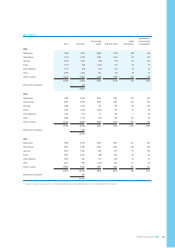
Philips 2005 Annual Report Download - page 137
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 137 of the 2005 Philips annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Philips Annual Report 2005 137
recognition occurs when the aforementioned criteria for revenue
recognition have been met, installation of the equipment has been
nalizedinaccordancewiththecontractuallyagreedspecications
and therefore the product is ready to be used by the customer, and
subsequently a signed acceptance protocol has been obtained from
the customer, or, in cases where such acceptance protocol is not
contractually required, when management has established on the basis
ofinstallationandworkowprotocolsthattheproducthasbeeninstalled
and is ready to be used by the customer in the way contractually agreed.
Typically, installation activities include, to a certain extent, assembly of
the equipment on the spot. Any payments by the customer are typically
contingent upon the completion of the installation process in accordance
with the contractual requirements and therefore, in such instances,
revenue recognition with respect to the equipment delivery is deferred
until the installation process is completed.
EITF Issue No. 00-21, ‘Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables’,
which was adopted in 2003, applies to some arrangements that occur in
the Medical Systems businesses in which delivered equipment requires
subsequent installation and training activities in order to become operable
for the customer. However, since payment for the equipment is typically
contingent upon the completion of the installation process, revenue
recognition is required to be deferred until the installation has been
completed. The Company recognizes revenues of the other deliverables
based on their relative fair values.
Revenues are recorded net of sales taxes, customer discounts, rebates
and similar charges. For products for which a right of return exists
duringadenedperiod,revenuerecognitionisdeterminedbasedonthe
historical pattern of actual returns, or in cases where such information
is lacking, revenue recognition is postponed until the return period has
lapsed. Return policies are typically in conformity with customary return
arrangements in local markets.
For products for which a residual value guarantee has been granted or
a buy-back arrangement has been concluded, revenue recognition takes
place in accordance with the requirements for lease accounting of
SFAS No.13, ‘Accounting for Leases’.
Shipping and handling costs billed to customers are recognized as
revenues. Expenses incurred for shipping and handling costs of internal
movements of goods are recorded as cost of sales. Shipping and handling
costs related to sales to third parties are reported as selling expenses
and disclosed separately. Service revenue related to repair and maintenance
activities for sold goods is recognized ratably over the service period or
as services are rendered.
A provision for product warranty is made at the time of revenue
recognitionandreectstheestimatedcostsofreplacementandfree-of-
charge services that will be incurred by the Company with respect to
the sold products. In cases where the warranty period is extended and
the customer has the option to purchase such an extension, which is
subsequently billed separately to the customer, revenue recognition
occurs on a straight-line basis over the contract period.
Royalty income, which is generally earned based upon a percentage of
salesoraxedamountperproductsold,isrecognizedonanaccrual
basis. Government grants, other than those relating to purchases of
assets,arerecognizedasincomeasqualiedexpendituresaremade.
Income taxes
Income taxes are accounted for using the asset and liability method.
Income tax is recognized in the income statement except to the extent
that it relates to an item recognized directly within stockholders’ equity,
including other comprehensive income (loss), in which case the related
tax effect is also recognized there.
Current-year deferred taxes related to prior-year equity items which
arise from changes in tax rates or tax laws are included in income.
Current tax is the expected tax payable on the taxable income for the
year, using tax rates enacted at the balance sheet date, and any adjustment
to tax payable in respect of previous years. Deferred tax assets and
liabilities are recognized for the expected tax consequences of temporary
differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their
reported amounts. Measurement of deferred tax assets and liabilities is
based upon the enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income
in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be
recovered or settled. Deferred tax assets, including assets arising from
loss carryforwards, are recognized if it is more likely than not that the
asset will be realized. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are not discounted.
Deferred tax liabilities for withholding taxes are recognized for
subsidiaries in situations where the income is to be paid out as
dividends in the foreseeable future, and for undistributed earnings
of minority shareholdings.
Changesintaxratesarereectedintheperiodthatincludesthe
enactment date.
Benetaccounting
The Company accounts for the cost of pension plans and postretirement
benetsotherthanpensionsinaccordancewithSFASNo.87,‘Employers’
AccountingforPensions’,andSFASNo.106,‘PostretirementBenets
other than Pensions’, respectively.
MostoftheCompany’sdened-benetplansarefundedwithplan
assets that have been segregated and restricted in a trust to provide for
thepensionbenetstowhichtheCompanyhascommitteditself.
When plan assets have not been segregated, the Company recognizes
a provision for such amounts.
Pensioncostsinrespectofdened-benetpensionplansprimarily
represent the increase in the actuarial present value of the obligation
forpensionbenetsbasedonemployeeserviceduringtheyearandthe
interest on this obligation in respect of employee service in previous
years, net of the expected return on plan assets.
Actuarial gains and losses arise mainly from changes in actuarial
assumptions and differences between actuarial assumptions and what
has actually occurred. They are recognized in the income statement,
over the expected average remaining service periods of the employees,
only to the extent that their net cumulative amount exceeds 10% of the
greater of the present value of the obligation or of the fair value of plan
assets at the end of the previous year (the corridor). Unrecognized
actuarialgainsandlossesarereectedonthebalancesheet.
Unrecognized gains and losses in the Netherlands, France and Thailand
are recognized by a straight-line amortization over the expected
average remaining service period without applying the corridor.
Intheeventthattheaccumulatedbenetobligation,calculatedasthe
presentvalueofthebenetsattributedtoemployeeservicerendered
and based on current and past compensation levels, exceeds the market
value of the plan assets and existing accrued pension liabilities, this
difference and the existing prepaid pension assets are recognized as
an additional minimum pension liability.
Obligationsforcontributionstodened-contributionpensionplansare
recognized as an expense in the income statement as incurred.
Incertaincountries,theCompanyalsoprovidespostretirementbenets
other than pensions. The cost relating to such plans consists primarily of
thepresentvalueofthebenetsattributedonanequalbasistoeach
yearofservice,interestcostontheaccumulatedpostretirementbenet
obligation, which is a discounted amount, and amortization of the
unrecognized transition obligation. This transition obligation is being
amortized through charges to earnings over a twenty-year period
beginning in 1993 in the USA and in 1995 for all other plans.
Unrecognized prior-service costs related to pension plans and
postretirementbenetsotherthanpensionsarebeingamortizedby
assigning a proportional amount to the income statements of a number
ofyears,reectingtheaverageremainingserviceperiodofthe
active employees.