RBS 2007 Annual Report Download - page 187
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 187 of the 2007 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
RBS Group • Annual Report and Accounts 2007 185
Financial statements
Continuing involvement
In certain securitisations of US residential mortgages,
substantially all the risks and rewards have been neither
transferred nor retained, but the Group has retained control, as
defined by IFRS, of the assets and continues to recognise the
assets to the extent of its continuing involvement which takes
the form of retaining certain subordinated bonds issued by the
securitisation SPEs. These bonds have differing rights and,
depending on their terms, they may expose the Group to
interest rate risk where they carry a fixed coupon or to credit
risk depending on the extent of their subordination. Certain
bonds entitle the Group to additional interest if the portfolio
performs better than expected and others give the Group the
right to prepayment penalties received on the securitised
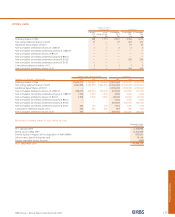
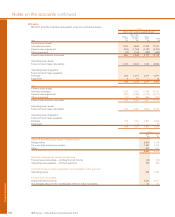
mortgages. At 31 December 2007, securitised assets were
£18.1 billion (2006 – £37.3 billion); retained interests £1,037
million (2006 – £930 million); subordinated assets £314 million
(2006 – £694 million) and related liabilities £314 million (2006 –
£694 million).
Derecognition
Other securitisations of the Group’s financial assets in the US
qualify for derecognition as substantially all the risks and rewards
of the assets have been transferred. The Group continues to
recognise any retained interests in the securitisation vehicles.
Financial risk management policies and objectives
The Group Board of directors sets the overall risk appetite and
philosophy; the risk and capital framework underpins delivery
of the Board’s strategy.
Risk and capital
It is the Group’s policy to optimise return to shareholders while
maintaining a strong capital base and credit rating to support
business growth and meet regulatory capital requirements at
all times.
Risk appetite is measured as the maximum level of retained
risk the Group will accept to deliver its business objectives.
Risk appetite is generally defined through both quantitative and
qualitative techniques including stress testing, risk
concentration, value-at-risk and risk underwriting criteria,
ensuring that appropriate principles, policies and procedures
are in place and applied.
The main financial risks facing the Group are as follows:
•Credit risk: is the risk arising from the possibility that the
Group will incur losses from the failure of customers to meet
their obligations.
•Funding and liquidity risk: is the risk that the Group is unable
to meet its obligations as they fall due.
•Market risk: the Group is exposed to market risk because of
positions held in its trading portfolios and its non-trading
businesses.
•Equity risk: gains or losses on equity investments.
•Insurance risk: the Group is exposed to insurance risk, either
directly through its businesses or through using insurance as
a tool to mitigate other risk exposures.
Credit risk
Credit risk is managed to achieve sustainable and superior
risk-reward performance while maintaining exposures within
acceptable risk appetite parameters. This is achieved through
the combination of governance, policies, systems and controls,
underpinned by sound commercial judgement as described
below.
•Policies and risk appetite: policies provide a clear framework
for the assessment, approval, monitoring and management
of credit risk where risk appetite sets the tolerance of loss.
Limits are used to manage concentration risk by single
name, sector and country.
•Decision makers: credit authority is granted to independent
persons or committees with the appropriate experience,
seniority and commercial judgement. Credit authority is not
extended to relationship managers. Specialist internal credit
risk departments independently oversee the credit process
and make credit decisions or recommendations to the
appropriate credit committee.
•Models: credit models are used to measure and assess risk
decisions and to aid on-going monitoring. Measures, such
as Probability of Default, Exposure at Default, Loss Given
Default (see page 186) and Expected Loss are calculated
using duly authorised models. All credit models are subject
to independent review prior to implementation and existing
models are reviewed on at least an annual basis.
31 Risk management