Bank of America 2014 Annual Report Download - page 191
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 191 of the 2014 Bank of America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Bank of America 2014 189
NOTE 6 Securitizations and Other Variable
Interest Entities
The Corporation utilizes variable interest entities (VIEs) in the
ordinary course of business to support its own and its customers’
financing and investing needs. The Corporation routinely
securitizes loans and debt securities using VIEs as a source of
funding for the Corporation and as a means of transferring the
economic risk of the loans or debt securities to third parties. The
assets are transferred into a trust or other securitization vehicle
such that the assets are legally isolated from the creditors of the
Corporation and are not available to satisfy its obligations. These
assets can only be used to settle obligations of the trust or other
securitization vehicle. The Corporation also administers,
structures or invests in other VIEs including CDOs, investment
vehicles and other entities. For more information on the
Corporation’s utilization of VIEs, see Note 1 – Summary of
Significant Accounting Principles.
The tables in this Note present the assets and liabilities of
consolidated and unconsolidated VIEs at December 31, 2014 and
2013, in situations where the Corporation has continuing
involvement with transferred assets or if the Corporation otherwise
has a variable interest in the VIE. The tables also present the
Corporation’s maximum loss exposure at December 31, 2014 and
2013 resulting from its involvement with consolidated VIEs and
unconsolidated VIEs in which the Corporation holds a variable
interest. The Corporation’s maximum loss exposure is based on
the unlikely event that all of the assets in the VIEs become
worthless and incorporates not only potential losses associated
with assets recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheet but also
potential losses associated with off-balance sheet commitments
such as unfunded liquidity commitments and other contractual
arrangements. The Corporation’s maximum loss exposure does
not include losses previously recognized through write-downs of
assets.
The Corporation invests in asset-backed securities (ABS)
issued by third-party VIEs with which it has no other form of
involvement. These securities are included in Note 3 – Securities
and Note 20 – Fair Value Measurements. In addition, the
Corporation uses VIEs such as trust preferred securities trusts in
connection with its funding activities. For additional information,
see Note 11 – Long-term Debt. The Corporation also uses VIEs in
the form of synthetic securitization vehicles to mitigate a portion
of the credit risk on its residential mortgage loan portfolio, as
described in Note 4 – Outstanding Loans and Leases. The
Corporation uses VIEs, such as cash funds managed within Global
Wealth & Investment Management (GWIM), to provide investment
opportunities for clients. These VIEs, which are not consolidated
by the Corporation, are not included in the tables in this Note.
Except as described below, the Corporation did not provide
financial support to consolidated or unconsolidated VIEs during
2014 or 2013 that it was not previously contractually required to
provide, nor does it intend to do so.
Mortgage-related Securitizations
First-lien Mortgages
As part of its mortgage banking activities, the Corporation
securitizes a portion of the first-lien residential mortgage loans it
originates or purchases from third parties, generally in the form
of RMBS guaranteed by government-sponsored enterprises, FNMA
and FHLMC (collectively the GSEs), or GNMA primarily in the case
of FHA-insured and U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)-
guaranteed mortgage loans. Securitization usually occurs in
conjunction with or shortly after origination or purchase. In
addition, the Corporation may, from time to time, securitize
commercial mortgages it originates or purchases from other
entities. The Corporation typically services the loans it securitizes.
Further, the Corporation may retain beneficial interests in the
securitization trusts including senior and subordinate securities
and equity tranches issued by the trusts. Except as described
below and in Note 7 – Representations and Warranties Obligations
and Corporate Guarantees, the Corporation does not provide
guarantees or recourse to the securitization trusts other than
standard representations and warranties.
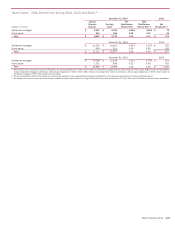
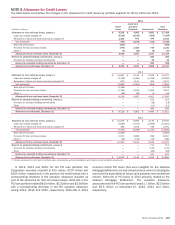
The table below summarizes select information related to first-
lien mortgage securitizations for 2014 and 2013.
First-lien Mortgage Securitizations
Residential Mortgage
Agency Non-agency - Subprime Commercial Mortgage
(Dollars in millions) 2014 2013 2014 2013 2014 2013
Cash proceeds from new securitizations (1) $ 36,905 $ 49,888 $809 $—
$ 5,710 $ 5,326
Gain on securitizations (2) 371 81 49 —68 119
(1) The Corporation transfers residential mortgage loans to securitizations sponsored by the GSEs or GNMA in the normal course of business and receives RMBS in exchange which may then be sold
into the market to third-party investors for cash proceeds.
(2) Substantially all of the first-lien residential and commercial mortgage loans securitized are initially classified as LHFS and accounted for under the fair value option. As such, gains are recognized on
these LHFS prior to securitization. The Corporation recognized $715 million and $2.0 billion of gains, net of hedges, on loans securitized during 2014 and 2013.
In addition to cash proceeds as reported in the table above,
the Corporation received securities with an initial fair value of $5.4
billion and $3.3 billion in connection with first-lien mortgage
securitizations in 2014 and 2013. All of these securities were
initially classified as Level 2 assets within the fair value hierarchy.
During 2014 and 2013, there were no changes to the initial
classification.
The Corporation recognizes consumer MSRs from the sale or
securitization of first-lien mortgage loans. Servicing fee and
ancillary fee income on consumer mortgage loans serviced,
including securitizations where the Corporation has continuing
involvement, were $1.8 billion and $2.9 billion in 2014 and 2013.
Servicing advances on consumer mortgage loans, including
securitizations where the Corporation has continuing involvement,
were $10.4 billion and $14.1 billion at December 31, 2014 and
2013. The Corporation may have the option to repurchase
delinquent loans out of securitization trusts, which reduces the
amount of servicing advances it is required to make. During 2014
and 2013, $5.2 billion and $10.8 billion of loans were repurchased
from first-lien securitization trusts primarily as a result of loan
delinquencies or to perform modifications. The majority of these
loans repurchased were FHA-insured mortgages collateralizing
GNMA securities. For more information on MSRs, see Note 23 –
Mortgage Servicing Rights.