Bank of America 2007 Annual Report Download - page 132
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 132 of the 2007 Bank of America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
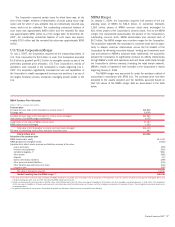
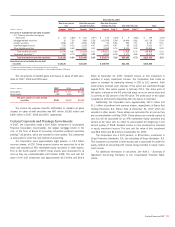
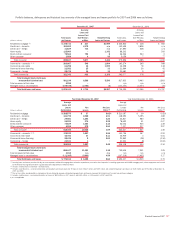
December 31, 2007 December 31, 2006
(Dollars in millions)
Contract/
Notional
(1)
Credit
Risk
Contract/
Notional
(1)
Credit
Risk
Interest rate contracts
Swaps
$22,472,949 $15,368
$18,185,655 $ 9,601
Futures and forwards
2,596,146 10
2,283,579 103
Written options
1,402,626 –
1,043,933 –
Purchased options
1,479,985 2,508
1,308,888 2,212
Foreign exchange contracts
Swaps
505,878 7,350
451,462 4,241
Spot, futures and forwards
1,600,683 4,124
1,234,009 2,995
Written options
341,148 –
464,420 –
Purchased options
339,101 1,033
414,004 1,391
Equity contracts
Swaps
56,300 2,026
32,247 577
Futures and forwards
12,174 10
19,947 24
Written options
166,736 –
102,902 –
Purchased options
195,240 6,337
104,958 7,513
Commodity contracts
Swaps
13,627 770
4,868 1,129
Futures and forwards
14,391 12
13,513 2
Written options
14,206 –
9,947 –
Purchased options
13,093 372
6,796 184
Credit derivatives
3,046,381 7,493
1,497,869 756
Credit risk before cash collateral
47,413
30,728
Less: Cash collateral applied
12,751
7,289
Total derivative assets
$34,662
$23,439
(1) Represents the total contract/notional amount of the derivatives outstanding and includes both short and long positions.
The table above presents the contract/notional amounts and credit
risk amounts at December 31, 2007 and 2006 of all the Corporation’s
derivative positions. These derivative positions are primarily executed in
the over-the-counter market.
The credit risk amounts take into consideration the effects of legally
enforceable master netting agreements, and on an aggregate basis have
been reduced by the cash collateral applied against derivative assets. At
December 31, 2007 and 2006, the cash collateral applied against
derivative assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheet was $12.8 billion
and $7.3 billion. In addition, at December 31, 2007 and 2006, the cash
collateral placed against derivative liabilities was $10.0 billion and $6.5
billion.
ALM Activities
Interest rate contracts and foreign exchange contracts are utilized in the
Corporation’s ALM activities. The Corporation maintains an overall interest
rate risk management strategy that incorporates the use of interest rate
contracts to minimize significant fluctuations in earnings that are caused
by interest rate volatility. The Corporation’s goal is to manage interest rate
sensitivity so that movements in interest rates do not significantly
adversely affect net interest income. As a result of interest rate fluctua-
tions, hedged fixed-rate assets and liabilities appreciate or depreciate in
market value. Gains or losses on the derivative instruments that are linked
to the hedged fixed-rate assets and liabilities are expected to substantially
offset this unrealized appreciation or depreciation. Interest income and
interest expense on hedged variable-rate assets and liabilities increase or
decrease as a result of interest rate fluctuations. Gains and losses on the
derivative instruments that are linked to these hedged assets and
liabilities are expected to substantially offset this variability in earnings.
Interest rate contracts, which are generally non-leveraged generic
interest rate and basis swaps, options and futures, allow the Corporation
to manage its interest rate risk position. Non-leveraged generic interest
rate swaps involve the exchange of fixed-rate and variable-rate interest
payments based on the contractual underlying notional amount. Basis
swaps involve the exchange of interest payments based on the contractual
underlying notional amounts, where both the pay rate and the receive rate
are floating rates based on different indices. Option products primarily
consist of caps, floors and swaptions. Futures contracts used for the
Corporation’s ALM activities are primarily index futures providing for cash
payments based upon the movements of an underlying rate index.
The Corporation uses foreign currency contracts to manage the for-
eign exchange risk associated with certain foreign currency-denominated
assets and liabilities, as well as the Corporation’s investments in foreign
subsidiaries. Foreign exchange contracts, which include spot and forward
contracts, represent agreements to exchange the currency of one country
for the currency of another country at an agreed-upon price on an agreed-
upon settlement date. Exposure to loss on these contracts will increase or
decrease over their respective lives as currency exchange and interest
rates fluctuate.
Fair Value, Cash Flow and Net Investment Hedges
The Corporation uses various types of interest rate and foreign exchange
derivative contracts to protect against changes in the fair value of its
assets and liabilities due to fluctuations in interest rates and exchange
rates (fair value hedges). The Corporation also uses these types of con-
tracts to protect against changes in the cash flows of its assets and
liabilities, and other forecasted transactions (cash flow hedges). During
the next 12 months, net losses on derivative instruments included in
accumulated OCI of approximately $1.3 billion ($820 million net-of-tax) are
expected to be reclassified into earnings. These net losses reclassified
into earnings are expected to impact net interest income related to the
respective hedged items.
130
Bank of America 2007