Bank of America 2008 Annual Report Download - page 95
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 95 of the 2008 Bank of America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
ASF Framework
In December 2007, the American Securitization Forum (ASF) issued the
Streamlined Foreclosure and Loss Avoidance Framework for Securitized
Adjustable Rate Mortgage Loans (the ASF Framework). The ASF Frame-
work was developed to address large numbers of subprime loans that are
at risk of default when the loans reset from their initial fixed interest rates
to variable rates. The objective of the framework is to provide uniform
guidelines for evaluating large numbers of loans for refinancing in an effi-
cient manner while complying with the relevant tax regulations and
off-balance sheet accounting standards for loan securitizations. The ASF
Framework targets loans that were originated between January 1, 2005
and July 31, 2007 and have an initial fixed interest rate period of 36
months or less, which are scheduled for their first interest rate reset
between January 1, 2008 and July 31, 2010.
The ASF Framework categorizes the targeted loans into three seg-
ments. Segment 1 includes loans where the borrower is likely to be able
to refinance into any available mortgage product. Segment 2 includes
loans where the borrower is current but is unlikely to be able to refinance
into any readily available mortgage product. Segment 3 includes loans
where the borrower is not current. If certain criteria are met, ASF Frame-
work loans in Segment 2 are eligible for fast-track modification under
which the interest rate will be kept at the existing initial rate, generally for
five years following the interest rate reset date. Upon evaluation,
if targeted loans do not meet specific criteria to be eligible for one of the
three segments, they are categorized as other loans, as shown in the
table below. These criteria include the occupancy status of the borrower,
structure and other terms of the loan. In January 2008, the SEC’s Office
of the Chief Accountant issued a letter addressing the accounting issues
relating to the ASF Framework. The letter concluded that the SEC would
not object to continuing off-balance sheet accounting treatment for
Segment 2 loans modified pursuant to the ASF Framework.
For those current loans that are accounted for off-balance sheet that
are modified, but not as part of the ASF Framework, the servicer must
perform on an individual basis, an analysis of the borrower and the loan
to demonstrate it is probable that the borrower will not meet the repay-
ment obligation in the near term. Such analysis shall provide sufficient
evidence to demonstrate that the loan is in imminent or reasonably fore-
seeable default. The SEC’s Office of the Chief Accountant issued a letter
in July 2007 stating that it would not object to continuing off-balance
sheet accounting treatment for these loans.
Prior to the acquisition of Countrywide on July 1, 2008, Countrywide
began making fast-track loan modifications under Segment 2 of the ASF
Framework in June 2008 and the off-balance sheet accounting treatment
of QSPEs that hold those loans was not affected. In addition, other work-
out activities relating to subprime ARMs including modifications (e.g.,
interest rate reductions and capitalization of interest) and repayment
plans were also made. These initiatives have continued subsequent to
the acquisition in an effort to work with all of our customers that are eligi-
ble and affected by loans that meet the requisite criteria. These fore-
closure prevention efforts will reduce foreclosures and the related losses
providing a solution for customers and protecting investors.
As of December 31, 2008, the principal balance of beneficial inter-
ests issued by the QSPEs that hold subprime ARMs totaled $56.5 billion
and the fair value of beneficial interests related to those QSPEs held by
the Corporation totaled $14 million. The table below presents a summary
of loans in QSPEs that hold subprime ARMs as of December 31, 2008 as
well as workout and payoff activity for the subprime loans by ASF catego-
rization for the six months ended December 31, 2008. Prior to the acquis-
ition of Countrywide on July 1, 2008, we did not originate or service
significant subprime residential mortgage loans, nor did we hold a sig-
nificant amount of beneficial interest in QSPEs of subprime residential
mortgage loans.
In October 2008 in agreement with several state attorneys general, we
announced the Countrywide National Homeownership Retention Program.
Under the program, we will systematically identify and seek to offer loan
modifications for eligible Countrywide subprime and pay option ARM bor-
rowers whose loans are in delinquency or scheduled for an interest rate or
payment change. For more information on our loan modification programs,
see Recent Events on page 22.
Complex Accounting Estimates
Our significant accounting principles, as described in Note 1 – Summary
of Significant Accounting Principles to the Consolidated Financial State-
ments, are essential in understanding the MD&A. Many of our significant
accounting principles require complex judgments to estimate values of
assets and liabilities. We have procedures and processes to facilitate
making these judgments.
The more judgmental estimates are summarized below. We have iden-
tified and described the development of the variables most important in
the estimation process that, with the exception of accrued taxes, involve
mathematical models to derive the estimates. In many cases, there are
numerous alternative judgments that could be used in the process of
determining the inputs to the model. Where alternatives exist, we have
used the factors that we believe represent the most reasonable value in
developing the inputs. Actual performance that differs from our estimates
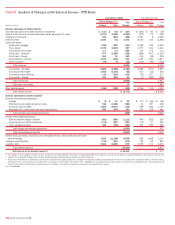
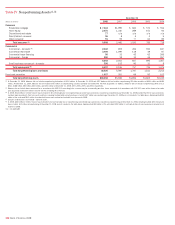
Table 43 QSPE Loans Subject to ASF Framework Evaluation (1)
December 31, 2008 Activity During the Six Months Ended December 31, 2008
(Dollars in millions) Balance Percent Payoffs
Fast-track
Modifications
Other
Workout
Activities Foreclosures
Segment 1 $ 2,568 4.5% $ 807 $ – $1,396 $ –
Segment 2 9,135 16.2 267 1,428 1,636 108
Segment 3 11,176 19.8 62 – 1,802 929
Total Subprime ARMs 22,879 40.5 1,136 1,428 4,834 1,037
Other loans 30,781 54.5 n/a n/a n/a n/a
Foreclosed properties 2,794 5.0 n/a n/a n/a n/a
Total
$56,454 100.0% $1,136 $1,428 $4,834 $1,037
(1) Represents loans that were acquired with the acquisition of Countrywide on July 1, 2008 that meet the requirements of the ASF Framework.
n/a = not applicable
Bank of America 2008
93