RBS 2007 Annual Report Download - page 196
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 196 of the 2007 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Financial statements
RBS Group • Annual Report and Accounts 2007
194
Notes on the accounts continued
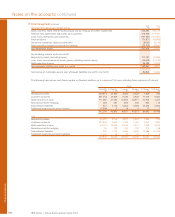
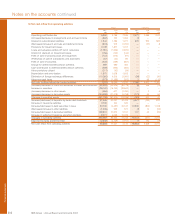
The tables below set out the Group’s structural foreign currency exposures.
Structural
Net investments Net foreign
in foreign investment currency
operations hedges exposures
2007 £m £m £m
US dollar 14,819 2,844 11,975
Euro 46,629 41,220 5,409
Swiss franc 910 863 47
Chinese RMB 2,600 1,938 662
Brazilian real 3,755 — 3,755
Other non-sterling 2,995 875 2,120
71,708 47,740 23,968
2006
US dollar 15,036 5,278 9,758
Euro 3,059 1,696 1,363
Swiss franc 462 457 5
Chinese RMB 3,013 — 3,013
Other non-sterling 132 107 25
21,702 7,538 14,164
The exposure in Chinese RMB arises from the Group’s strategic investment in Bank of China.
Retranslation gains and losses on the Group’s net investments
in operations together with those on instruments hedging these
investments are recognised directly in equity. Changes in
foreign currency exchange rates will affect equity in proportion
to the structural foreign currency exposure. A five percent
strengthening of foreign currencies would result in a loss of
£1,140 million (2006 – £670 million) recognised in equity. A five
percent weakening of foreign currencies would result in a gain
of £1,200 million (2006 – £710 million) recognised in equity.
Equity risk
Non-trading equity positions can result in changes in the
Group’s non-trading income and reserves arising from
changes in equity prices/income.
The types, nature and amounts of exchange-traded exposures,
private equity exposures, and other exposures vary significantly.
Such exposures may take the form of listed and unlisted equity
shares, equity warrants and options, linked equity fund
investments, private equity and venture capital investments,
preference shares classified as equity and capital stock in the
Federal Home Loans Bank and Federal Reserve Bank.
Risk is managed within limits approved by GALCO through the
execution of cash and derivative instruments. Execution of the
hedging is carried out by the relevant division through the
Group’s treasury function. The residual risk position is reported
to divisional asset and liability committees, GALCO and the
Board.
Non-trading interest rate VaR
Non-trading interest rate VaR for the Group’s treasury and
retail and commercial banking activities was £42.9 million at
31 December 2007 (2006 – £40.2 million) with the major
exposure being to changes in longer term US dollar interest
rates. During the year, the maximum VaR was £53.6 million
(2006 – £98.7 million), the minimum £32.9 million (2006 –
£40.2 million) and the average £43.2 million (2006 – £76.6 million).
Citizens was the main contributor to overall non-trading interest
rate VaR. It invests in a portfolio of highly rated and liquid
investments, principally mortgage-backed securities issued by
US Government-backed entities. This balance sheet
management approach is common for US retail banks where
mortgages are originated and then sold to Federal agencies
for funding through the capital markets.
Currency risk
The Group does not maintain material non-trading open
currency positions other than the structural foreign currency
translation exposures arising from its investments in foreign
subsidiaries and associated undertakings and their related
currency funding. The Group’s policy in relation to structural
positions is to match fund the structural foreign currency
exposure arising from net asset value, including goodwill, in
foreign subsidiaries, equity accounted investments and
branches, except where doing so would materially increase the
sensitivity of either the Group’s or the subsidiary’s regulatory
capital ratios to currency movements. The policy requires
structural foreign exchange positions to be reviewed regularly
by GALCO. Foreign exchange differences arising on the
translation of foreign operations are recognised directly in
equity together with the effective portion of foreign exchange
differences arising on hedging instruments.
Equity classification of foreign currency denominated
preference share issuances requires that these shares be held
on the balance sheet at historic cost. Consequently, these
share issuances have the effect of increasing the Group’s
structural foreign currency position.
31 Risk management (continued)