Regions Bank 2008 Annual Report Download - page 151
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 151 of the 2008 Regions Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.addition to using forward contracts to economically hedge mortgage loans held for sale, Regions’ derivative
portfolio also included forward contracts entered into to offset the impact of changes in interest rates on Regions’
mortgage loan pipeline designated for future sale, also referred to as interest rate lock commitments. At
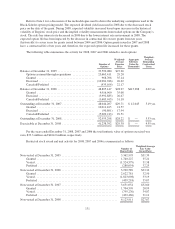
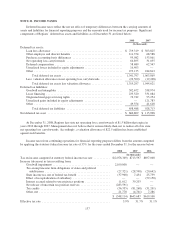
December 31, 2008 and 2007, Regions had $1,015.8 million and $251.2 million, respectively, in notional
amounts of rate lock commitments with a fair value of $8.8 million and a net negative fair value of ($816,000),
respectively.
In the normal course of business, Morgan Keegan enters into underwriting and forward and future
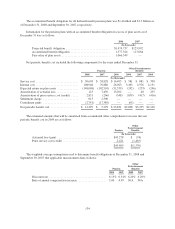
commitments on U.S. Government and municipal securities. For the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007,
the contractual amounts of future commitments to purchase such securities were approximately $494,000 and
$3.1 million, respectively. For the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, the contractual amounts of future
commitments to sell such securities were $60.8 million and $50.2 million, respectively. The brokerage subsidiary
typically settles its position by entering into equal but opposite contracts and, as such, the contract amounts do
not necessarily represent future cash requirements. Settlement of the transactions relating to such commitments is
not expected to have a material effect on the subsidiary’s financial position. Transactions involving future
settlement give rise to market risk, which represents the potential loss that can be caused by a change in the
market value of a particular financial instrument. The exposure to market risk is determined by a number of
factors, including size, composition and diversification of positions held, the absolute and relative levels of
interest rates, and market volatility.
Additionally, in the normal course of business, Morgan Keegan enters into transactions for delayed delivery,
to-be-announced securities, which are recorded on the consolidated balance sheets at fair value. Risks arise from
the possible inability of counterparties to meet the terms of their contracts and from unfavorable changes in
interest rates or the market values of the securities underlying the instruments. The credit risk associated with
these contracts is typically limited to the cost of replacing all contracts on which the Company has recorded an
unrealized gain. For exchange-traded contracts, the clearing organization acts as the counterparty to specific
transactions and, therefore, bears the risk of delivery to and from counterparties.
The Company also maintains a derivatives trading portfolio of interest rate swaps, option contracts, and
futures and forward commitments used to meet the needs of its customers. The portfolio is used to generate
trading profit and help clients manage market risk. The Company is subject to the credit risk that a counterparty
will fail to perform. These trading derivatives are recorded in other assets and other liabilities. The net fair value
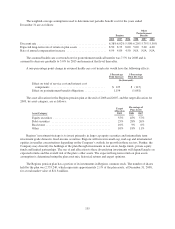
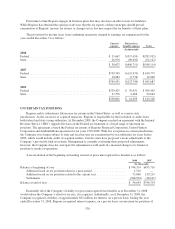
of the trading portfolio at December 31, 2008 and 2007 was $145.6 million and $36.2 million, respectively.
Regions has both bought and sold credit protection in the form of participations on interest rate swaps (swap
participations). These swap participations, which meet the definition of credit derivatives, were entered into in
the ordinary course of business to serve the credit needs of customers. Credit derivatives, whereby Regions has
purchased credit protection, entitle Regions to receive a payment from the counterparty when the customer fails
to make payment on any amounts due to Regions upon early termination of the swap transaction and have
maturities between 2012 and 2026. Credit derivatives whereby Regions has sold credit protection have maturities
between 2009 and 2015. For contracts where Regions sold credit protection, Regions would be required to make
payment to the counterparty when the customer fails to make payment on any amounts due to the counterparty
upon early termination of the swap transaction. Regions bases the current status of the prepayment/performance
risk on bought and sold credit derivatives on recently issued internal risk ratings consistent with the risk
management practices of unfunded commitments. Refer to Note 25 for additional information.
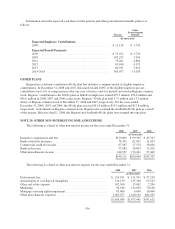
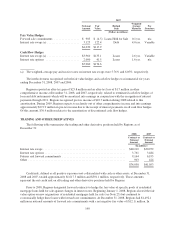
Regions’ maximum potential amount of future payments under these contracts is approximately $62.1
million. This scenario would only occur if variable interest rates were at zero percent and all counterparties
defaulted with zero recovery. The fair value of sold protection at December 31, 2008 was a liability of
approximately $83,000. In transactions where Regions has sold credit protection, recourse to collateral associated
with the original swap transaction is available to offset some or all of Regions’ obligation.
141