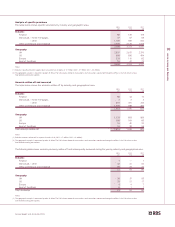
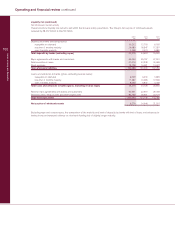
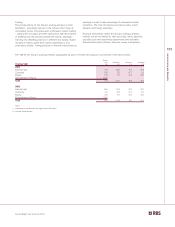
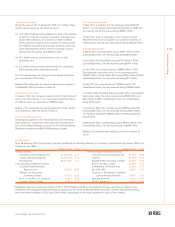
RBS 2003 Annual Report Download - page 111
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 111 of the 2003 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
109
Annual Report and Accounts 2003
Operating and financial review
Insurance risk
The Group is exposed to insurance risk, either directly through
its businesses or through using insurance as a tool to reduce
other risk exposures:
•Insurance is a source of risk where the Group sells and
underwrites general insurance and life assurance. The
essence of an insurance contract is the transfer of risk from
the policyholder to the insurer.
The management of insurance risk is overseen by a Pricing
Committee that meets weekly to review underwriting factors,
e.g. car groups, terms and conditions, claims experience. This
is supplemented by a range of system controls and processes
including risk acceptance, with regular independent reviews of
underwriting across the business. Primary focus is on high
volume and relatively straightforward products for example
home and motor. This facilitates the generation of
comprehensive underwriting and claims data, which is used
to monitor and accurately price the risks accepted. This
attention to data analysis is reinforced by tight controls on
costs and claims handling procedures.
Underwriting concentrations and catastrophe exposure are
reviewed and, where necessary, mitigated by reinsurance
which is spread across a number of reinsurers. Reviews of
the Group’s general insurance reserves by external
actuaries are conducted annually.
Investment strategy reflects the maturity of underwriting
liabilities and is governed through Investment Management
Committees, with involvement and oversight from Group
Treasury. The Group’s underwriting experience, the level of
retained risk and solvency are monitored at divisional and
Group level.
•The Insurance Sourcing Department is responsible for the
Group-wide purchase of insurance as a means of reducing
other risk exposures. As such, it is a key component of the
Group Insurance Risk Management process and reports its
activities to the GEMC.
Enterprise risk
In order to adequately identify and manage the full range of
Enterprise risk, the Group has separately defined operational
and external risk:
Operational risk is defined as the risk arising from within the
organisation from:
•People – risks arising from an inappropriate level of staff,
inadequately skilled or managed people.
•Process – risk caused by inadequate or failed internal
processes.
•Systems – risks of inadequately designed or maintained
systems.
•Assets – risk of damage, misappropriation or theft of the
Group’s physical, logical and intangible assets.
External risk is defined as the risk arising from outside of the
organisation in three main areas:
•Business – risks arising from product performance,
competitor activity, supplier unreliability or customer activity.
•Political – risks caused by political unrest or uncertainty,
activity by public interest groups or extremists, and non-
compliance with, or changes to, current legislation.
•Environment – risks arising due to demographic, macro
economic, technical, cultural or environmental change.
Enterprise risk also includes the potential or actual impact on
corporate reputation arising from any of the Group’s activities.
Enterprise risk management is achieved through monitoring the
Group’s exposure to direct or indirect loss using a range of
policies, procedures, data, analytical tools and reporting
techniques. In particular, Group-wide risk management processes
ensure that Enterprise risk issues are quickly escalated and
resolved, that the risks inherent in new products are fully evaluated,
and that emerging external risks are actively monitored.
Operational risk exposures and loss events for each division
are captured through monthly Risk and Control returns, which
provide details on the change of risk exposures for each risk
category in the light of improving/deteriorating trends and the
risk profile of each division.