Bank of America 2005 Annual Report Download - page 101
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 101 of the 2005 Bank of America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
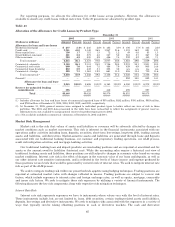
For reporting purposes, we allocate the allowance for credit losses across products. However, the allowance is
available to absorb any credit losses without restriction. Table 25 presents our allocation by product type.
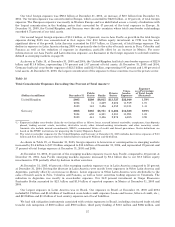
Table 25
Allocation of the Allowance for Credit Losses by Product Type
December 31
2005 2004 2003 2002 2001
(Dollars in millions) Amount Percent Amount Percent Amount Percent Amount Percent Amount Percent
Allowance for loan and lease losses
Residential mortgage .................. $ 277 3.4% $ 240 2.8% $ 185 3.0% $ 108 1.7% $ 145 2.3%
Creditcard .......................... 3,301 41.0 3,148 36.5 1,947 31.6 1,031 16.2 821 13.1
Homeequitylines..................... 136 1.7 115 1.3 72 1.2 49 0.8 83 1.3
Direct/Indirect consumer .............. 421 5.2 375 4.3 347 5.6 361 5.7 367 5.8
Other consumer ...................... 380 4.8 500 5.9 456 7.4 332 5.2 443 7.1
Total consumer ................... 4,515 56.1 4,378 50.8 3,007 48.8 1,881 29.6 1,859 29.6
Commercial—domestic ................ 2,100 26.1 2,101 24.3 1,756 28.5 2,231 35.1 1,901 30.3
Commercial real estate ................ 609 7.6 644 7.5 484 7.9 439 6.9 905 14.4
Commercial lease financing ............ 232 2.9 442 5.1 235 3.8 n/a n/a n/a n/a
Commercial—foreign .................. 589 7.3 1,061 12.3 681 11.0 855 13.4 730 11.6
Total commercial(1) ................ 3,530 43.9 4,248 49.2 3,156 51.2 3,525 55.4 3,536 56.3
General(2) ............................ — — — — — — 952 15.0 883 14.1
Allowance for loan and lease
losses ..................... 8,045 100.0% 8,626 100.0% 6,163 100.0% 6,358 100.0% 6,278 100.0%
Reserve for unfunded lending
commitments ..................... 395 402 416 493 597
Total .................... $8,440 $9,028 $6,579 $6,851 $6,875
(1) Includes allowance for loan and lease losses of commercial impaired loans of $55 million, $202 million, $391 million, $919 million,
and $763 million at December 31, 2005, 2004, 2003, 2002, and 2001, respectively.
(2) At December 31, 2005, general reserves were assigned to individual product types to better reflect our view of risk in these
portfolios. The 2004 and 2003 data presented in the table have been reclassified to reflect the assignment of general reserves.
Information was not available to assign general reserves by product types prior to 2003.
n/a = Not available; included in commercial—domestic at December 31, 2002 and 2001.
Market Risk Management
Market risk is the risk that values of assets and liabilities or revenues will be adversely affected by changes in
market conditions such as market movements. This risk is inherent in the financial instruments associated with our
operations and/or activities including loans, deposits, securities, short-term borrowings, long-term debt, trading account
assets and liabilities, and derivatives. Market-sensitive assets and liabilities are generated through loans and deposits
associated with our traditional banking business, our customer and proprietary trading operations, our ALM process,
credit risk mitigation activities, and mortgage banking activities.
Our traditional banking loan and deposit products are nontrading positions and are reported at amortized cost for
assets or the amount owed for liabilities (historical cost). While the accounting rules require a historical cost view of
traditional banking assets and liabilities, these positions are still subject to changes in economic value based on varying
market conditions. Interest rate risk is the effect of changes in the economic value of our loans and deposits, as well as
our other interest rate sensitive instruments, and is reflected in the levels of future income and expense produced by
these positions versus levels that would be generated by current levels of interest rates. We seek to mitigate interest rate
risk as part of the ALM process.
We seek to mitigate trading risk within our prescribed risk appetite using hedging techniques. Trading positions are
reported at estimated market value with changes reflected in income. Trading positions are subject to various risk
factors, which include exposures to interest rates and foreign exchange rates, as well as equity, mortgage, commodity
and issuer risk factors. We seek to mitigate these risk exposures by utilizing a variety of financial instruments. The
following discusses the key risk components along with respective risk mitigation techniques.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk represents exposures we have to instruments whose values vary with the level of interest rates.
These instruments include, but are not limited to, loans, debt securities, certain trading-related assets and liabilities,
deposits, borrowings and derivative instruments. We seek to mitigate risks associated with the exposures in a variety of
ways that typically involve taking offsetting positions in cash or derivative markets. The cash and derivative
65