BB&T 2010 Annual Report Download - page 19
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 19 of the 2010 BB&T annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.General Business Development
BB&T is a regional financial holding company. BB&T has maintained a long-term focus on a strategy that
includes expanding and diversifying the BB&T franchise in terms of revenues, profitability and asset size. This
strategy has encompassed both organic growth and acquisitions of complementary banks and financial businesses.
During the 1990’s and through 2003, BB&T’s growth resulted largely from mergers and acquisitions as the
economics of business combinations were compelling. Since that time, BB&T has focused more on organic growth
and strategic acquisitions, including the FDIC-assisted acquisition of Colonial.
Merger and Acquisition Strategy
BB&T’s growth in business, profitability and market share has historically been enhanced by strategic
mergers and acquisitions. Management intends to remain disciplined and focused with regard to future merger
and acquisition opportunities. BB&T will continue to assess bank and thrift acquisitions subject to market
conditions and suitable candidates, primarily within BB&T’s existing footprint, and will pursue economically
advantageous acquisitions of insurance agencies, specialized lending businesses, and fee income generating
financial services businesses. BB&T’s acquisition strategy is focused on three primary objectives:
Što pursue assisted and unassisted acquisitions of banks and thrifts with compatible cultures that will
enhance BB&T’s community banking and customer delivery system;
Što acquire companies in niche markets that provide products or services that can be offered through the
existing distribution system to BB&T’s current customer base; and
Što consider strategic nonbank acquisitions in markets that are economically feasible and provide positive
long-term benefits.
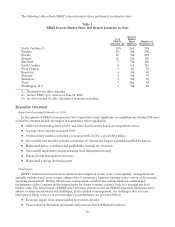
BB&T completed acquisitions of 33 community banks and thrifts, 80 insurance agencies and 32 nonbank
financial services providers over the last fifteen years. In the long-term, BB&T expects to continue to take
advantage of the consolidation in the financial services industry and expand and enhance its franchise through
mergers and acquisitions. The consideration paid for these acquisitions may be in the form of cash, debt or BB&T
common stock. The amount of consideration paid to complete these transactions may be in excess of the fair value
of the underlying net assets acquired, which could have a dilutive effect on BB&T’s earnings. In addition,
acquisitions often result in significant front-end charges against earnings. However, BB&T’s disciplined approach
to mergers and acquisitions typically requires that acquisitions be accretive to earnings by year three, driven
primarily by revenue enhancements and cost savings that are especially incident to in-market bank and thrift
acquisitions.
Risk Management
In the normal course of business BB&T encounters inherent risk in its business activities. Risk is managed
on a decentralized basis with risk decisions made as closely as possible to where the risk occurs. Centrally risk
oversight is managed at the corporate level through oversight, policies and reporting. The principal types of
inherent risk include compliance, credit, liquidity, market, operational, reputation and strategic risks.
Compliance risk
Compliance risk is the risk to earnings, capital, or reputation arising from violations of or noncompliance with
current and changing laws, regulations, supervisory guidance, regulatory expectations, or the rules, standards, or
codes of conduct of self regulatory organizations.
Credit risk
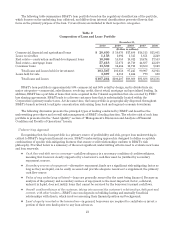
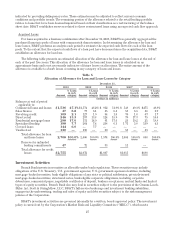
Credit risk is the risk to earnings or capital arising from the default, inability, or unwillingness of a borrower,
obligor, or counterparty to meet the terms of any financial obligation with BB&T or otherwise perform as agreed.
Credit risk exists in all activities where success depends on the performance of a borrower, obligor, or
counterparty. Credit risk arises when BB&T funds are extended, committed, invested, or otherwise exposed
through actual or implied contractual agreements, whether on or off the balance sheet. Credit risk also occurs
when the credit quality of an issuer whose securities or other instruments the bank holds deteriorates. For
additional information concerning BB&T’s management of credit risk, see the “Lending Activities” section below.
19