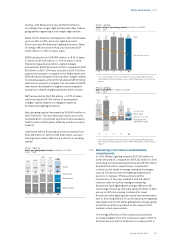
Philips 2014 Annual Report Download - page 69
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 69 of the 2014 Philips annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Risk management 7.2
Annual Report 2014 69
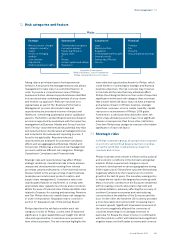
7.2 Risk categories and factors
Risks
Strategic
• Macroeconomic changes
• Changes in industry/
market
• Growth of emerging
markets
• Joint ventures
• Acquisitions
• Intellectual property rights
Operational
• Transformation programs
• Innovation process
• Intellectual Property
• Supply chain
• IT
• People
• Product quality and liability
• Reputation
Compliance
• Legal
• Market practices
• Regulatory
• General Business Principles
• Internal controls
• Data privacy/Product
security
Financial
• Treasury
• Tax
• Pensions
• Accounting and reporting
Corporate Governance
Philips Business Control Framework
Philips General Business Principles
Taking risks is an inherent part of entrepreneurial
behavior. A structured risk management process allows
management to take risks in a controlled manner. In
order to provide a comprehensive view of Philips’
business activities, risks and opportunities are identied
in a structured way combining elements of a top-down
and bottom-up approach. Risks are reported on a
regular basis as part of the ‘Business Performance
Management’ process. All relevant risks and
opportunities are prioritized in terms of impact and
likelihood, considering quantitative and/or qualitative
aspects. The bottom-up identication and prioritization
process is supported by workshops with the respective
management at Business, Market and Group Function
level. The top-down element allows potential new risks
and opportunities to be discussed at management level
and included in the subsequent reporting process, if
found to be applicable. Reported risks and
opportunities are analyzed for potential cumulative
eects and are aggregated at Business, Market and
Group level. Philips has a structured risk management
process to address dierent risk categories: Strategic,
Operational, Compliance and Financial risks.
Strategic risks and opportunities may aect Philips’
strategic ambitions. Operational risks include adverse
unexpected developments resulting from internal
processes, people and systems, or from external events
that are linked to the actual running of each business
(examples are solution and product creation, and
supply chain management). Compliance risks cover
unanticipated failures to implement, or comply with,
appropriate laws, regulations, policies and procedures.
Within the area of Financial risks, Philips identies risks
related to Treasury, Accounting and reporting, Pensions
and Tax. Philips does not classify these risk categories
in order of importance. Separation risk is covered in
section 7.7, Separation risk, of this Annual Report.
Philips describes the risk factors within each risk
category in order of Philips’ current view of expected
signicance, to give stakeholders an insight into which
risks and opportunities it considers more prominent
than others at present. The risk overview highlights the
main risks and opportunities known to Philips, which
could hinder it in achieving its strategic and nancial
business objectives. The risk overview may, however,
not include all the risks that may ultimately aect
Philips. Describing risk factors in their order of expected
signicance within each risk category does not mean
that a lower listed risk factor may not have a material
and adverse impact on Philips’ business, strategic
objectives, revenues, income, assets, liquidity, capital
resources or achievement of Philips’ 2016 goals.
Furthermore, a risk factor described after other risk
factors may ultimately prove to have more signicant
adverse consequences than those other risk factors.
Over time Philips may change its view as to the relative
signicance of each risk factor.
7.3 Strategic risks
As Philips’ business is global, its operations are exposed
to economic and political developments in countries
across the world that could adversely impact its
revenues and income.
Philips’ business environment is inuenced by political
and economic conditions in the domestic and global
markets. Philips experienced changes in macro
economic development in various geographies during
2014 in particular in China where customer demand was
negatively aected by the lowest level of economic
growth in the last 24 years. The monetary easing policy
in Japan did not result in the targeted economic growth.
Macro economic conditions in the Eurozone weakened
with increasing concerns about lack of growth and
potential deation, adversely aecting the recovery of
southern European economies and reintroducing
concerns about the stability of the Eurozone and the
euro. On the other the hand the US economy provided
a more favorable environment with increasing macro
economic growth. Signicant downward movement of
the oil price negatively aected the currencies of
countries depending on oil and gas revenues. In
particular for Russia the lower oil price in combination
with the political conict with Ukraine had a signicant
negative impact on the Russian economy and currency.