Bank of America 2014 Annual Report Download - page 161
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 161 of the 2014 Bank of America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Bank of America 2014 159
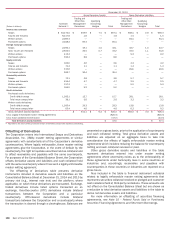
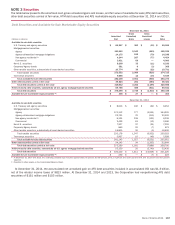
Offsetting of Derivatives
December 31, 2014 December 31, 2013
(Dollars in billions)
Derivative
Assets
Derivative
Liabilities
Derivative
Assets
Derivative
Liabilities
Interest rate contracts
Over-the-counter $ 386.6 $ 373.2 $ 381.7 $ 365.9
Exchange-traded 0.1 0.1 0.4 0.3
Over-the-counter cleared 365.7 368.7 351.2 356.5
Foreign exchange contracts
Over-the-counter 133.0 139.9 82.9 83.9
Equity contracts
Over-the-counter 19.5 16.7 20.3 17.6
Exchange-traded 8.6 7.8 8.4 9.8
Commodity contracts
Over-the-counter 10.2 11.9 6.3 7.4
Exchange-traded 7.4 7.7 3.3 2.9
Over-the-counter cleared 0.1 0.6 ——
Credit derivatives
Over-the-counter 30.8 30.2 44.0 38.9
Over-the-counter cleared 7.0 6.8 5.8 5.9
Total gross derivative assets/liabilities, before netting
Over-the-counter 580.1 571.9 535.2 513.7
Exchange-traded 16.1 15.6 12.1 13.0
Over-the-counter cleared 372.8 376.1 357.0 362.4
Less: Legally enforceable master netting agreements and cash collateral received/paid
Over-the-counter (545.7)(545.5)(505.0) (495.4)
Exchange-traded (13.9) (13.9) (11.2) (11.2)
Over-the-counter cleared (372.5)(375.5)(356.6) (362.4)
Derivative assets/liabilities, after netting 36.9 28.7 31.5 20.1
Other gross derivative assets/liabilities 15.8 18.2 16.0 17.3
Total derivative assets/liabilities 52.7 46.9 47.5 37.4
Less: Financial instruments collateral (1) (13.3) (8.9)(10.1) (4.6)
Total net derivative assets/liabilities $ 39.4 $38.0 $ 37.4 $ 32.8
(1) These amounts are limited to the derivative asset/liability balance and, accordingly, do not include excess collateral received/pledged.
ALM and Risk Management Derivatives
The Corporation’s asset and liability management (ALM) and risk
management activities include the use of derivatives to mitigate
risk to the Corporation including derivatives designated in
qualifying hedge accounting relationships and derivatives used in
other risk management activities. Interest rate, foreign exchange,
equity, commodity and credit contracts are utilized in the
Corporation’s ALM and risk management activities.
The Corporation maintains an overall interest rate risk
management strategy that incorporates the use of interest rate
contracts, which are generally non-leveraged generic interest rate
and basis swaps, options, futures and forwards, to minimize
significant fluctuations in earnings caused by interest rate
volatility. The Corporation’s goal is to manage interest rate
sensitivity and volatility so that movements in interest rates do
not significantly adversely affect earnings or capital. As a result
of interest rate fluctuations, hedged fixed-rate assets and liabilities
appreciate or depreciate in fair value. Gains or losses on the
derivative instruments that are linked to the hedged fixed-rate
assets and liabilities are expected to substantially offset this
unrealized appreciation or depreciation.
Market risk, including interest rate risk, can be substantial in
the mortgage business. Market risk is the risk that values of
mortgage assets or revenues will be adversely affected by changes
in market conditions such as interest rate movements. To mitigate
the interest rate risk in mortgage banking production income, the
Corporation utilizes forward loan sale commitments and other
derivative instruments, including purchased options, and certain
debt securities. The Corporation also utilizes derivatives such as
interest rate options, interest rate swaps, forward settlement
contracts and eurodollar futures to hedge certain market risks of
mortgage servicing rights (MSRs). For more information on MSRs,
see Note 23 – Mortgage Servicing Rights.
The Corporation uses foreign exchange contracts to manage
the foreign exchange risk associated with certain foreign currency-
denominated assets and liabilities, as well as the Corporation’s
investments in non-U.S. subsidiaries. Foreign exchange contracts,
which include spot and forward contracts, represent agreements
to exchange the currency of one country for the currency of another
country at an agreed-upon price on an agreed-upon settlement
date. Exposure to loss on these contracts will increase or decrease
over their respective lives as currency exchange and interest rates
fluctuate.
The Corporation enters into derivative commodity contracts
such as futures, swaps, options and forwards as well as non-
derivative commodity contracts to provide price risk management
services to customers or to manage price risk associated with its
physical and financial commodity positions. The non-derivative
commodity contracts and physical inventories of commodities
expose the Corporation to earnings volatility. Cash flow and fair
value accounting hedges provide a method to mitigate a portion
of this earnings volatility.