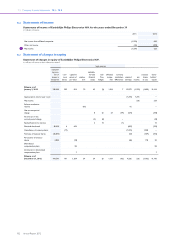
Philips 2012 Annual Report Download - page 187
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 187 of the 2012 Philips annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
14 Sustainability statements 14 - 14
Annual Report 2012 187
14 Sustainability statements
Approach to sustainability reporting
Philips has a long tradition of sustainability reporting, beginning in 1999
when we published our first environmental annual report. In 2003, we
expanded our reporting with the launch of our first sustainability annual
report, which provided details of our social and economic performance
in addition to our environmental results.
As a next step, we decided to publish an integrated financial, social and
environmental report, reflecting the progress we have made embedding
sustainability in our way of doing business in 2008. This is also supported
by the inclusion of sustainability in the Philips Commitments and the
company strategy.
This is our fifth annual integrated financial, social and environmental
report.
Tracking trends
We continuously follow external trends to determine the issues most
relevant for our company and those where we can make a positive
contribution to society at large. In addition to our own research, we
make use of a variety of sources, including the United Nations
Environmental Programme (UNEP), World Bank, World Business
Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), World Economic
Forum and World Health Organization. Our work also involves
tracking topics of concern to governments, regulatory bodies,
academia, and non-governmental organizations, and following the
resulting media coverage.
Stakeholder engagement
Across all our activities we seek to engage stakeholders to gain their
feedback on specific areas of our business. Working in partnerships is
crucial in delivering on our vision to make the world healthier and more
sustainable through innovation. We participate in meetings and task
forces as a member of organizations including the WBCSD, Electronic
Industry Citizenship Coalition (EICC), Carbon Disclosure Project
Supply Chain, European Committee of Domestic Equipment
Manufacturers (CECED), Federation of National Manufacturers
Associations for Luminaires and Electrotechnical Components for
Luminaires in the European Union (CELMA), European Coordination
Committee of the Radiological, Electromedical and Healthcare IT
Industry (COCIR), Digital Europe, European Lamp Companies
Federation (ELC), European Roundtable of Industrialists (ERT),
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), Environmental
Leadership Council of the Information Technology Industry Council
(ELC ITIC), Consumer Electronics Association (CEA), Association of
Home Appliance Manufacturers (AHAM) and Healthcare Plastics
Recycling Council (HPRC).
In 2011, a multi-stakeholder project with the Sustainable Trade
Initiative (IDH), a number of NGOs, and electronic companies was
started. The program focuses on improving working circumstances in
the electronics industry in China.
Furthermore, we engaged with a number of NGOs, including Enough,
GoodElectronics, MakeITfair, the leading Dutch labor union (FNV), the
Chinese Institute of Public and Environmental Affairs, SOMO, Amnesty
International and Greenpeace.
Biodiversity
Philips’ commitment to the subject of biodiversity made several
significant steps forward in 2012. This was led mainly by the Philips
Leaders for Nature (LFN) team which is part of the IUCN Netherlands
committee LFN program. The program brings companies, NGOs and
government together to work on the topic of business and biodiversity.
The Philips LFN team grew both in the number of team members, local
and company-wide initiatives, as well as widening the scope of
discussions on the internal company-wide social network platform. This
year the LFN team not only took an active part for the 5th year in the
LFN programs but was represented on the LFN organizing committee
for the second year running.
In October, the Philips LFN team organized the Philips sustainability
week. This was planned to coincide with the Dutch Sustainability
awareness day. The Philips activities took place across multiple sites
and were intended to raise awareness of sustainability and biodiversity
among Philips employees in the Netherlands. The program included
education around biodiversity, sustainable transport, recycling, green
products, and reducing your footprint by adopting a more vegetarian
diet. There were also recycling and biodiversity restoration activities
at the Philips Innovation Campus in Bangalore, Cleveland, Klagenfurt,
Reedsville, and the Eindhoven High-Tech Campus amongst others.
The Philips Drachten site green teams have started a program to
investigate opportunities for biodiversity restoration locally. This is part
of a campaign to raise awareness that healthy ecosystems are the very
foundations of our existence. The teams carried out a biodiversity scan
of their site and are implementing recommended actions to increase
site biodiversity. This will enable the restoration of the local flora and
fauna and creating a pleasant outdoor environment for Drachten
employees.
In November, the LFN team together with the Philips Corporate
Sustainability Office organized the first and very successful Business
Ecosystems Training (BET). The training was web-based and nearly 200
Philips employees from all sectors and 21 countries participated. This
was the first of a series of trainings intended to increase the knowledge
and understanding of the links between ecosystems and business. The
BET program was developed by the WBCSD, its member companies
and partners, and the IUCN. The training included an introduction to
biodiversity and ecosystems, the link to Philips (risks and opportunities)
what Philips and other companies have done and can do to include
natural capital into their everyday activities.
Philips policy continues to focus on:
• Continuing to reduce the impact of our operations through our
Green Operations program, focusing on CO2 emissions, water,
waste and restricted and hazardous substances
• Continuing our EcoDesign activities, resulting in Green Products
• Study concepts such as ‘Cradle to Cradle’, ‘Biomimicry’ and ‘The
Natural Step’ – all focused on learning or imitating nature’s
remarkably efficient designs – for our Sustainable Innovation efforts
• Continuing our global partnership with IUCN, the International
Union for the Conservation of Nature. Together we are exploring
how specific lighting technology can redress the disturbance of fauna
around the world, enabling it to co-exist with human sea and coastal
development, for instance.
Reporting standards
In this report, we have followed relevant best practice standards and
international guidelines while reporting on our sustainability
performance. Most important are the Global Reporting Initiative’s
(GRI) G3.1 Sustainability Reporting Guidelines.
With regard to the GRI Application Levels system, we assessed
ourselves at the A+ level. A detailed overview of our Management
Approach and the G3.1 Core Indicators is provided at the end of this
section.
We signed on to the United Nations Global Compact in March 2007,
joining thousands of companies from all regions of the world as well as
international labor and civil society organizations to advance 10
universal principles in the areas of human rights, labor, the environment
and anti-corruption. Our General Business Principles, Sustainability and
Environmental Policies, and our Supplier Sustainability Declaration are
the cornerstones that enable us to live up to the standards set by the
Global Compact. This is closely monitored and reported, as illustrated
throughout this report, which is also our annual Communication on
Progress (COP) submitted to the UN Global Compact Office.
Material issues and our focus
Based on ongoing trend analysis and stakeholder input, we identify the
key material issues for our company from a sustainability perspective.
We have mapped the issues in the table below, taking into account the:
• level of concern to society at large and stakeholders, versus impact
on Philips, and