RBS 2008 Annual Report Download - page 87
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 87 of the 2008 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
86
Business review continued
RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2008
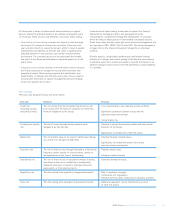
Credit risk mitigation (audited)
The Group takes a number of steps to mitigate credit risk. The key risk
mitigants are as follows:
•Real estate: the most common form of security held is real estate
within the consumer and wholesale businesses.
•Financial collateral: is taken to support credit exposures in the non-
trading book. Financial collateral is also taken in Global Markets and
Regional Markets to support trading book exposures and is
incorporated in E* (adjustment to the exposure value) calculations.
•Other physical collateral: the Group takes a wide range of other
physical collateral including business assets (stock and inventory,
plant and machinery, equipment), project assets, intangible assets
which provide a future cashflow and real value, commodities,
vehicles, rail stock, aircraft, ships and receivables (not purchased).
•Guarantees: third party guarantees are taken from banks,
government entities, export credit agencies, and corporate entities.
The Group’s recovery value estimation methodology is sensitive to the
variations in the credit quality of guarantors. Standby letters of credit
are also given value in LGD models. Conditional guarantees are
accepted, in accordance with internal requirements, and are included
as appropriate in PD and LGD estimates (e.g. small firms loan
guarantee schemes, completion guarantees). Personal guarantees
are considered in the normal credit process where there is a charge
over specific assets. While personal guarantees may be called for
and are always accepted, no value is given to unsupported personal
guarantees in any credit models.
•Credit derivatives: credit derivative activity is conducted through
designated units within GBM to ensure consistency and appropriate
control. Group policies are designed to ensure that the credit
protection is appropriate to support offset for an underlying trading
book asset or improvement to the LGD of a banking book asset.
Within the banking book, credit derivatives are used as risk and
capital management tools. The principal counterparties are banks,
investment firms and other market participants, with the majority
subject to collateralisation under a credit support annex. In
accordance with internal policy, stress testing is conducted on the
counterparty credit risk created by the purchase of credit protection.
•Minimum standards (for example loan to value, legal certainty) are
ensured through the policy framework.
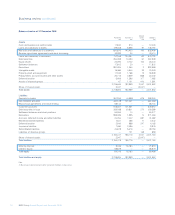
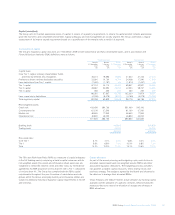
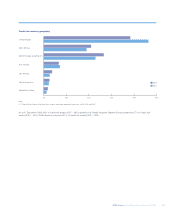
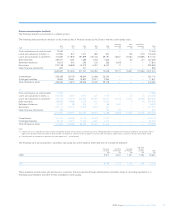
2008 2007
Credit risk assets (unaudited) £bn £bn
Global Markets 469.8 307.4
Regional Markets
– UK Retail & Commercial Banking 223.5 202.1
– US Retail & Commercial Banking 82.9 58.1
– Europe & Middle East Retail & Commercial Banking 64.7 47.1
– Asia Retail & Commercial Banking 7.5 6.8
RBS Insurance 4.6 5.1
Other 2.0 —
Group before RFS Holdings minority interest 855.0 626.6
RFS Holdings minority interest 176.8 206.0
Group 1,031.8 832.6
Note:
(1) Excluding reverse repurchase agreements and issuer risk.
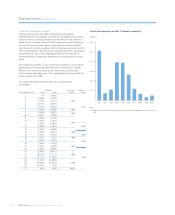
Credit risk assets as at 31 December 2008 were £855.0 billion (2007 – £626.6 billion), an increase of £228.4 billion during the year.
Pages 86 to 93 include analyses of credit risk assets on a pro forma basis, excluding RFS Holdings minority interests and share of shared assets, in
line with management’s view of the business.
Facilities included within RFS Holdings minority interests have not been migrated to RBS risk systems, as they will not be part of the Group following
separation of the ABN AMRO business.
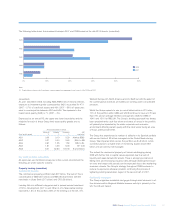
Credit risk assets (audited)
Credit risk assets consist of loans and advances (including overdraft facilities), instalment credit, finance lease receivables and other traded instruments
across all customer types. The Group uses a series of models to measure the size of its exposure to credit risk and to calculate expected EAD in both
its trading and banking books. In so doing, the Group recognises the effects of credit risk mitigation that reduces potential loss.