RBS 2008 Annual Report Download - page 83
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 83 of the 2008 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
82
Business review continued
RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2008
Basel II
The Group adopted Basel II on 1 January 2008. Pillar 1 focuses on the
calculation of minimum capital required to support the credit, market
and operational risks in the business. For credit risk, the majority of the
Group uses the Advanced Internal Ratings Based Approach (AIRB) for
calculating RWAs, making the Group one of a small number of banks
whose risk systems and approaches have reached the regulatory
standards.
For operational risk, the Group uses The Standardised Approach (TSA),
which calculates operational risk-weighted assets based on gross
income. In line with other banks, the Group is considering adopting the
Advanced Measurement Approach (AMA) for all or part of the business.
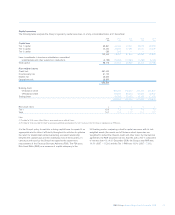
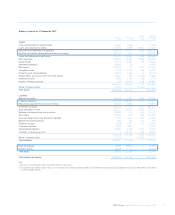
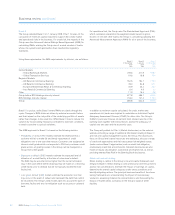
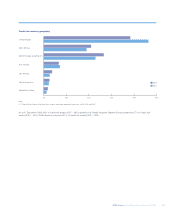
Using these approaches, the RWA requirements, by division, are as follows:
Basel II Basel II Basel I
31 December 1 January 31 December
2008 2008 2007
£bn £bn £bn
Global Markets
– Global Banking & Markets 278.5 211.9 188.7
– Global Transaction Services 19.6 16.8 15.4
Regional Markets
– UK Retail & Commercial Banking 152.5 153.1 179.0
– US Retail & Commercial Banking 78.0 53.8 57.1
– Europe & Middle East Retail & Commercial Banking 30.9 30.3 36.7
– Asia Retail & Commercial Banking 6.4 4.9 3.3
Other 11.9 15.3 9.8
Group before RFS Holdings minority interest 577.8 486.1 490.0
RFS Holdings minority interest 118.0 147.4 119.0
Group 695.8 633.5 609.0
Basel II is cyclical, unlike Basel I where RWAs are stable through the
cycle. Changes in RWA totals are driven by external economic factors
and their impact on the risk profile of the underlying portfolio of assets,
rather than changes in the asset mix. Whilst Basel II tries to reduce this
variation by incorporating measures correlated to downturn conditions,
it remains sensitive to cyclical variations.
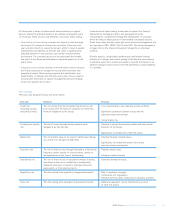
The AIRB approach to Basel II is based on the following metrics.
•Probability of default (PD) models estimate the likelihood that a
customer will fail to make full and timely repayment of credit
obligations over a one year time horizon. Customers are assigned an
internal credit grade which corresponds to PD. Every customer credit
grade across all grading scales in the Group can be mapped to a
Group level credit grade.
•Exposure at default (EAD) models estimate the expected level of
utilisation of a credit facility at the time of a borrower’s default.
The EAD may be assumed to be higher than the current utilisation
(e.g. in the case where further drawings may be made on a revolving
credit facility prior to default) but will not typically exceed the total
facility limit.
•Loss given default (LGD) models estimate the economic loss that
may occur in the event of default and represent the debt that cannot
be recovered. The Group’s LGD models take into account the type of
borrower, facility and any risk mitigation such as security or collateral
held.
In addition to minimum capital calculated, for credit, market and
operational risk, banks are required to undertake an Individual Capital
Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP) for other risks. The Group’s
ICAAP, in particular, focuses on pension fund, interest rate risk in the
banking book together with stress tests to assess the adequacy of
capital over one year and the economic cycle.
The Group will publish its Pillar 3 (Market disclosures) on the external
website, providing a range of additional information relating to Basel II
and risk and capital management across the Group. The disclosures
focus on Group level capital resources and adequacy, discuss a range
of credit risk approaches and their associated risk weighted assets
(under various Basel II approaches) such as credit risk mitigation,
counterparty credit risk and provisions. Detailed disclosures are also
made on equity, securitisation, operational and market risk, as well as
providing Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book disclosures.
Stress and scenario testing
Stress testing is central to the Group’s risk and capital framework and
integral to Basel II. Stress testing is used at divisional and Group level to
assess risk concentrations, estimate the impact of earnings on capital,
determine the overall capital adequacy under stress conditions and
identify mitigating actions. The principal business benefits of the stress
testing framework are: understanding the impact of recessionary
scenarios; assessing material risk concentrations; and forecasting the
impact of market stress scenarios on the Group’s balance sheet
liquidity.