RBS 2008 Annual Report Download - page 111
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 111 of the 2008 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2008110
Business review continued
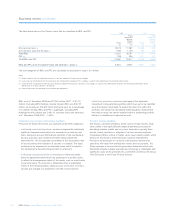
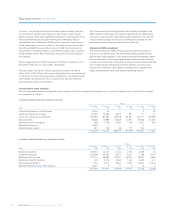
Backtesting, stress testing and sensitivity analysis (audited)
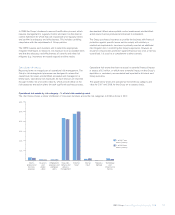
The Group undertakes a programme of daily backtesting, which
compares the actual profit or loss realised in trading activity to the VaR
estimation. The results of the backtesting process are one of the
methods by which the Group monitors the ongoing suitability of its VaR
model.
A ‘Risks not in VaR’ framework has been developed to address those
market risks not adequately captured by the market standard VaR
methodology. Where risks are not included in the model various non-VaR
controls (e.g. position monitoring, sensitivity limits, triggers or stress
limits) are in place.
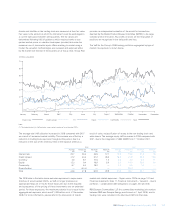
The Group undertakes daily stress testing to identify the potential losses
in excess of VaR. Stress testing is used to calculate a range of trading
book exposures which result from exceptional but plausible market
events. Stress testing measures the impact of abnormal changes in
market rates and prices on the fair value of the Group`s trading
portfolios. GEMC approves the high-level market stress test limit for the
Group. The Group calculates historical stress tests and hypothetical
stress tests.
Historical stress tests calculate the loss that would be generated if the
market movements that occurred during historical market events were
repeated. Hypothetical stress tests calculate the loss that would be
generated if a specific set of adverse market movements were to occur.
Stress testing is also undertaken at key trading strategy level, for those
strategies where the associated market risks are not adequately
captured by VaR. Stress test exposures are discussed with senior
management and are reported to GRC, GEMC and the Board. Breaches
in the Group`s market risk stress testing limits are monitored and
reported.
In addition to VaR and stress testing, the Group calculates a wide range
of sensitivity and position risk measures, for example interest rate
ladders or option revaluation matrices. These measures provide
valuable additional controls, often at individual desk or strategy level.
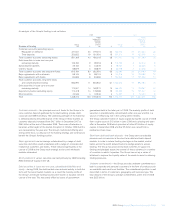
Model validation governance (audited)
Pricing models are developed and owned by the front office. Where
pricing models are used as the basis of books and records valuations,
they are all subject to independent review and sign-off. Models are
assessed by MPRC as having either immaterial or material model risk
(valuation uncertainty arising from choice of modelling assumptions),
the assessment being made on the basis of expert judgement. Those
models assessed as having material model risk are prioritised for
independent quantitative review. Independent quantitative review aims
to quantify model risk by comparing model outputs against alternative
independently developed models. The results of independent
quantitative review are used by Market Risk to inform risk limits and by
Finance to inform reserves. Governance over this process is provided
by MPRC, a forum which brings together front office quants, market risk,
finance and QuaRC (Quantitative Research Centre, Group Risk’s
independent quantitative model review function). Risk (market risk,
incremental default risk, counterparty credit risk) models are developed
both within business units and by Group functions. Risk models are also
subject to independent review and sign-off. Meetings are held with the
FSA every quarter to discuss the traded market risk, including changes
in models, management, back testing results, other risks not included in
the VaR framework and other model performance statistics.
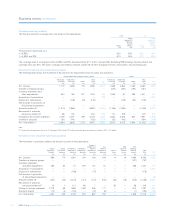
Risk control (audited)
All divisions that are exposed to market risk in the course of their
business are required to comply with the requirements of the Group’s
Market Risk Policy Standards (MRPS). The main risk management tools
are delegated authorities, specifically hard limits and discussion
triggers, independent model valuation, a robust and efficient risk system
and timely and accurate management information.
Limits form part of the dealing authorities and constitute one of the
cornerstones of the market risk management framework. Upon
notification of a limit breach, the appropriate body must take one of the
following actions:
•Instructions can be given to reduce positions so as to bring the
Group within the agreed limits.
•A temporary increase in the limit (for instance, in order to allow
orderly unwinding of positions) can be granted.
•A permanent increase in the limit can be granted.
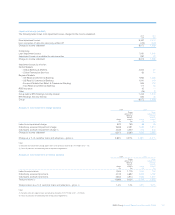
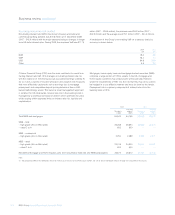
Non-traded portfolios (audited)
Risks in non-traded portfolios mainly arise in retail and commercial
banking assets and liabilities and financial investments designated as
available-for-sale and held-to-maturity.
Group Treasury is responsible for setting and monitoring the adequacy
and effectiveness of management, using a framework that identifies,
measures, monitors and controls the underlying risk. GALCO approves
the Group’s non-traded market risk appetite, expressed as statistical
and non-statistical risk limits, which are delegated to the businesses
responsible.
Various banking regulators review non-trading market risk as part of
their regulatory oversight. As home regulator, the FSA has responsibility
for reviewing non-trading market risk at a Group consolidated level.