Philips 2009 Annual Report Download - page 171
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 171 of the 2009 Philips annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
IFRIC Interpretation 13 ‘Customer Loyalty Programmes’
IFRIC 13 addresses recognition and measurement of the obligation to
provide free or discounted goods or services in the future. The
interpretation clarifies that where goods or services are sold together
with a customer loyalty incentive (for example, loyalty points or free
products), the arrangement is a multiple-element arrangement and the
consideration receivable from the customer is allocated between the
components of the arrangement in using fair values.
IFRIC Interpretation 15 ‘Agreements for the Construction of Real Estate’
IFRIC 15 applies to the accounting for revenue and associated expenses
by entities that undertake the construction of real estate directly or
through subcontractors. Agreements in the scope of this Interpretation
are agreements for the construction of real estate. In addition to the
construction of real estate, such agreements may include the delivery of
other goods or services.
IFRIC 16 ‘Hedges of a Net Investment in Foreign Operations’
IFRIC 16 applies to an entity that hedges the foreign currency risk
arising from its net investments in foreign operations and wishes to
qualify for hedge accounting in accordance with IAS 39. It does not apply
to other types of hedge accounting. The main change in practice is to
eliminate the possibility of an entity applying hedge accounting for a
hedge of the foreign exchange differences between the functional
currency of a foreign operation and the presentation currency of the
Parent’s Consolidated financial statements.
IFRS accounting standards effective as from 2010 and onwards
The following standards and amendments to existing standards have
been published and are mandatory for the Company beginning on or
after January 1, 2010 or later periods, but the Company has not early
adopted them:
Amendment to IFRS 2 ‘Group Cash-settled and Share-based Payment
Transactions’
In addition to incorporating IFRIC 8, ‘Scope of IFRS 2’, and IFRIC 11,
‘IFRS 2 – Group and treasury share transactions’, the amendments
expand on the guidance in IFRIC 11 to address the classification of
group arrangements that were not covered by that interpretation. The
new guidance is not expected to have a material impact on the
Company’s Consolidated financial statements and will be applied on
January 1, 2010.
Revision to IFRS 3, ‘Business Combinations’
The revised standard continues to apply the acquisition method to
business combinations, with some significant changes. For example, all
payments to purchase a business are to be recorded at fair value at the
acquisition date, with contingent payments classified as debt
subsequently re-measured through the income statement. The
definition of a business has been broadened, which is likely to result in
more acquisitions being treated as business combinations. There is a
choice on an acquisition-by-acquisition basis to measure the non-
controlling interest in the acquiree at fair value or at the non-controlling
interest’s proportionate share of the acquiree’s net assets. All
acquisition-related costs other than share and debt issuance costs,
should be expensed. The Company will apply IFRS 3 (revised)
prospectively to all business combinations from January 1, 2010.
IFRS 9 ‘Financial Instruments’
This standard introduces certain new requirements for classifying and
measuring financial assets. IFRS 9 divides all financial assets that are
currently in the scope of IAS 39 into two classifications, those measured
at amortized cost and those measured at fair value. The standard along
with proposed expansion of IFRS 9 for classifying and measuring
financial liabilities, de-recognition of financial instruments, impairment,
and hedge accounting will be applicable from the year 2013, although
entities are permitted to adopt earlier. The Company is evaluating the
impact that this new standard will have on the Company’s Consolidated
financial statements.
Revised IAS 24 ‘Related Parties Disclosures’
The revised standard simplifies the definition of a related party,
clarifying its intended meaning and eliminating inconsistencies from the
definition. The Company will apply IAS 24 (revised) retrospectively
from January 1, 2011. As the change in accounting policy only impacts
disclosures, there is no impact on the Company’s Consolidated financial
statements.
Revision to IAS 27 ‘Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements’
The revised standard requires the effects of all transactions with non-
controlling interests to be recorded in equity if there is no change in
control and these transactions will no longer result in goodwill or gains
and losses. The standard also specifies the accounting when control is
lost. Any remaining interest in the entity is remeasured to fair value, and
a gain or loss is recognized in profit or loss. The Company will apply IAS
27 (revised) prospectively to transactions with non-controlling
interests from January 1, 2010.
Amendment to IAS 32 ‘Classification of Rights Issues’
The amendment addresses the accounting for rights issues (rights,
options or warrants) that are denominated in a currency other than the
functional currency of the issuer. Previously, such rights issues are
accounted for as derivative liabilities. The amendment requires that,
provided certain conditions are met, such rights issues are classified as
equity regardless of the currency in which the exercise price is
denominated. This amendment is applicable to the Company on
January 1, 2011 and is not expected to have a material impact on the
Company’s Consolidated financial statements.
Amendment to IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’
The amendment is part of the IASB’s annual improvements project
published in April 2009 and the Company will apply IAS 38
(amendment) from the date IFRS 3 (revised) is adopted. The
amendment clarifies guidance in measuring the fair value of an intangible
asset acquired in a business combination and it permits the grouping of
intangible assets as a single asset if each asset has similar useful
economic lives. The amendment is not expected to result in a material
impact on the Company’s Consolidated financial statements.
Amendment to IAS 39 ‘Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement
– Eligible Hedged Items’
The amendment to IAS 39 provides additional guidance on the
designation of a hedged item. The amendment clarifies how the existing
principles underlying hedge accounting should be applied in two
particular situations. It clarifies the designation of a one-sided risk in a
hedged item and inflation in a financial hedged item. This amendment
will be adopted on January 1, 2010 and is not expected to have a
material impact on the Company’s Consolidated financial statements.
Amendments to IFRIC 9 and IAS 39 ‘Embedded Derivatives’
The amendments require entities to assess whether they need to
separate an embedded derivative from a hybrid (combined) financial
instrument when financial assets are reclassified out of the fair value
through profit or loss category. When the fair value of an embedded
derivative that would be separated cannot be measured reliably, the
reclassification of the hybrid (combined) financial asset out of the fair
value through profit or loss category is not permitted. The amendments
are applicable to the Company on January 1, 2010 and expected not to
have a material impact on the Company’s Consolidated financial
statements.
Amendment to IFRIC 14 ‘Prepayments of a Minimum Funding Requirement’
This amendment allows for the recognition of an asset for any surplus
arising from the voluntary prepayment of minimum funding
contributions for defined-benefit plans in respect of future service. The
amendment to IFRIC 14 will be adopted on January 1, 2011, will be
applied retrospectively and is not expected to have a material impact on
the Company’s Consolidated financial statements.
IFRIC 17, ‘Distribution of Non-cash Assets to Owners’
The interpretation is part of the IASB’s annual improvements project
published in April 2009. This interpretation provides guidance on
accounting for arrangements whereby an entity distributes non-cash
assets to shareholders either as a distribution of reserves or as
dividends. IFRS 5 has also been amended to require that assets are
classified as held for distribution only when they are available for
distribution in their present condition and the distribution is highly
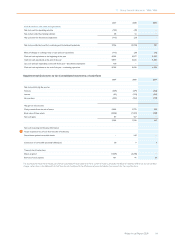
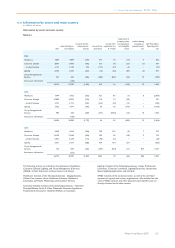
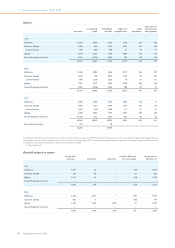
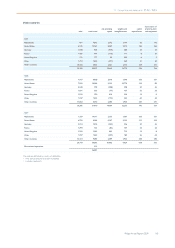
11 Group financial statements 11.11 - 11.11
Philips Annual Report 2009 171