RBS 2008 Annual Report Download - page 104
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 104 of the 2008 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
103RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2008
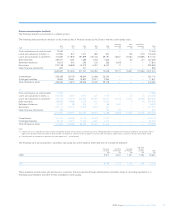
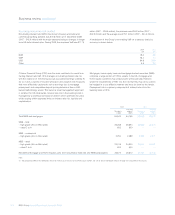
Liquidity risk (audited)
The Group’s liquidity policy is designed to ensure that the Group can at
all times meet its obligations as they fall due.
Liquidity management within the Group addresses the overall balance
sheet structure and the control, within prudent limits, of risk arising from
the mismatch of maturities across the balance sheet and from exposure
to undrawn commitments and other contingent obligations.
The management of liquidity risk within the Group is undertaken within a
formal governance structure. The Group Board of Directors oversees
the liquidity risk appetite and strategy of the Group; the Group
Executive Management Committee reviews the key liquidity metrics and
trends in the context of the Group’s overall risk profile; the Group Asset
and Liability Management Committee (GALCO), chaired by the Group
Finance Director and including the chief executives of the business
divisions as well as the Group Treasurer, Group Chief Risk Officer and
heads of other relevant Group functions, sets explicit metrics across a
number of asset and liability targets and these are cascaded to the
business and monitored by the Group Treasury and risk functions.
Group Treasury has overall responsibility for the daily monitoring and
control of the Group’s liquidity and funding positions. The Liquidity
Managers’ Forum is chaired and directed by the Group Treasurer with
membership including the Head of Short Term Markets and Financing,
GBM. The forum typically meets weekly with more frequent, ad hoc,
meetings as necessary. There are Regional and Country ALCOs that
oversee Group policy in our business in Europe, Asia and the Americas.
The Group is divided into Liquidity Reporting Units each of which is
required to have its own liquidity limits and contingency funding plan. In
addition, all subsidiaries and branches outside the UK are required to
comply with local regulatory liquidity requirements and are subject to
Group Treasury oversight.
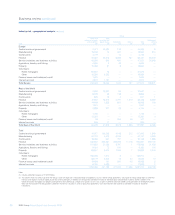
Management of term structure
The Group evaluates on a regular basis its structural liquidity risk and
applies a variety of balance sheet management and term funding
strategies to maintain this risk within its normal policy parameters. The
degree of maturity mismatch within the overall long-term structure of the
Group’s assets and liabilities is managed within internal policy
guidelines, aimed at ensuring term asset commitments may be funded
on an economic basis over their life. In managing its overall term
structure, the Group analyses and takes into account the effect of retail
and corporate customer behaviour on actual asset and liability
maturities where they differ materially from the underlying contractual
maturities.
Daily management
The primary focus of the daily management activity is to ensure access
to sufficient liquidity to meet cash flow obligations within key time
horizons, in particular out to one month ahead. The short-term maturity
structure of the Group’s liabilities and assets is managed daily to
ensure that all material or potential cash flow obligations, arising from
undrawn commitments and other contingent obligations can be met.
Potential sources include cash inflows from maturing assets, new
borrowings or the sale of various debt securities held (after allowing for
appropriate haircuts). Short-term liquidity risk is generally managed on
a consolidated basis with liquidity mismatch limits in place for
subsidiaries and non-UK branches which have material local treasury
activities, thereby assuring that the daily maintenance of the Group’s
overall liquidity risk position is not compromised. ABN AMRO, Citizens
Financial Group and RBS Insurance manage liquidity locally, given
different regulatory regimes, subject to review by Group Treasury. As
integration of ABN AMRO’s businesses within the Group proceeds, the
liquidity risk policies, parameters and metrics used will be progressively
aligned within a single framework.
Stress testing
The Group performs stress tests to simulate how events may impact its
funding and liquidity capabilities. Such tests inform the overall balance
sheet structure and help define suitable limits for control of the risk
arising from the mismatch of maturities across the balance sheet and
from undrawn commitments and other contingent obligations. The form
and content of stress tests are updated where required as market
conditions evolve.
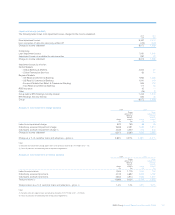
Contingency planning
Contingency funding plans have been developed to anticipate and
respond to approaching or actual material deterioration in market
conditions. The Group reviews its contingency plans in the light of
evolving market conditions. The contingency funding plan covers: the
available sources of contingent funding to supplement cash flow
shortages; the lead times to obtain such funding; the roles and
responsibilities of those involved in the contingency plans, including the
communication lines for escalation of events which give rise to liquidity
stress; assumptions, including the expected change impact of market
conditions; and the ability and circumstances within which the Group
accesses central bank liquidity.
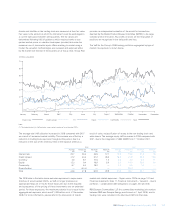
Global developments (unaudited)
The global financial system has experienced its greatest crisis in the
post war period and the dislocation became most acute in the second
half of 2008. This loss of confidence in the world’s banking system led
to massive dislocation in the capital markets and resulted in the
effective closure of the term debt and securitisation markets and money
markets. Government intervention in, and support for, the international
financial system has increased to unprecedented levels taking the form
of capital injections, guaranteed funding, asset insurance schemes and
expanded facilities from a number of central banks:
•In September 2007, the Bank of England announced that to alleviate
strains in longer-maturity money markets, it would conduct auctions to
provide funds at three month maturity against a wider range of
collateral, including mortgage collateral, than in its weekly open
market operations.