Toyota 2012 Annual Report Download - page 17
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 17 of the 2012 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Management and
Corporate Information Investor Information
Changes for Making
Ever-Better Cars
Toyota Global Vision Business and
Performance Review Financial Section President
ʼ
s Message Medium- to Long-Term
Growth Initiatives Special Feature
TOYOTA ANNUAL REPORT 2012
Toyota’
s History in Emerging Markets
Special Feature: Toyota’
s Efforts in Emerging Markets
Toyota’
s Basic Global Expansion
Policy
Relationship and activities
associated with ASEAN
0
500
1,000
1,500
2,000
2,500
3,000
1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 1970
- Establishment of automotive
industry infrastructure Shift from country-based
production to
region-based production
Global production structure
- IMV introduction
- Global exports
- Scouting for suppliers
Start of mutual production
support of parts in ASEAN
Asian currency
crisis
Foundation
period
“Tamaraw”
“Kijang”
Growth
period
Development
period
“Soluna”
“Vios”
“IMV”
“Avanza”
Unit
(Thousands of units)
Year
1988 Before
1970
1998
ASEAN Market
Toyota’
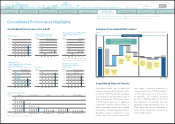
s History in Emerging Markets Progress of the Automotive Industry in the ASEAN Emerging Markets
Egypt
1979
2012
“Fortuner”
Russia
1960s
2007
“Camry”
South
Africa
1962
1962
“Stout”
Brazil
1958
1959
“Bandeirante”
India
1985
1999
“Qualis”
Malaysia
1967
1982
“Corolla”
Thailand
1962
1964
“Hilux”
Taiwan
1949
1986
“Dyna”
Philippines
1962
1976
“Tamaraw”
Market
Upper: Year sales started
Middle: Year production started
Low: First model produced locally
Indonesia
1971
1977
“Kijang”
China
1964
1999
“Coaster”
1
Toyota’
s basic philosophy on operations in
emerging markets is to be contributive to the
development and welfare of the country. This
philosophy calls on us to contribute through the auto
industry to the development of the economy,
employment, transportation infrastructure, etc., of
the countries in which we operate by cultivating and
developing the supporting industries and engaging
in operations that are based locally.
When Toyota sets up operations in a country we
become a corporate citizen there, and through the
auto industry we contribute to society via foundation
activities, environmental conservation, and human
resources training. We emphasize dialogue with local
communities for sustainable growth in every country
in which we do business.
Toyota has a long history of efforts in emerging
markets, particularly in the ASEAN nations,
where we have been promoting exports and local
production since the 1960s.
From 1970 through 1990 was a period of foundation
in which we sought to deliver vehicles that would
please local consumers. We introduced the Tamaraw
in the Philippines in 1976, and the following year
brought the Kijang to Indonesia. The Philippines
and Indonesia are places where families tend to
be large, so it was necessary to provide dual-use
vehicles that could be used for business and family
transport. Unpaved roads were common, so van-
type multi-purpose vehicles were favored. We opted
to make bodies by bending and welding sheet
rather than importing stamping equipment, so as
to make less expensive vehicles. We cultivated staff
and suppliers and developed new products locally.
Our goal was to prepare infrastructure for the auto
industry, and find and develop local suppliers.
During the growth period of 1990 through
2000, the ASEAN countries were transitioning
from country-based production to mutually
complementary regional production, due to the
gradual materialization of the ASEAN Free Trade
Agreement as well as the difficulties in achieving
mass production and cost reduction at the single-
country-market scale. The Memorandum of
Understanding on Brand-to-Brand Complementation
on the Automotive Industry and other tariff
exemptions on parts provided the impetus for each
country to mass produce parts in its area of
expertise, making for efficient plant investment
through expansion of scale and volume efficiency and
leading to the growth of the parts-supply industry.
The Asian currency crisis of 1997 that took place
amidst these developments was a direct blow to
ASEAN and had a great impact on the automobile
market, but that experience provided the foundation
for the later development of the IMV Project and other
global vehicles. The volume of parts imported from
Japan was broadly cut in response to the collapse
of the ASEAN currencies, with a concurrent rise in
the ratio of local procurement and the establishment
of an export structure that exploited low-priced
currencies. Quality was also improved to bolster
exports, and cost-reduction efforts were made. The
cooperation and support of governments and local
communities, as well as the strengthening of after-
sales service and the parts business, enabled the
creation of a profitable structure without impacting
sales. This ushered in the development period from
2000 through 2010, during which the foundation of
the Asian auto industry grew markedly.
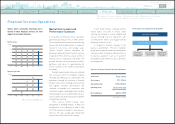
Period of Foundation
Preparing the automobile industry
infrastructure and finding/growing suppliers
Period of Growth
Growing the parts-supply industry through
mutual complementation of production
Development Period
Overcoming the currency crisis and moving
toward global production
Search NextPrev page 17
Contents
0821