RBS 2008 Annual Report Download - page 119
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 119 of the 2008 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2008118
Business review continued
Operational risk (unaudited)
Operational risk is the risk of financial loss or reputational impact
resulting from fraud; human error; ineffective or inadequately designed
processes or systems; improper behaviour; legal events; or from
external events. Operational risk is an integral and unavoidable part of
the Group’s business as it is inherent in the processes it operates to
provide services to customers and generate profit for shareholders.
An objective of operational risk management is not to remove
operational risk altogether, but to manage the risk to an acceptable
level, taking into account the cost of minimising the risk with the
resultant reduction in exposure. Strategies to manage operational risk
include avoidance, transfer, and mitigation by controls or risk
acceptance.
To ensure appropriate responsibility is allocated for the management,
reporting and escalation of operational risk, the Group operates a three
lines of defence model which outlines principles for the roles,
responsibilities and accountabilities for operational risk management.
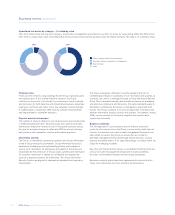
Operational Risk – three lines of defence model
1st Line of defence
The Business
Accountable for the ownership and day-to-day
management and control of operational risk.
Responsible for implementing
processes in compliance with Group policies.
Responsible for testing key controls and
monitoring compliance with Group policies.
2nd Line of defence
Operational Risk
Responsible for the implementation and
maintenance of the operational risk
framework, tools and methodologies.
Responsible for oversight and challenge on
the adequacy of the risk and control
processes operating in the business.
3rd Line of defence
Group Internal Audit
Responsible for providing independent
assurance on the design, adequacy and
effectiveness of the Group’s system of
internal controls.
The three lines of defence model and the Operational Risk Policy and
Principles (ORPP) apply throughout the Group and are implemented
taking into account the nature and scale of the underlying business. The
ORPP provides the direction for delivering effective operational risk
management. It comprises principles, minimum standards and
processes that enable the consistent identification, assessment,
management, monitoring and reporting of operational risk across the
Group. The objectives of the ORPP are to protect the Group from
financial loss or damage to its reputation, its customers or staff and to
ensure that it meets all necessary regulatory and legal requirements.
The Group-wide processes defined in the ORPP are supported by the
following key operational risk management techniques:
•Risk and control assessments: business units identify and assess
operational risks to ensure that they are effectively managed,
prioritised, documented and aligned to risk appetite.
•Scenario analysis: scenarios for operational risk are used to assess
the possible impact of extreme but plausible operational risk loss
events. Scenario assessments provide a forward-looking basis for
managing exposures that are beyond the Group’s risk appetite.
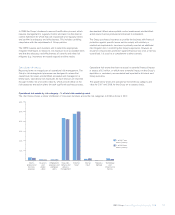
•Loss data management: each business unit`s internal loss data
management process captures all operational risk loss events above
£10,000. This is used to enhance the adequacy and effectiveness of
controls, identify opportunities to prevent or reduce the impact of re-
occurrence, identify emerging themes, enable formal loss event
reporting and inform risk and control assessments and scenario
analysis. Escalation of individual events to senior management is
determined by the seriousness of the event. Operational loss events
are categorised under the following headings:
– Clients, products and business practices;
– Technology and infrastructure failures;
– Employment practices and workplace safety;
– Internal fraud;
– External fraud;
– Execution, delivery and process management;
– Malicious damage; and
– Disaster and public safety.
•Key risk indicators: business units monitor key risk indicators against
their material risks. These indicators are used to monitor the
operational risk profile and exposure to losses against thresholds
which trigger risk management actions.
•New product approval process: ensures that all new products or
significant variations to existing products are subject to a
comprehensive risk assessment. Products are evaluated and
approved by specialist areas and are subject to executive approval
prior to launch.