RBS 2005 Annual Report Download - page 105
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 105 of the 2005 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
section
01
Operating and
financial review
103
Operating and financial review
Annual Report and Accounts 2005
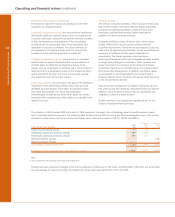
The tables below set out the Group’s structural foreign currency exposures.
Foreign
currency Structural
Net investments borrowings foreign
in foreign hedging net currency
operations investments exposures
2005 £m £m £m
US dollar 15,452 6,637 8,815
Euro 2,285 139 2,146
Swiss franc 431 430 1
Chinese RMB 914 — 914
Other non-sterling 76 72 4
19,158 7,278 11,880
2004
US dollar 12,367 6,580 5,787
Euro 2,086 1,349 737
Swiss franc 398 392 6
Other non-sterling 116 112 4
14,967 8,433 6,534
The US dollar open structural foreign currency exposure reflects the action taken to mitigate the effect of the acquisition in 2004 of
Charter One on the Group’s capital ratios. However, the increase in this position and the Euro structural exposure over 2004 is largely
a result of the exclusion from the table of preference shares classified as equity under IFRS. These instruments continue to be
considered part of the currency funding of foreign operations for asset and liability management purposes. The exposure in Chinese
RMB arises from the Group’s strategic investment in Bank of China.
●Equity risk
Non-trading equity risk arises principally from the Group’s
strategic investments, its venture capital activities and its
general insurance business. General insurance investment
strategy is discussed below under insurance risk.
VaR is not an appropriate risk measure for the Group’s venture
capital investments, which comprise a mix of quoted and
unquoted investments, or its portfolio of strategic investments.
These investments are carried at fair value with changes in fair
value recorded in profit or loss, or in equity.
Insurance risk
The Group is exposed to insurance risk, either directly through
its businesses or through using insurance as a tool to reduce
other risk exposures.
An insurance contract transfers risk from the policyholder to
the insurer, whereby, in return for a premium paid,
the insurer indemnifies the policyholder on the occurrence of
specified events.
Insurance risk is the risk of fluctuations in the timing, frequency
and severity of insured events, relative to the expectations of
the Group at the time of underwriting. This risk is managed
according to the following separate components:
•Underwriting and pricing risk,
•Claims management risk,
•Reinsurance risk,
•Reserving risk
Insurance risk is predictable, especially with the analysis of
large volumes of data over time. There is, however, uncertainty
around the predictions from various sources, for example,
volatility of the weather. However, the Group has documented
risk policies, coupled with governance frameworks to oversee
and control and hence minimise the risks.
Underwriting and pricing risk
The Group manages underwriting and pricing risk through a
wide range of processes and forums, which include:
•Underwriting guidelines which exist for all business
transacted restricting the types and classes of business that
may be accepted;
•Pricing policies which are set by pricing committees, by
product line and by brand;
•Centralised control of policy wordings and any subsequent
changes
Reinsurance and insurance of Group assets are centrally
controlled in the same department as insurance risk and both
have a similar framework of robust controls and processes.