).
Historical cost is used as the measurement basis unless otherwise indicated.
Consolidation principles
Theconsolidatednancialstatementsincludetheaccountsof
Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. (the ‘Company’) and all entities in
which a direct or indirect controlling interest exists through voting
rights or qualifying variable interests. All intercompany balances
andtransactionshavebeeneliminatedintheconsolidatednancial
statements. Net income is reduced by the portion of the earnings of
subsidiaries applicable to minority interests. The minority interests are
disclosed separately in the consolidated statements of income and in
the consolidated balance sheets.
The Company applies Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
Interpretation No. 46(R) ‘Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities’. In
accordance with Interpretation of Accounting Research Bulletin No. 51
‘Consolidated Financial Statements’, the Company consolidates entities
in which variable interests are held to an extent that would require the
Company to absorb a majority of the entity’s expected losses, receive a
majority of the entity’s expected residual returns, or both.
Investments in unconsolidated companies
Investments in companies in which the Company does not have the
abilitytodirectlyorindirectlycontrolthenancialandoperating
decisions,butdoespossesstheabilitytoexertsignicantinuence,are
accounted for using the equity method. Generally, in the absence of
demonstrableproofofsignicantinuence,itispresumedtoexistifat
least 20% of the voting stock is owned. The Company’s share of the net
income of these companies is included in results relating to unconsolidated
companies in the consolidated statements of income. The Company
recognizes an impairment loss when an other-than-temporary decline in
the value of an investment occurs. When the Company’s share of losses
exceeds the carrying amount of an investment accounted for by the
equity method, the Company’s carrying amount of that investment is
reduced to zero and recognition of further losses is discontinued unless
the Company has guaranteed obligations of the investee or is otherwise
committedtoprovidefurthernancialsupportfortheinvestee.
Accounting for capital transactions of a subsidiary or an
unconsolidated company
The Company recognizes dilution gains or losses arising from the sale
or issuance of stock by a consolidated subsidiary or an unconsolidated
entity which the Company is accounting for using the equity method
of accounting in the income statement, unless the Company or the
subsidiary either has reacquired or plans to reacquire such shares. In
such instances, the result of the transaction will be recorded directly
in stockholders’ equity as a non-operating gain or loss.
The dilution gains or losses are presented in the income statement
under Other business income (expenses) if they relate to consolidated
subsidiaries. Dilution gains and losses related to unconsolidated companies
are presented under Results relating to unconsolidated companies.
Foreign currencies
Thenancialstatementsofforeignentitiesaretranslatedintoeuros.
Assets and liabilities are translated using the exchange rates on the
respective balance sheet dates. Income and expense items in the income
statementandcashowstatementaretranslatedatweightedaverage
exchange rates during the year. The resulting translation adjustments
are recorded as a separate component of other comprehensive income
(loss) within stockholders’ equity. Cumulative translation adjustments
are recognized as income or expense upon partial or complete disposal
or substantially complete liquidation of a foreign entity.
The functional currency of foreign entities is generally the local currency,
unless the primary economic environment requires the use of another
currency. When foreign entities conduct their business in economies
consideredtobehighlyinationary,theyrecordtransactionsinthe
Company’s reporting currency (the euro) instead of their local currency.
Gains and losses arising from the translation or settlement of foreign-
currency-denominated monetary assets and liabilities into the local
currency are recognized in income in the period in which they arise.
However, currency differences on intercompany loans that have the
nature of a permanent investment are accounted for as translation
differences as a separate component of other comprehensive income
(loss) within stockholders’ equity.
