BB&T 2012 Annual Report Download - page 90
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 90 of the 2012 BB&T annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
68
Strategic risk
Strategic risk is the risk to earnings, capital, enterprise value, and to the achievement of BB&T’ s Vision, Mission, Purpose,
and business objectives that arises from BB&T’ s business strategy, adverse business decisions, improper or ineffective
implementation of decisions, or lack of responsiveness to changes in business environment. Strategic risk is a function of the
compatibility of BB&T’ s strategic goals, the business strategies developed to achieve those goals, the resources deployed
against these goals, and the quality of implementation.
Risk Governance
The management of risk has always been an enterprise-wide initiative at BB&T. It is part of BB&T’ s mission statement that
risk is managed to optimize the long-term return to shareholders, while providing a safe and sound investment.
The Chief Risk Officer leads the RMO, which designs, organizes and manages BB&T’ s risk framework. The management of
risk begins at the business level through risk identification and management programs. The RMO is responsible for ensuring
effective risk management oversight, measurement, monitoring, reporting and consistency of controls.
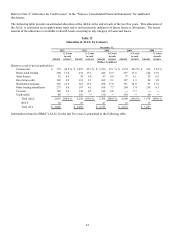
Market Risk Management
The effective management of market risk is essential to achieving BB&T’ s strategic financial objectives. As a financial
institution, BB&T’ s most significant market risk exposure is interest rate risk in its balance sheet; however, market risk also
includes product liquidity risk, price risk and volatility risk in BB&T’ s lines of business. The primary objectives of market
risk management are to minimize any adverse effect that changes in market risk factors may have on net interest income, and
to offset the risk of price changes for certain assets recorded at fair value. Market Risk Management also performs the
enterprise-wide IPV function.
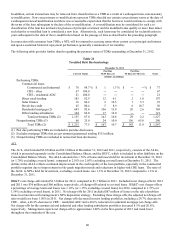
Interest Rate Market Risk (Other than Trading)
BB&T actively manages market risk associated with asset and liability portfolios with a focus on the strategic pricing of asset
and liability accounts and management of appropriate maturity mixes of assets and liabilities. The goal of these activities is
the development of appropriate maturity and repricing opportunities in BB&T’ s portfolios of assets and liabilities that will
produce reasonably consistent net interest income during periods of changing interest rates. These portfolios are analyzed for
proper fixed-rate and variable-rate mixes under various interest rate scenarios.
The asset/liability management process is designed to achieve relatively stable NIM and assure liquidity by coordinating the
volumes, maturities or repricing opportunities of earning assets, deposits and borrowed funds. Among other things, this
process gives consideration to prepayment trends related to securities, loans and leases and certain deposits that have no
stated maturity. Prepayment assumptions are developed using a combination of market data and internal historical
prepayment experience for residential mortgage-related loans and securities, and internal historical prepayment experience
for client deposits with no stated maturity and loans that are not residential mortgage related. These assumptions are subject
to monthly back-testing, and are adjusted as deemed necessary to reflect changes in interest rates relative to the reference rate
of the underlying assets or liabilities. On a monthly basis, BB&T evaluates the accuracy of its interest rate forecast
simulation model, which includes an evaluation of its prepayment assumptions, to ensure that all significant assumptions
inherent in the model appropriately reflect changes in the interest rate environment and related trends in prepayment activity.
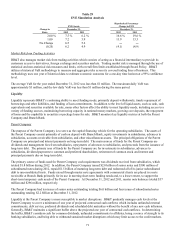
It is the responsibility of the MRLCC to determine and achieve the most appropriate volume and mix of earning assets and
interest-bearing liabilities, as well as to ensure an adequate level of liquidity and capital, within the context of corporate
performance goals. The MRLCC also sets policy guidelines and establishes long-term strategies with respect to interest rate
risk exposure and liquidity. The MRLCC meets regularly to review BB&T’ s interest rate risk and liquidity positions in
relation to present and prospective market and business conditions, and adopts funding and balance sheet management
strategies that are intended to ensure that the potential impact on earnings and liquidity as a result of fluctuations in interest
rates is within acceptable standards.
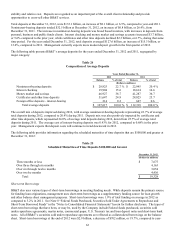
BB&T uses derivatives primarily to manage economic risk related to securities, commercial loans, MSRs and mortgage
banking operations, long-term debt and other funding sources. BB&T also uses derivatives to facilitate transactions on
behalf of its clients. As of December 31, 2012, BB&T had derivative financial instruments outstanding with notional
amounts totaling $73.3 billion, with a net fair value of $13 million. See Note 19 “Derivative Financial Instruments” in the
“Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” herein for additional disclosures.
The majority of BB&T’ s assets and liabilities are monetary in nature and, therefore, differ greatly from most commercial and
industrial companies that have significant investments in fixed assets or inventories. Fluctuations in interest rates and actions
of the FRB to regulate the availability and cost of credit have a greater effect on a financial institution’ s profitability than do