Bank of America 2007 Annual Report Download - page 88
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 88 of the 2007 Bank of America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
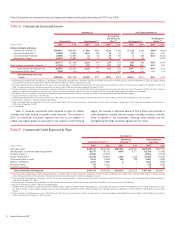
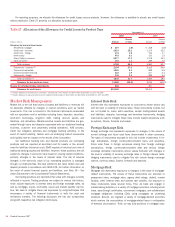
For reporting purposes, we allocate the allowance for credit losses across products. However, the allowance is available to absorb any credit losses
without restriction. Table 27 presents our allocation by product type.
Table 27 Allocation of the Allowance for Credit Losses by Product Type
December 31
2007 2006
(Dollars in millions) Amount
Percent
of Total Amount
Percent
of Total
Allowance for loan and lease losses
Residential mortgage
$ 207 1.8%
$ 248 2.8%
Credit card – domestic
2,919 25.2
3,176 35.2
Credit card – foreign
441 3.8
336 3.7
Home equity
963 8.3
133 1.5
Direct/Indirect consumer
2,077 17.9
1,378 15.3
Other consumer
151 1.3
289 3.2
Total consumer
6,758 58.3
5,560 61.7
Commercial – domestic
(1)
3,194 27.6
2,162 24.0
Commercial real estate
1,083 9.3
588 6.5
Commercial lease financing
218 1.9
217 2.4
Commercial – foreign
335 2.9
489 5.4
Total commercial
(2)
4,830 41.7
3,456 38.3
Allowance for loan and lease losses
11,588 100.0%
9,016 100.0%
Reserve for unfunded lending commitments
518
397
Allowance for credit losses
$12,106
$9,413
(1) Includes allowance for small business commercial – domestic loans of $1.4 billion and $578 million at December 31, 2007 and 2006.
(2) Includes allowance for loan and lease losses for impaired commercial loans of $123 million and $43 million at December 31, 2007 and 2006.
Market Risk Management
Market risk is the risk that values of assets and liabilities or revenues will
be adversely affected by changes in market conditions such as market
movements. This risk is inherent in the financial instruments associated
with our operations and/or activities including loans, deposits, securities,
short-term borrowings, long-term debt, trading account assets and
liabilities, and derivatives. Market-sensitive assets and liabilities are gen-
erated through loans and deposits associated with our traditional banking
business, customer and proprietary trading operations, ALM process,
credit risk mitigation activities and mortgage banking activities. In the
event of market volatility, factors such as underlying market movements
and liquidity have an impact on the results of the Corporation.
Our traditional banking loan and deposit products are nontrading
positions and are reported at amortized cost for assets or the amount
owed for liabilities (historical cost). GAAP requires a historical cost view of
traditional banking assets and liabilities. However, these positions are still
subject to changes in economic value based on varying market conditions,
primarily changes in the levels of interest rates. The risk of adverse
changes in the economic value of our nontrading positions is managed
through our ALM activities. We have elected to fair value certain loan and
deposit products in accordance with SFAS 159. For further information on
fair value of certain financial assets and liabilities, see Note 19 – Fair
Value Disclosures to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Our trading positions are reported at fair value with changes currently
reflected in income. Trading positions are subject to various risk factors,
which include exposures to interest rates and foreign exchange rates, as
well as mortgage, equity, commodity, issuer and market liquidity risk fac-
tors. We seek to mitigate these risk exposures by using techniques that
encompass a variety of financial instruments in both the cash and
derivatives markets. The following discusses the key risk components
along with respective risk mitigation techniques.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk represents exposures to instruments whose values vary
with the level or volatility of interest rates. These instruments include, but
are not limited to, loans, debt securities, certain trading-related assets
and liabilities, deposits, borrowings and derivative instruments. Hedging
instruments used to mitigate these risks include related derivatives such
as options, futures, forwards and swaps.
Foreign Exchange Risk
Foreign exchange risk represents exposures to changes in the values of
current holdings and future cash flows denominated in other currencies.
The types of instruments exposed to this risk include investments in for-
eign subsidiaries, foreign currency-denominated loans and securities,
future cash flows in foreign currencies arising from foreign exchange
transactions, foreign currency-denominated debt and various foreign
exchange derivative instruments whose values fluctuate with changes in
the level or volatility of currency exchange rates or foreign interest rates.
Hedging instruments used to mitigate this risk include foreign exchange
options, currency swaps, futures, forwards and deposits.
Mortgage Risk
Mortgage risk represents exposures to changes in the value of mortgage-
related instruments. The values of these instruments are sensitive to
prepayment rates, mortgage rates, agency debt ratings, default, market
liquidity, other interest rates and interest rate volatility. Our exposure to
these instruments takes several forms. First, we trade and engage in
market-making activities in a variety of mortgage securities including whole
loans, pass-through certificates, commercial mortgages, and collateralized
mortgage obligations including CDOs using mortgages as underlying
collateral. Second, we originate a variety of mortgage-backed securities
which involves the accumulation of mortgage-related loans in anticipation
of eventual securitization. Third, we may hold positions in mortgage secu-
86
Bank of America 2007