RBS 2003 Annual Report Download - page 139
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 139 of the 2003 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Annual Report and Accounts 2003
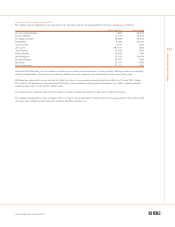
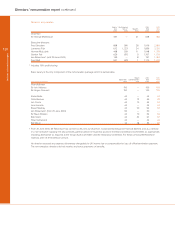
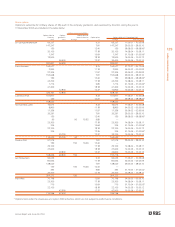
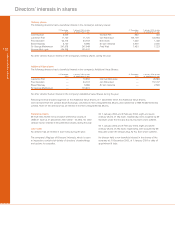
137
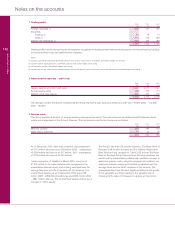
Accounting policies
The accounts have been prepared in accordance with applicable
Accounting Standards in the UK and the Statements of
Recommended Accounting Practice issued by the British
Bankers’ Association and by the Finance and Leasing
Association. The Statement of Recommended Practice issued
by the Association of British Insurers (1998) has been followed
by the insurance members of the Group; they have been
consolidated in the recognised manner for banking groups, in
particular, by using the embedded value method for life business.
A summary of the more important accounting policies is set
out below. The consolidated accounts are prepared in
accordance with the special provisions of Part VII of the
Companies Act 1985 (“the Act”) relating to banking groups.
The accounts of the company are prepared in accordance
with section 226 of, and Schedule 4 to, the Act and, as
permitted by section 230(3) of the Act, no profit and loss
account is presented.
1 Accounting convention and bases of consolidation
The accounts are prepared under the historical cost
convention modified by the periodic revaluation of premises
and certain investments. To avoid undue delay in the
presentation of the Group’s accounts, the accounts of certain
subsidiary undertakings have been made up to 30 November.
There have been no changes in respect of these subsidiary
undertakings, in the period from their balance sheet dates to
31 December, that materially affect the view given by the
Group’s accounts.
2 Revenue recognition
Interest is credited to the profit and loss account as it accrues
unless there is significant doubt that it can be collected (as
described in the accounting policy on loans and advances).
Fees in respect of services are recognised as the right to
consideration accrues through performance to customers.
Services are in respect of financial services related products,
the arrangement is generally contractual, the cost of providing
this service is incurred as the service is rendered and the
price is usually fixed and always determinable.
The application of the Group’s policy to significant fee types is
outlined below.
Loan origination fees: up-front lending fees are recognised as
income when receivable except where they are charged in lieu
of interest or charged to cover the cost of a continuing service
to the borrower, in which case they are credited to income over
the life of the advance.
Commitment and utilisation fees: these are generally
determined as a percentage of the outstanding used or
unused facility. They are usually charged to the customer in
arrears and recognised when charged.
Payment services: this comprises income received for payment
services including cheques cashed, direct debits, Clearing
House Automated Payments (the UK electronic settlement
system) and BACS payments (the automated clearing house
that processes direct debits and direct credits). These are
generally charged on a per transaction basis. The income is
earned when the payment or transaction occurs. Payment
services income is usually charged to the customer’s account,
monthly or quarterly in arrears. Accruals are raised for services
provided but not charged at period end.
Card related services: fees from credit card business include:
Commission received from retailers for processing credit
and debit card transactions: income is accrued to the profit
and loss account as the service is performed.
Interchange received: as issuer, the Group receives a fee
(interchange) each time a cardholder purchases goods and
services. The Group also receives interchange fees from
other card issuers for providing cash advances through its
branch and Automated Teller Machine networks. These fees
are accrued once the transaction has taken place.
An annual fee payable by a credit card holder is charged at
the beginning of each year but is deferred and taken to
income over the period of the service i.e. 12 months.
Insurance brokerage: this is made up of fees and commissions
received from the agency sale of insurance. Commission on
the sale of an insurance contract is earned at the inception of
the policy as the insurance has been arranged and placed.
However, provision is made where commission is refundable in
the event of policy cancellation in line with estimated
cancellations.
Securities and derivatives held for trading are recorded at fair
value. Changes in fair value are recognised in dealing profits
together with dividends from, and interest receivable and
payable on, trading business assets and liabilities.
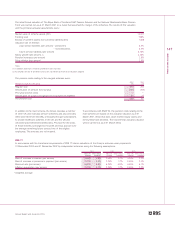
3 Goodwill
Goodwill is the excess of the cost of acquisition of subsidiary
and associated undertakings over the fair value of the Group’s
share of net tangible assets acquired. Goodwill arising on
acquisitions of subsidiary and associated undertakings after 1
October 1998 is capitalised on the balance sheet and
amortised on a straight-line basis over its estimated useful
economic life, currently over periods up to 20 years.
Capitalised goodwill is reviewed for impairment at the end of
the first full year following an acquisition and subsequently if
events or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying
value may not be recoverable in full. Goodwill arising on
acquisitions of subsidiary and associated undertakings prior to
1 October 1998, previously charged directly against profit and
loss account reserves, was not reinstated under the transitional
provisions of FRS 10 ‘Goodwill and Intangible Assets’. It will be
written back only on disposal and reflected in the calculation of
the gains or losses arising.
Accounting policies