Derivativenancialinstruments
TheCompanyusesderivativenancialinstrumentsprincipallyin
the management of its foreign currency risks and to a more limited
extent for interest rate and commodity price risks. In compliance
with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 133,
‘Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities’, SFAS
No. 138, ‘Accounting for Certain Derivative Instruments and Certain
Hedging Activities’, and SFAS No. 149 ‘Amendment of Statement 133 on
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities’, the Company measures
allderivativenancialinstrumentsbasedonfairvaluesderivedfrom
market prices of the instruments or from option pricing models, as
appropriate. Gains or losses arising from changes in the fair value of
the instruments are recognized in the income statement during the
period in which they arise to the extent that the derivatives have been
designated as a hedge of recognized assets or liabilities, or to the extent
that the derivatives have no hedging designation or are ineffective. The
gains and losses on the designated derivatives substantially offset the
changes in the values of the recognized hedged items, which are also
recognized as gains and losses in the income statement.
Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is highly effective and that
isdesignatedandqualiesasafairvaluehedge,alongwiththelossor
gainonthehedgedasset,orliabilityorunrecognizedrmcommitment
of the hedged item that is attributable to the hedged risk, are recorded
in the income statement.
Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is highly effective and
thatisdesignatedandqualiesasacashowhedge,arerecordedin
accumulated other comprehensive income, until earnings are affected
bythevariabilityincashowsofthedesignatedhedgeditem.Changes
in the fair value of derivatives that are highly effective as hedges and
that are designated and qualify as foreign currency hedges are recorded
in either earnings or accumulated other comprehensive income,
depending on whether the hedge transaction is a fair value hedge or
acashowhedge.
The Company formally assesses, both at the hedge’s inception and on an
ongoing basis, whether the derivatives that are used in hedging transactions
arehighlyeffectiveinoffsettingchangesinfairvaluesorcashowsof
hedged items. When it is established that a derivative is not highly
effective as a hedge or that it has ceased to be a highly effective hedge,
the Company discontinues hedge accounting prospectively. When hedge
accounting is discontinued because it has been established that the
derivativenolongerqualiesasaneffectivefairvaluehedge,theCompany
continues to carry the derivative on the balance sheet at its fair value,
and no longer adjusts the hedged asset or liability for changes in fair
value. When hedge accounting is discontinued because it is probable
that a forecasted transaction will not occur within a period of two
months from the originally forecasted transaction date, the Company
continues to carry the derivative on the balance sheet at its fair value,
and gains and losses that were accumulated in other comprehensive
income are recognized immediately in earnings. In all other situations
in which hedge accounting is discontinued, the Company continues to
carry the derivative at its fair value on the balance sheet, and recognizes
any changes in its fair value in earnings.
For interest rate swaps that are unwound, the gain or loss upon
unwinding is released to income over the remaining life of the underlying
nancialinstruments,basedontherecalculatedeffectiveyield.
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include all cash balances and short-term
highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or
less that are readily convertible into known amounts of cash. They are
stated at face value.
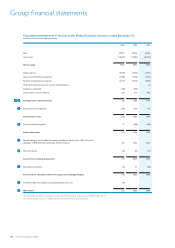
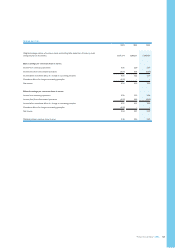
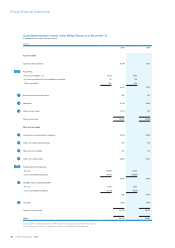
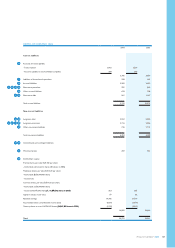
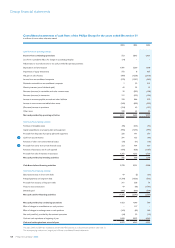
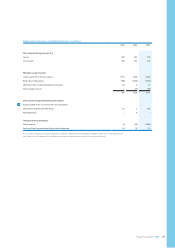
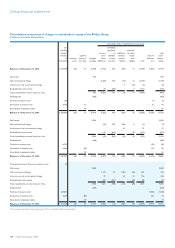
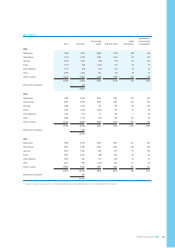
Groupnancialstatements