RBS 2008 Annual Report Download - page 116
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 116 of the 2008 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
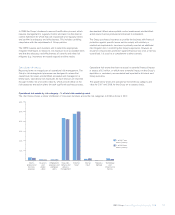
115RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2008
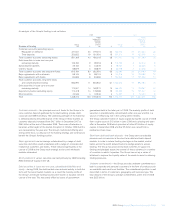
Risk control (unaudited)
The prime risk control mechanism for non-traded market risk exposures
is the completion of monthly IRRBB and quarterly FXRBB returns by the
Group’s business units, collated as part of month-end reporting by
Group Treasury to GALCO. In relation to equity risk, risk is mitigated by
proper controls in relation to identification of risk prior to investing.
Financial control functions are required to confirm to Group Treasury
that returns materially capture all balance sheet items and thus
reconcile to core source systems.
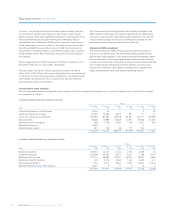
Monthly returns by the Group’s business units, collated as part of
month-end reporting by Group Treasury to GALCO, are used to build a
Group IRRBB VaR position and to ensure businesses comply with
materiality limits on a pre and post hedge basis for interest rates, as
stipulated by Group Treasury.
For FXRBB, the Group policy states that any foreign currency exposure
is managed to de-minimus limits. Group Treasury monitors adherence to
this policy via a quarterly return.
For both IRRBB and FXRBB information is included in regulatory and
statutory returns.
Group Market Risk exercise independent oversight and governance of
the interest rate and foreign exchange exposures managed in Group
Treasury by granting market risk limits in addition to authorising Group
Treasury to deal in specific instruments for the purpose of managing the
Group's non-trading interest rate and foreign exchange exposures. All
market risk methodologies that relate to limits specified under this
delegated authority are applied under the direction of Group Market
Risk.
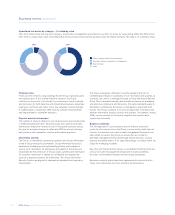
Insurance risk (unaudited)
The Group is exposed to insurance risk directly through its general and
life insurance businesses.
Insurance risk arises through fluctuations in the timing, frequency and/or
severity of insured events, relative to the expectations at the time of
underwriting. Insurance risk is managed in four distinct ways:
•Underwriting and pricing risk management: is managed through the
use of underwriting guidelines which detail the class, nature and type
of business that may be accepted, pricing policies by product line
and brand and centralised control of wordings and any subsequent
changes.
•Claims risk management: is handled using a range of automated
controls and manual processes.
•Reserving risk management: is the risk that the technical reserves
are assessed incorrectly such that insufficient funds have been
retained to handle and pay claims as the amounts fall due, both in
relation to those claims which have already occurred or will occur in
future periods of insurance. Claims development data provides
information on the historical pattern of reserving risk.
•Reinsurance risk management: is used to protect against adverse
claims experience on business within normal risk appetite (e.g.
catastrophic events, adverse frequency of large claims) and to
provide protection on business not within its risk appetite (e.g. quota
share reinsurance on certain classes of business).
The aggregate amount of business by product and entity is determined
through the business plans.
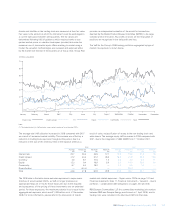
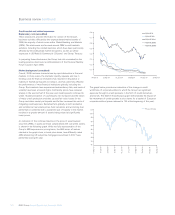
Overall, insurance risk is predictable over time, given the large volumes
of data. Uncertainty does exist, especially around predictions such as
the variations in weather. Risk is minimised through the application of
documented risk policies, coupled with governance frameworks.
General insurance business
The Group`s focus in its general insurance operation is on high volume,
relatively straightforward products. The key insurance risks are as
follows:
•Motor insurance contracts (private and commercial): claims
experience varies due to a range of factors, including age, gender
and driving experience together with the type of vehicle and location.
•Property insurance contracts (residential and commercial): the
major causes of claims for property insurance are weather (flood,
storm), theft, fire, subsidence and various types of accidental
damage.
•Other commercial insurance contracts: risk arises from business
interruption and loss arising from the negligence of the insured
(liability insurance). Business interruption claims arise from the losses
of income, revenue and/or profit as a result of property damage
claims. Liability insurance includes employer’s liability and
public/products liability.
Most general insurance contracts are written on an annual basis, which
means that the Group’s liability extends for a 12 month period, after
which the Group is entitled to decline to renew or can impose renewal
terms by amending the premium, terms and conditions.
An analysis of gross and net insurance claims can be found in Note 24
on the report and accounts (see page 231).