Bank of America 2012 Annual Report Download - page 111
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 111 of the 2012 Bank of America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Bank of America 2012 109
Reserve for Unfunded Lending Commitments
In addition to the allowance for loan and lease losses, we also
estimate probable losses related to unfunded lending
commitments such as letters of credit, financial guarantees,
unfunded bankers’ acceptances and binding loan commitments,
excluding commitments accounted for under the fair value option.
Unfunded lending commitments are subject to the same
assessment as funded loans, including estimates of probability
of default and LGD. Due to the nature of unfunded commitments,
the estimate of probable losses must also consider utilization. To
estimate the portion of these undrawn commitments that is likely
to be drawn by a borrower at the time of estimated default, analyses
of the Corporation’s historical experience are applied to the
unfunded commitments to estimate the funded EAD. The expected
loss for unfunded lending commitments is the product of the
probability of default, the LGD and the EAD, adjusted for any
qualitative factors including economic uncertainty and inherent
imprecision in models.
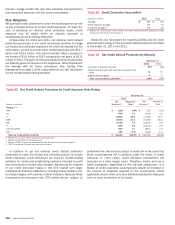
The reserve for unfunded lending commitments at
December 31, 2012 was $513 million, $201 million lower than
December 31, 2011 driven by improved credit quality in the
unfunded portfolio and accretion of purchase accounting
adjustments on acquired Merrill Lynch unfunded positions.
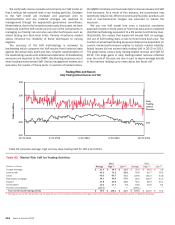
Market Risk Management
Market risk is the risk that values of assets and liabilities or
revenues will be adversely affected by changes in market
conditions. This risk is inherent in the financial instruments
associated with our operations and/or activities including loans,
deposits, securities, short-term borrowings, long-term debt, trading
account assets and liabilities, and derivatives. Market-sensitive
assets and liabilities are generated through loans and deposits
associated with our traditional banking business, customer and
other trading operations, the ALM process, credit risk mitigation
activities and mortgage banking activities. In the event of market
volatility, factors such as underlying market movements and
liquidity have an impact on the results of the Corporation.
Our traditional banking loan and deposit products are
nontrading positions and are generally reported at amortized cost
for assets or the amount owed for liabilities (historical cost).
However, these positions are still subject to changes in economic
value based on varying market conditions, primarily changes in
the levels of interest rates. The risk of adverse changes in the
economic value of our nontrading positions is managed through
our ALM activities. We have elected to account for certain assets
and liabilities under the fair value option. For further information
on the fair value of certain financial assets and liabilities, see Note
21 – Fair Value Measurements to the Consolidated Financial
Statements.
Our trading positions are reported at fair value with changes
currently reflected in income. Trading positions are subject to
various risk factors, which include exposures to interest rates and
foreign exchange rates, as well as mortgage, equity, commodity,
issuer, credit and market liquidity risk factors. We seek to mitigate
these risk exposures by using techniques that encompass a variety
of financial instruments in both the cash and derivatives markets.
The following discusses the key risk components along with
respective risk mitigation techniques.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk represents exposures to instruments whose
values vary with the level or volatility of interest rates. These
instruments include, but are not limited to, loans, debt securities,
certain trading-related assets and liabilities, deposits, borrowings
and derivatives. Hedging instruments used to mitigate these risks
include derivatives such as options, futures, forwards and swaps.
Foreign Exchange Risk
Foreign exchange risk represents exposures to changes in the
values of current holdings and future cash flows denominated in
currencies other than the U.S. dollar. The types of instruments
exposed to this risk include investments in non-U.S. subsidiaries,
foreign currency-denominated loans and securities, future cash
flows in foreign currencies arising from foreign exchange
transactions, foreign currency-denominated debt and various
foreign exchange derivatives whose values fluctuate with changes
in the level or volatility of currency exchange rates or non-
U.S. interest rates. Hedging instruments used to mitigate this risk
include foreign exchange options, currency swaps, futures,
forwards, foreign currency-denominated debt and deposits.
Mortgage Risk
Mortgage risk represents exposures to changes in the value of
mortgage-related instruments. The values of these instruments
are sensitive to prepayment rates, mortgage rates, agency debt
ratings, default, market liquidity, government participation and
interest rate volatility. Our exposure to these instruments takes
several forms. First, we trade and engage in market-making
activities in a variety of mortgage securities including whole loans,
pass-through certificates, commercial mortgages and
collateralized mortgage obligations including CDOs using
mortgages as underlying collateral. Second, we originate a variety
of MBS which involves the accumulation of mortgage-related loans
in anticipation of eventual securitization. Third, we may hold
positions in mortgage securities and residential mortgage loans
as part of the ALM portfolio. Fourth, we create MSRs as part of
our mortgage origination activities. See Note 1 – Summary of
Significant Accounting Principles and Note 24 – Mortgage Servicing
Rights to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional
information on MSRs. Hedging instruments used to mitigate this
risk include contracts and derivatives such as options, swaps,
futures and forwards.
Equity Market Risk
Equity market risk represents exposures to securities that
represent an ownership interest in a corporation in the form of
domestic and foreign common stock or other equity-linked
instruments. Instruments that would lead to this exposure include,
but are not limited to, the following: common stock, exchange-
traded funds, American Depositary Receipts, convertible bonds,
listed equity options (puts and calls), OTC equity options, equity
total return swaps, equity index futures and other equity derivative
products. Hedging instruments used to mitigate this risk include
options, futures, swaps, convertible bonds and cash positions.