RBS 2008 Annual Report Download - page 85
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 85 of the 2008 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299
 |
 |

84
Business review continued
RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2008
Credit risk
Principles for credit risk management (audited)
The key principles for credit risk management in the Group are as
follows:
•A credit risk assessment of the customer and credit facilities is
undertaken prior to approval of credit exposure. Typically, this
includes both quantitative and qualitative elements including, the
purpose of the credit and sources of repayment; compliance with
affordability tests; repayment history; ability to repay; sensitivity to
economic and market developments; and risk-adjusted return based
on credit risk measures appropriate to the customer and facility type.
•Credit risk authority is specifically granted in writing to individuals
involved in the granting of credit approval, whether this is individually
or collectively as part of a credit committee. In exercising credit
authority, individuals are required to act independently of business
considerations and must declare any conflicts of interest.
•Credit exposures, once approved, are monitored, managed and
reviewed periodically against approved limits. Lower quality
exposures are subject to more frequent analysis and assessment.
•Credit risk management works with business functions on the ongoing
management of the credit portfolio, including decisions on mitigating
actions taken against individual exposures or broader portfolios.
•Customers with emerging credit problems are identified early and
classified accordingly. Remedial actions are implemented promptly
and are intended to restore the customer to a satisfactory status and
minimise any potential loss to the Group.
•Stress testing of portfolios is undertaken to assess the potential credit
impact of non-systemic scenarios and wider macroeconomic events
on the Group’s income and capital.
Specialist credit risk teams oversee the credit process independently,
making credit decisions within their discretion, or recommending
decisions to the appropriate credit committee.
Assessments of corporate borrower and transaction risk are undertaken
using fundamental credit analysis and the application of general
corporate and certain specialist counterparty credit risk models.
Financial markets counterparties are approved by a dedicated credit
function which specialises in traded market product risk. Specialist
credit grading models exist for certain bank and non-bank financial
institutions.
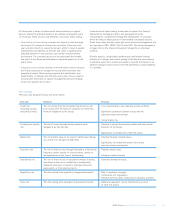
Different approaches are used for the management of wholesale and
retail businesses:
•Wholesale businesses: exposures are aggregated to determine the
appropriate level of credit approval required and to facilitate
consolidated credit risk management. Credit applications for
corporate customers are prepared by relationship managers (RMs) in
the units originating the credit exposures, or by the RM team with
lead responsibility for a counterparty where a customer has
relationships with different divisions and business units across the
Group. This includes the assignment of counterparty credit grades
and LGD estimates using approved models, which are also
independently checked by the credit team.
•Retail businesses: the retail business makes a large volume of small
value credit decisions. Credit decisions will typically involve an
application for a new or additional product or a change in facilities on
an existing product. The majority of these decisions are based upon
automated strategies utilising industry standard credit and behaviour
scoring techniques.
